What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is mild gum disease caused by plaque that builds up on your teeth and gums. Plaque contains bacteria that can irritate your gums and cause an infection.
What increases my risk for gingivitis?
- Not brushing or flossing your teeth every day, or not cleaning your teeth well enough to remove plaque
- Not visiting your dentist regularly for exams and cleanings
- Diseases or conditions that decrease your immune system, such as pregnancy, diabetes, or HIV infection
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Certain types of medicines, such as steroids, drugs that treat depression, or birth control pills
- Dental problems that make it hard to remove plaque, such as bridges or dentures that do not fit right, or crooked teeth
- Older age, or a family history of gum disease
What are the signs and symptoms of gingivitis?
You may have any of the following:
- Red, swollen gums
- Painful gums
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss your teeth
- Halitosis (bad breath) that is new or worse than before
How is gingivitis diagnosed?
Your dentist will check your gums for swelling and redness. Your dentist will also use a dental probe to check for bleeding. X-rays may be taken of your mouth and teeth.
How is gingivitis treated?
Gingivitis that is found early and is not too bad can be treated with good dental care at home. You may need to visit your dentist more often for dental cleanings. During these visits, your dentist may need to remove hard plaque from your teeth with tools. Your dentist may also need to treat any dental problems that make it hard for you to clean your teeth well.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- chlorhexidine
- Peridex
- Periogard
- PerioChip
- Acclean
View more treatment options
What can I do to prevent or manage gingivitis?
Gingivitis may lead to a more serious form of gum disease called periodontitis. Periodontitis can cause other dental problems, and you may even may even lose your teeth. Gingivitis may come back if you do not care for your teeth properly at home. The following can help prevent gingivitis or prevent it from getting worse between dental visits:
- Brush your teeth 2 times each day to remove plaque. Brush for at least 2 minutes. Use fluoride toothpaste. A battery-powered toothbrush may remove plaque better than a regular toothbrush. Your dentist can help you decide on the right toothbrush for you.
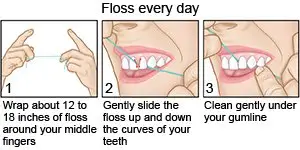
- Floss your teeth at least 1 time each day. Use dental floss to clean between and around each tooth.
- Use dental rinse, if directed. A dental rinse helps reduce plaque and decrease swollen gums. Ask your dentist which kind to use.
- Get regular checkups. See your dentist regularly for dental cleanings and oral exams.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can prevent treatments for gum disease from working. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have new trouble swallowing.
When should I call my dentist?
- The bleeding in your gums gets worse.
- You cannot use a toothbrush, or you cannot use dental floss.
- You have a sore or lump on your gums that stays for over 3 weeks.
- You have a fever.
- You have 1 or more teeth that are loose for over 3 weeks, and you do not know why.
- Your face or neck is swollen.
- Your gums are more painful, or become painful.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2023 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.




