What is basal cell carcinoma?

Basal cell cancer is the most common form of skin cancer diagnosed in the United States.
Basal cells are small, round skin cells normally found in the upper part of your skin. When these cells become cancerous, they usually turn into small skin tumors that can destroy skin and nearby tissues. They can grow large over time, causing damage around and under them. Basal cell tumors rarely spread beyond the original cancer site.
Basal cell cancer can grow on any part of the body. However, most basal cell cancers are found on some part of the face. This can cause disfigurement, and can interfere with the function of the eyelids, nose, and mouth.
|
|
Basal cell cancer often develops because of repeated, long-term exposure to the sun. People with light skin and blue eyes are at particularly high risk. Less often, basal cell cancer may be caused by exposure to arsenic or certain industrial pollutants. Older people who received X-ray treatment for acne as teenagers are at higher risk of developing basal cell cancer.
Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
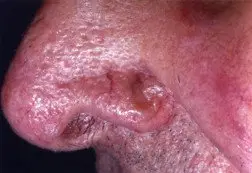
Basal cell skin cancer usually appears as a tiny, painless bump with a pink, pearly surface. As the cancer slowly grows, the center of the bump may become sore and develop into a crater that bleeds, crusts, or forms a scab.
|
|
A rare type of basal cell cancer may look like a small scar.
Although it is commonly located on the face, basal cell cancer can develop on the ears, back, neck and other skin surfaces frequently exposed to the sun.
Diagnosing basal cell carcinoma
Your doctor will examine your skin. He or she will do a biopsy, which involves removing skin so it can be examined in a laboratory. The doctor may remove some, or all, of the abnormal skin for the biopsy.
Expected duration of basal cell carcinoma
Once a basal cell cancer develops on the skin, it usually grows slowly. It can become very large, especially if it is on your lower back, the back of your shoulder or some other area that you do not usually see in the mirror.
Preventing basal cell carcinoma
Unprotected exposure to sunlight increases your risk of developing basal cell cancer. You can help to reduce this risk in several ways:
- Apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher before you go outdoors.
- Limit your time outdoors when the sun is at its peak (in most parts of the United States, from about 10 a.m. to 3 p.m.).
- Wear sunglasses with ultraviolet light protection.
- Wear long pants, a shirt with long sleeves and a hat with a wide brim.
- Be aware that some drugs may increase your skin's risk of damage from the sun. These include certain antibiotics, and drugs used to treat psychiatric illness, high blood pressure, heart failure, acne and allergies. If you take prescription medications, ask your doctor if you need to take extra precautions to limit sun exposure.
- Be aware that some skin care products can make your skin more vulnerable to damage from sunlight. These include products containing alpha-hydroxy acids.
If a basal cell cancer develops on your skin, early detection may limit damage. Examine your skin thoroughly every one to two months. Use a mirror to check your skin on less visible areas, such as your back, shoulders, upper arms, buttocks and the soles of your feet.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- fluorouracil
- Efudex
- Aldara
- Erivedge
- imiquimod
View more treatment options
Treating basal cell carcinoma
Determining the right treatment depends on many factors, including:
- The size and location of the cancer
- Whether it has returned after previous treatment
- Age
- A patient's general health.
Treatments for superficial basal cell cancer with low risk of recurrence include:
- Curettage and electrodessication. A sharp instrument scrapes away visible cancer. Then an electric probe kills remaining microscopic cancer cells.
- Excision. Visible cancer and some healthy tissue is cut away, then the skin is stitched closed.
Less invasives treatments for low-risk superficial basal cell cancer include:
- Topical imiquimod cream (Aldara)
- Topical fluorouracil. An anticancer drug applied directly to the skin.
- Photodynamic therapy, which kills cancer with chemicals and light.
- Cryosurgery. Cancerous cells are frozen with liquid nitrogen.
The most common treatments for larger basal cell cancers with a higher risk of recurrence are:
- Moh's micrographic surgery. The tumor is shaved away in thin layers. Each layer is checked under a microscope to see if it contains cancerous cells. This procedure preserves as much healthy skin as possible while making sure that all of the cancer is removed.
- Radiation. High energy rays are used to destroy the cancer.
Once treatment is finished and the cancer is gone, the doctor will schedule regular follow up skin examinations. Once you have been diagnosed with basal cell cancer, you are at higher risk to develop another basal cell cancer.
When to call a professional
Call your doctor or a dermatologist (a doctor who specializes in skin problems) if you notice:
- A pearly nodule on your skin
- A new skin growth
- A skin ulcer that does not heal.
Prognosis
The outlook is usually excellent. Most basal cell cancers are cured if they are treated early.
Additional Info
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
https://www.cancer.gov/
American Cancer Society (ACS)
https://www.cancer.org/
American Academy of Dermatology
https://www.aad.org/
The Skin Cancer Foundation
https://www.skincancer.org/