Drug Detail:Xiidra (Lifitegrast ophthalmic solution 5%)
Drug Class: Ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
XIIDRA® (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution), for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2016
Indications and Usage for Xiidra
Xiidra (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) 5% is a lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) antagonist indicated for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of dry eye disease (DED). (1)
Xiidra Dosage and Administration
One drop twice daily in each eye (approximately 12 hours apart). (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Ophthalmic solution containing lifitegrast 50 mg/mL (5%). (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity. (4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence 5%-25%) following the use of Xiidra were instillation-site irritation, dysgeusia, and decreased visual acuity. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Xiidra
Xiidra® (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) 5% is indicated for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of dry eye disease (DED).
2. Xiidra Dosage and Administration
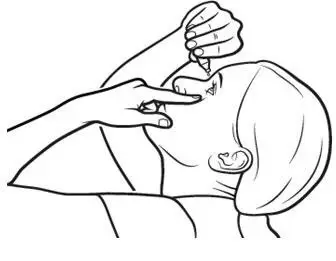
Instill one drop of Xiidra twice daily (approximately 12 hours apart) into each eye using a single-use container. Discard the single-use container immediately after using in each eye.
Contact lenses should be removed prior to the administration of Xiidra and may be reinserted 15 minutes following administration.
4. Contraindications
Xiidra is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to lifitegrast or to any of the other ingredients in the formulation [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Xiidra. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Rare serious cases of hypersensitivity, including anaphylactic reaction, bronchospasm, respiratory distress, pharyngeal edema, swollen tongue, urticaria, allergic conjunctivitis, dyspnea, angioedema, and allergic dermatitis have been reported. Eye swelling and rash have also been reported [see Contraindications (4)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on Xiidra use in pregnant women to inform any drug-associated risks. Intravenous (IV) administration of lifitegrast to pregnant rats, from premating through gestation day 17, did not produce teratogenicity at clinically relevant systemic exposures. Intravenous administration of lifitegrast to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis produced an increased incidence of omphalocele at the lowest dose tested, 3 mg/kg/day (400-fold the human plasma exposure at the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD], based on the area under the curve [AUC] level). Since human systemic exposure to lifitegrast following ocular administration of Xiidra at the RHOD is low, the applicability of animal findings to the risk of Xiidra use in humans during pregnancy is unclear [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Data
Animal Data
Lifitegrast administered daily by IV injection to rats, from premating through gestation day 17, caused an increase in mean pre-implantation loss and an increased incidence of several minor skeletal anomalies at 30 mg/kg/day, representing 5,400-fold the human plasma exposure at the RHOD of Xiidra, based on AUC. No teratogenicity was observed in the rat at 10 mg/kg/day (460-fold the human plasma exposure at the RHOD, based on AUC). In the rabbit, an increased incidence of omphalocele was observed at the lowest dose tested, 3 mg/kg/day (400-fold the human plasma exposure at the RHOD, based on AUC), when administered by IV injection daily from gestation days 7 through 19. A fetal no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) was not identified in the rabbit.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of lifitegrast in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, systemic exposure to lifitegrast from ocular administration is low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered, along with the mother’s clinical need for Xiidra and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Xiidra.
11. Xiidra Description
The chemical name for lifitegrast is (S)-2-(2-(benzofuran-6-carbonyl)-5,7-dichloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6-carboxamido)-3-(3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)propanoic acid. The molecular formula of lifitegrast is C29H24Cl2N2O7S and its molecular weight is 615.5 g/mol. The structural formula of lifitegrast is:
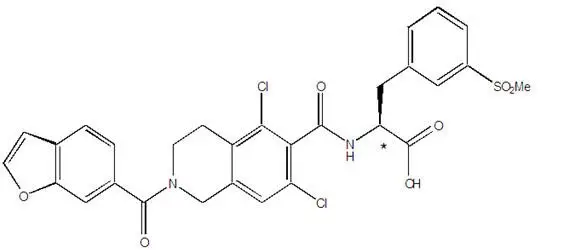
*Chiral center
Lifitegrast is a white to off-white powder, which is soluble in water.
Xiidra (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) 5% is a lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) antagonist supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow colored, isotonic solution of lifitegrast with a pH of 7.0-8.0, and an osmolality range of 200-330 mOsmol/kg.
Xiidra contains Active: lifitegrast 50 mg/mL; Inactives: sodium chloride, sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous, sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate, and water for injection. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH).
12. Xiidra - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lifitegrast binds to the integrin LFA-1, a cell surface protein found on leukocytes and blocks the interaction of LFA-1 with its cognate ligand intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). ICAM-1 may be overexpressed in corneal and conjunctival tissues in DED. LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction can contribute to the formation of an immunological synapse resulting in T-cell activation and migration to target tissues. In vitro studies demonstrated that lifitegrast may inhibit T-cell adhesion to ICAM-1 in a human T-cell line and may inhibit secretion of inflammatory cytokines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The exact mechanism of action of lifitegrast in DED is not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a subset of DED patients (n = 47) enrolled in a Phase 3 trial, the pre-dose (trough) plasma concentrations of lifitegrast were measured after 180 and 360 days of topical ocular dosing (one drop twice daily) with Xiidra (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) 5%. A total of nine of the 47 patients (19%) had plasma lifitegrast trough concentrations above 0.5 ng/mL (the lower limit of assay quantitation). Trough plasma concentrations that could be quantitated ranged from 0.55 ng/mL to 3.74 ng/mL.
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of lifitegrast for the treatment of DED were assessed in a total of 1181 patients (1067 of which received lifitegrast 5%) in four 12-week, randomized, multi-center, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies. Patients were randomized to Xiidra or vehicle (placebo) in a 1:1 ratio and dosed twice a day. Use of artificial tears was not allowed during the studies. The mean age was 59 years (range, 19-97 years). The majority of patients were female (76%). Enrollment criteria included minimal signs (i.e., Corneal Fluorescein Staining and non-anesthetized Schirmer Tear Test) and symptoms (i.e., Eye Dryness Score (EDS) and Ocular Discomfort Score) severity scores at baseline.
Effects on Symptoms of Dry Eye Disease
Eye dryness score was rated by patients using a visual analogue scale (0 = no discomfort, 100 = maximal discomfort) at each study visit. The average baseline EDS was between 40 and 70. A larger reduction in EDS favoring Xiidra was observed in all studies at Day 42 and Day 84 (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Mean Change (SD) From Baseline and Treatment Difference (Xiidra – Vehicle) in Eye Dryness Score in 12-Week Studies in Patients With Dry Eye Disease
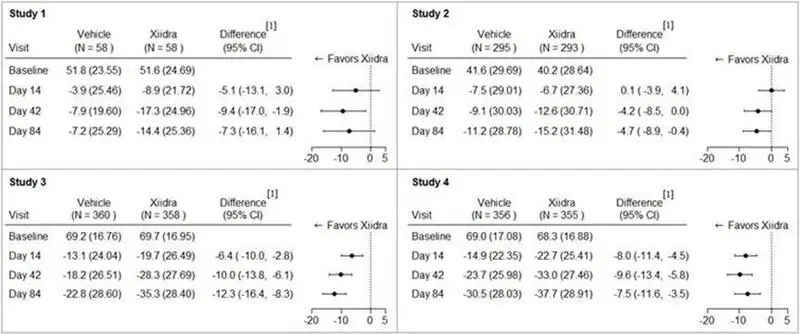
[1] Based on analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model adjusted for baseline value in Study 1, and ANCOVA model adjusted for baseline value and randomization stratification factors in Studies 2-4. All randomized and treated patients were included in the analysis and missing data were imputed using last-available data. In Study 1, one Xiidra-treated subject who did not have a baseline value was excluded from analysis.
Effects on Signs of Dry Eye Disease
Inferior fluorescein corneal staining score (ICSS) (0 = no staining, 1 = few/rare punctate lesions, 2 = discrete and countable lesions, 3 = lesions too numerous to count but not coalescent, 4 = coalescent) was recorded at each study visit. The average baseline ICSS was approximately 1.8 in Studies 1 and 2, and 2.4 in Studies 3 and 4. At Day 84, a larger reduction in ICSS favoring Xiidra was observed in three of the four studies (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Mean Change (SD) From Baseline and Treatment Difference (Xiidra – Vehicle) in Inferior Corneal Staining Score in 12-Week Studies in Patients With Dry Eye Disease
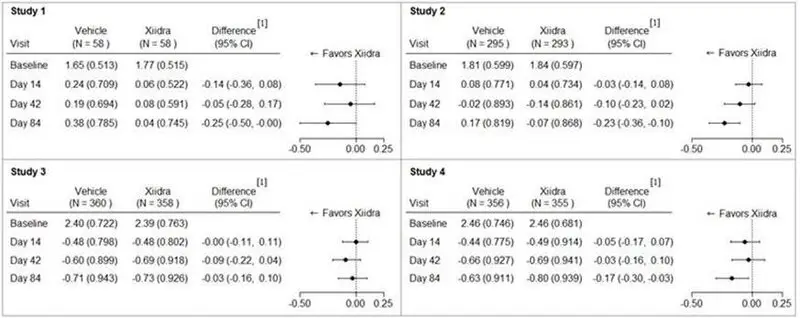
[1] Based on ANCOVA model adjusted for baseline value in Study 1, and ANCOVA model adjusted for baseline value and randomization stratification factors in Studies 2-4. All randomized and treated patients were included in the analysis and missing data were imputed using last-available data. In Study 2, one vehicle-treated subject who did not have a study eye designated was excluded from analysis.
| XIIDRA
lifitegrast solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |