What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is a condition that causes small pockets along your intestine called diverticula to become inflamed or infected. This is caused by hard bowel movement, food, or bacteria that get stuck in the pockets.
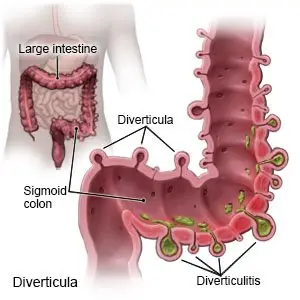 |
What are the signs and symptoms of diverticulitis?
- Pain in the lower left side of your abdomen
- Fever and chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- An urge to urinate or have a bowel movement more often than usual
- Bloody bowel movements
- Bloating and gas
How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you. He or she will ask questions about your symptoms and health history. You may need any of the following:
- Blood and urine tests may show signs of infection or inflammation.
- CT scan or ultrasound pictures may be used to find problems in your intestines. You may be given contrast liquid to help your intestines show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- A colonoscopy is used to look at your intestines with a scope. A scope (long bendable tube with a light on the end) is used to take pictures. This test may show swollen diverticula or bleeding. Samples may be taken from your digestive tract and sent to a lab for tests. Bleeding may be controlled with tools that are inserted through the scope.
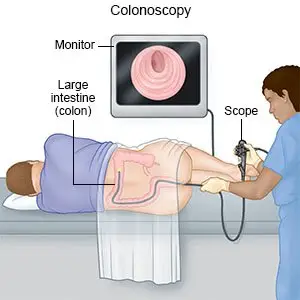
How is diverticulitis treated?
Mild diverticulitis can be treated at home. You may need to rest and follow a clear liquid diet until your diverticulitis gets better. You will be admitted to the hospital if you have severe diverticulitis. You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- An IV may be used to give you liquids and nutrition. You may not be able to eat or drink anything until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
- Drainage may be done to reduce inflammation or treat infection. Your healthcare provider may insert a small tube through an incision in your abdomen to drain pus from infected diverticula.
- Surgery may be needed if there is a hole in your bowel or a large amount of swelling. A healthcare provider will remove the infected or inflamed areas of your colon.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- metronidazole
- Flagyl
- Cipro
- ciprofloxacin
- Bactrim DS
View more treatment options
How can I manage my symptoms?
A clear liquid diet will allow your intestines to heal. A clear liquid diet includes any liquids that you can see through. Examples include water, ginger-ale, cranberry or apple juice, frozen fruit ice, or broth. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on a clear liquid diet.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have bowel movement or foul-smelling discharge leaking from your vagina or in your urine.
- You have severe diarrhea.
- You urinate less than usual or not at all.
- You are not able to have a bowel movement.
- You cannot stop vomiting.
- You have severe abdominal pain, a fever, and your abdomen is larger than usual.
- You have new or increased blood in your bowel movements.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have pain when you urinate.
- Your symptoms get worse or do not go away.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2023 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.




