Drug Detail:Zorvolex (Diclofenac [ dye-kloe-fen-ak ])
Drug Class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (5.1)
- ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (5.2)
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warning | 5/2016 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events (5.1) | 5/2016 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Heart Failure and Edema (5.5) | 5/2016 |
Indications and Usage for Zorvolex
ZORVOLEX is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated for
- management of mild to moderate acute pain (1)
- management of osteoarthritis pain.(1)
Zorvolex Dosage and Administration
- Use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. (2)
- The dosage for acute pain is 18 mg or 35 mg orally three times a day. (2)
- The dosage for osteoarthritis pain is 35 mg orally three times a day. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules: 18 mg and 35 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to diclofenac or any components of the drug product (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop (5.3)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure (5.4, 7)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ZORVOLEX in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure (5.5)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZORVOLEX in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function (5.6)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs (5.7)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity) (5.8)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue ZORVOLEX at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity (5.9)
- Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus: Avoid use in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation (5.10, 8.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia (5.11, 7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) are edema, nausea, headache, dizziness, vomiting, constipation, pruritus, diarrhea, flatulence, pain in extremity, abdominal pain, sinusitis, alanine aminotransferase increased, blood creatinine increased, hypertension, and dyspepsia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Iroko Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-877-757-0676 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking ZORVOLEX with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended (7)
- ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB), or Beta-Blockers: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure (7)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function (7)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects (7)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels (7)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Use of NSAIDs during the third trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation (5.10, 8.1)
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of ZORVOLEX in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2016
Related/similar drugs
aspirin, prednisone, acetaminophen, tramadol, ibuprofen, meloxicam, naproxenFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Zorvolex
ZORVOLEX is indicated for:
- Management of mild to moderate acute pain
- Management of osteoarthritis pain
2. Zorvolex Dosage and Administration
2.1 General Dosing Instructions
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of ZORVOLEX and other treatment options before deciding to use ZORVOLEX. Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
The effectiveness of ZORVOLEX when taken with food has not been studied in clinical studies. Taking ZORVOLEX with food may cause a reduction in effectiveness compared to taking ZORVOLEX on an empty stomach [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
2.2 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic disease may require reduced doses of ZORVOLEX compared to patients with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. As with other diclofenac products, start treatment at the lowest dose. If efficacy is not achieved with the lowest dose, discontinue use.
2.3 Non-Interchangeability with Other Formulations of Diclofenac
ZORVOLEX capsules are not interchangeable with other formulations of oral diclofenac even if the milligram strength is the same. ZORVOLEX capsules contain diclofenac free acid whereas other diclofenac products contain a salt of diclofenac, i.e., diclofenac potassium or sodium. A 35 mg dose of ZORVOLEX is approximately equal to 37.6 mg of sodium diclofenac or 39.5 mg of potassium diclofenac. Therefore, do not substitute similar dosing strengths of other diclofenac products without taking this into consideration.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
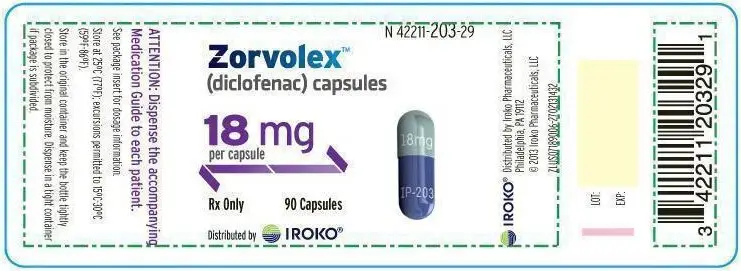
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules: 18 mg - blue body and light green cap (imprinted IP-203 on the body and 18 mg on the cap in white ink).
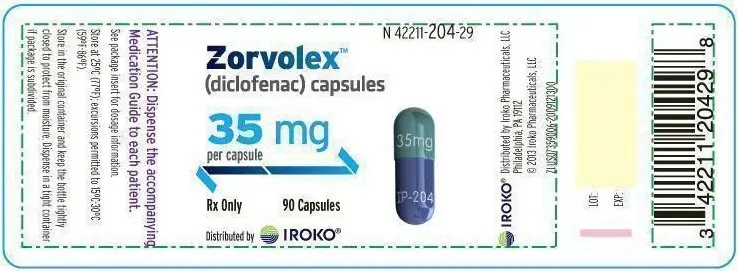
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules: 35 mg - blue body and green cap (imprinted IP-204 on the body and 35 mg on the cap in white ink).
4. Contraindications
ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to diclofenac or any components of the drug product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)]
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)]
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as diclofenac, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2%-4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials of diclofenac-containing products, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (SGOT) were observed in about 2% of approximately 5,700 patients at some time during diclofenac treatment (ALT was not measured in all studies).
In a large, open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated with oral diclofenac sodium for 2-6 months, patients were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of patients and included marked elevations (greater than 8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In that open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (greater than 8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic. Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations.
In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the first 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
In a European retrospective population-based, case-controlled study, 10 cases of diclofenac associated drug-induced liver injury with current use compared with non-use of diclofenac were associated with a statistically significant 4-fold adjusted odds ratio of liver injury. In this particular study, based on an overall number of 10 cases of liver injury associated with diclofenac, the adjusted odds ratio increased further with female gender, doses of 150 mg or more, and duration of use for more then 90 days.
Physicians should measure transaminases at baseline and periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with ZORVOLEX, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, transaminases should be monitored within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reactions can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), ZORVOLEX should be discontinued immediately.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue ZORVOLEX immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with ZORVOLEX, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Exercise caution when prescribing ZORVOLEX with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., acetaminophen, antibiotics, and anti-epileptics).
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of diclofenac may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of ZORVOLEX in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If ZORVOLEX is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Diclofenac has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to diclofenac and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]. When ZORVOLEX is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions, and to discontinue the use of ZORVOLEX at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.10 Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Diclofenac may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.11 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with ZORVOLEX has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions, such as coagulation disorders, concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
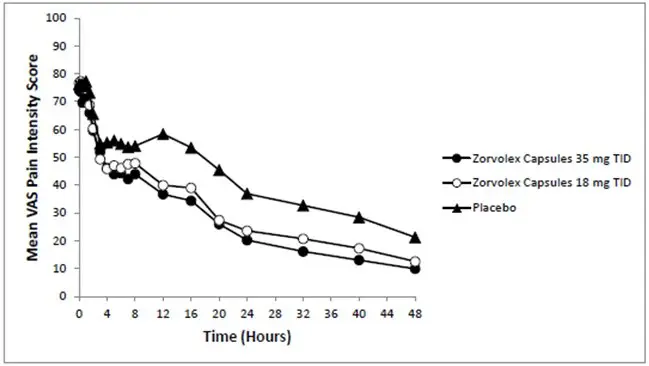
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Acute Pain
Two-hundred sixteen (216) patients received ZORVOLEX in the completed, 48-hour, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of acute pain following bunionectomy. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 1.
| Adverse Reactions | ZORVOLEX 18 mg or 35 mg three times daily*
N = 216 |
Placebo* N = 106 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Edema | 33% | 32% |
| Nausea | 27% | 37% |
| Headache | 13% | 15% |
| Dizziness | 10% | 16% |
| Vomiting | 9% | 12% |
| Constipation | 8% | 4% |
| Pruritus | 7% | 6% |
| Flatulence | 3% | 2% |
| Pain in Extremity | 3% | 1% |
| Dyspepsia | 2% | 1% |
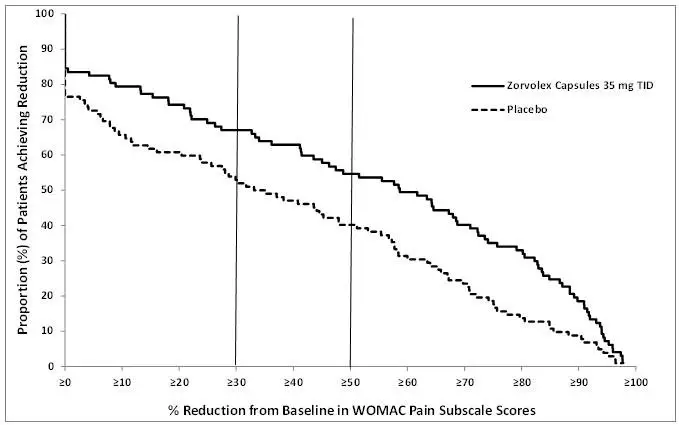
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Osteoarthritis Pain
Two-hundred two (202) patients received ZORVOLEX in the completed, 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of osteoarthritis pain of the knee or hip. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 2.
| Adverse Reactions | ZORVOLEX 35 mg N=202 | Placebo N=103 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Nausea | 7% | 2% |
| Diarrhea | 6% | 3% |
| Headache | 4% | 3% |
| Abdominal Pain Upper | 3% | 1% |
| Sinusitis | 3% | 1% |
| Vomiting | 3% | 1% |
| Alanine Aminotransferase Increased | 2% | 0 |
| Blood Creatinine Increased | 2% | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 2% | 1% |
| Flatulence | 2% | 0 |
| Hypertension | 2% | 1% |
Six-hundred one (601) patients received ZORVOLEX 35 mg either twice or three times daily in a 52-week, open-label, clinical trial in osteoarthritis pain of the knee or hip. Of those, 360 (60%) patients completed the trial. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 3.
| Adverse Reactions | ZORVOLEX 35 mg N=601 |
|---|---|
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 8% |
| Headache | 8% |
| Urinary tract infection | 7% |
| Diarrhea | 6% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 6% |
| Nausea | 6% |
| Constipation | 5% |
| Sinusitis | 5% |
| Osteoarthritis | 5% |
| Cough | 4% |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 4% |
| Back pain | 3% |
| Dyspepsia | 3% |
| Procedural pain | 3% |
| Bronchitis | 3% |
| Hypertension | 3% |
| Abdominal pain upper | 3% |
| Influenza | 3% |
| Arthralgia | 3% |
| Contusion | 3% |
| Vomiting | 3% |
| Abdominal discomfort | 2% |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 2% |
| Dizziness | 2% |
| Fall | 2% |
| Abdominal pain | 2% |
7. Drug Interactions
See Table 4 for clinically significant drug interactions with diclofenac.
| Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of ZORVOLEX with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. ZORVOLEX is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection. |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: |
|
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of diclofenac with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | The concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed. In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration. |
| Inhibitors or Inducers of Cytochrome P450 2C9 | |
| Clinical Impact: | Diclofenac is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, predominantly by CYP2C9. Co-administration of diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of diclofenac whereas co-administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g. rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of diclofenac. |
| Intervention: | A dosage adjustment may be warranted when diclofenac is administered with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C prior to 30 weeks gestation; Category D starting 30 weeks gestation.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ZORVOLEX in pediatric patients has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.13)].
Diclofenac is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
10. Overdosage
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
11. Zorvolex Description
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules are a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, available as hard gelatin capsules of 18 mg and 35 mg for oral administration. The chemical name is 2-[(2, 6-dichlorophenyl) amino] benzeneacetic acid. The molecular weight is 296.15. Its molecular formula is C14H11Cl2NO2, and it has the following chemical structure.
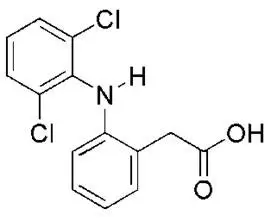
Diclofenac acid is a white to slight yellowish crystalline powder. Diclofenac acid has a pKa of 4.18 and a logP of 3.03. It is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
The inactive ingredients in ZORVOLEX include a combination of lactose monohydrate, sodium lauryl sulfate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium and sodium stearyl fumarate. The capsule shells contain gelatin, titanium dioxide, and dyes FD&C blue #1, FD&C blue #2, FDA/E172 Yellow Iron Oxide and FDA/E172 Black Iron Oxide. The imprinting on the gelatin capsules is white edible ink. The 18 mg capsules have a blue body imprinted with IP-203 and light green cap imprinted with 18 mg in white ink. The 35 mg capsules have a blue body imprinted with IP-204 and green cap imprinted with 35 mg in white ink.
12. Zorvolex - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of ZORVOLEX, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Diclofenac is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Diclofenac concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because diclofenac is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The relative bioavailability of ZORVOLEX 35 mg capsules was compared to diclofenac potassium immediate-release (IR) tablets 50 mg in 39 healthy subjects under fasted and fed conditions in a single-dose crossover study.
ZORVOLEX 35 mg capsules do not result in an equivalent systemic exposure to 50 mg diclofenac potassium IR tablets.
When taken under fasted conditions, a 20% lower dose of diclofenac in ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in a 23% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 26% lower mean peak concentration (Cmax) compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets. The time to reach peak concentration (Tmax) was similar for ZORVOLEX and diclofenac potassium IR tablets and was ~1 hour for both.
When taken under fed conditions, a 20% lower dose of diclofenac in ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in a 23% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 48% lower mean Cmax compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets. The Tmax for ZORVOLEX was delayed by approximately 1 hour compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets (3.32 hours vs. 2.33 hours, respectively).
When taken under fed conditions, ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in an 11% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 60% lower mean Cmax compared to fasted conditions. Whereas diclofenac potassium IR tablets under fed conditions resulted in 8% - 10% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and 28% - 43% lower mean Cmax compared to fasted conditions, based on the results from two individual food effect studies. The Tmax for ZORVOLEX was delayed by approximately 2.32 hours under fed conditions compared to fasted conditions (3.32 hours vs. 1.00 hour, respectively), while the Tmax for diclofenac potassium IR tablets was delayed by approximately 1.00 - 1.33 hours under fed conditions compared to fasted conditions (1.70 vs. 0.74 hours and 2.33 vs. 1.00 hours, respectively in two studies).
There were no differences in elimination half-life between ZORVOLEX and diclofenac potassium IR tablets under fasted or fed conditions.
16. How is Zorvolex supplied
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules are supplied as:
- 18 mg - blue body and light green cap (imprinted IP-203 on the body and 18 mg on the cap in white ink)
- NDC (42211-203-23), Bottles of 30 capsules
- NDC (42211-203-29), Bottles of 90 capsules
- 35 mg - blue body and green cap (imprinted IP-204 on the body and 35 mg on the cap in white ink)
- NDC (42211-204-23), Bottles of 30 capsules
- NDC (42211-204-29), Bottles of 90 capsules
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with ZORVOLEX and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued or Revised: May 2016 | ||
| Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) | |||
| What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
|
||
NSAIDs should only be used:
|
|||
| What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain. |
|||
| Who should not take NSAIDs? Do not take NSAIDs:
|
|||
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first. |
|||
| What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?"
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms: |
|||
|
|
||
| Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | |||
|
|
||
| If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
Other information about NSAIDs
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals. |
|||
| Manufactured (under license from iCeutica Pty Ltd) for and Distributed by:
Iroko Pharmaceuticals, LLC One Kew Place 150 Rouse Boulevard Philadelphia, PA 19112 For more information, go to www.iroko.com or call 1-877-757-0676. |
|||
| ZORVOLEX
diclofenac capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZORVOLEX
diclofenac capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Iroko Pharmaceuticals LLC (796831217) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent CTS, LLC | 962674474 | manufacture(42211-203, 42211-204) | |