What is leishmaniasis?
Leishmaniasis is an infection caused by a parasite. The female sandfly carries the parasite and passes it to you through a bite. The infection may affect your skin, mucus membranes, or organs. The infection can also spread throughout your body.
What are the signs and symptoms of leishmaniasis?
Signs and symptoms may be mild or severe and can develop weeks or months after you were bitten. Skin lesions (sores) can also appear years later, after you have surgery or a skin injury. You may have any of the following, depending on the part of your body that is affected:
- Skin ulcers (sores that break open)
- Skin sores that start as small dots and become large scaly or crusty areas, or darkened skin
- Pain in a skin sore, usually if it is infected with bacteria
- Fever, fatigue, or weight loss
- Diarrhea and abdominal pain or tenderness
- Jaundice (yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes)
- Extra tissue that grows in your nose, or holes in the cartilage of your nose
- Hoarse speech, tooth problems, or a cough
How is leishmaniasis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Tell him or her if you know you were bitten by a sandfly. Your provider may ask if you recently travelled to an area where sandflies are common. These include tropical areas, the Middle East, and southern Europe. The symptoms of leishmaniasis are similar to other health problems. The following tests are commonly used to rule out other health problems and diagnose leishmaniasis:
- A biopsy is a procedure used to take a sample of a skin lesion. The sample is tested for the parasite.
- Blood tests are used to check for antibodies. Antibodies are made by your immune system to help you fight infection, such as leishmaniasis. Blood tests may also be used to check your liver function and how well your blood clots.
How is leishmaniasis treated?
Skin sores may go away on their own without treatment. This may take months or years, and you may have scars from the sores. You may need treatment for leishmaniasis, that is severe or affects areas other than your skin. Your healthcare provider may use more than one kind of treatment.
- Medicines may be given to kill the parasite. The medicine may be given as a pill, injection, or through an IV. You may need to put medicated creams or ointments on your skin sores to help them heal. Antibiotics may be needed if you develop a bacterial infection in any of the skin sores.
- Procedures may be used to remove large skin lesions, repair skin damage, or treat the scars they leave behind. Procedures include using cold, heat, a laser, or electricity to remove the lesion. Surgery may be needed if the area is large or caused more damage beyond the bite area.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- allopurinol
- amphotericin b
- Amphocin
- Fungizone
- Pentam
View more treatment options
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Rest as needed. Leishmaniasis can make you more tired than usual. Rest can help you feel better.
- Drink more liquids as directed. Liquids help prevent dehydration and help your organs work correctly. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods can help increase your energy and help you gain weight if you lost too much. If you have less appetite than usual, try eating small meals several times during the day. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish, whole-grain breads, and cooked beans. Your healthcare provider or dietitian can help you create healthy meal plans.
- Care for your mouth if needed. Leishmaniasis that affects the mucus membranes can make your mouth more sensitive. Use a toothbrush with soft bristles or that is made for sensitive mouths. Brush and floss gently. Do not use mouthwash. Some kinds can burn or sting if you have sores in your mouth.
What can I do to prevent leishmaniasis?
- Protect yourself when you go to places where sand flies are found. If possible, stay inside from dusk to dawn. Sand flies feed (bite) during the night hours. They tend to be less active during the hottest times of the day. You can still get bitten if you disturb the sand flies during the day. Keep your skin covered when you are outside. Wear pants and long-sleeved shirts. Wear thick socks and high boots that cover your ankles. Tuck your socks into your pants legs.
- Put screens on all windows of your home if you live where sand flies are common. Sand flies are smaller than mosquitos. Screens need to have very small holes to prevent the sand flies from getting in.
- Apply bug repellant. Only spray the repellant in an open area so you do not breathe it in. Follow the directions that come with the repellant. Wash the repellant off as soon as you come inside. Wash all sprayed clothing before you wear it again. Repellant may contain DEET or permethrin:
- Spray DEET on your clothing and bare skin. Do not spray your face directly. Put a small amount on your hands and apply to your face. Avoid the eye and lip areas. Do not apply DEET to a child who is younger than 2 months.
- Spray permethrin only on your clothing. Do not spray your skin.
- Put bed nets over the beds in your home. The bed nets will help keep sand flies from biting you as you sleep. Some bed nets are soaked in insecticide. You can also spray insecticide on the nets if needed. Insecticide can also be sprayed on screens and curtains to help protect window areas.
What can I do to prevent the spread of germs?
 |
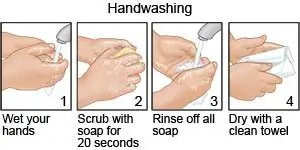
- Wash your hands often. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Use soap and water every time. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Wash the front and back of your hands, and in between your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available. Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth without washing your hands first.
- Cover a sneeze or cough. Use a tissue that covers your mouth and nose. Throw the tissue away in a trash can right away. Use the bend of your arm if a tissue is not available. Wash your hands well with soap and water or use a hand sanitizer.
- Stay away from others while you are sick. Avoid crowds as much as possible.
What do I need to know if I am HIV-positive and have leishmaniasis?
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your HIV status. The signs and symptoms of leishmaniasis you have may be unusual or severe.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about medicines you are using to control HIV. Your provider will need to create a specific plan to treat your leishmaniasis infection.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your heart is beating faster than usual.
- You have trouble urinating or are urinating very little.
- You have severe abdominal pain.
When should I call my doctor?
- Your skin or the whites of your eyes turn yellow.
- You see blood in your urine or bowel movement.
- Your skin has signs of infection, such as pus or swelling.
- Your symptoms do not get better with treatment.
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2023 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.




