Drug Detail:Aralast np (Alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor [ al-fa-1-pro-tee-nase-in-hib-i-tor ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous respiratory agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ARALAST NP (Alpha1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Human))
For Intravenous Use. Lyophilized Powder for Solution for Injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 2002
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration, Reconstitution (2.2) | 12/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration, Administration (2.3) | 12/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Aralast NP
ARALAST NP is an Alpha1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Human) (Alpha1-PI) indicated for chronic augmentation therapy in adults with clinically evident emphysema due to severe congenital deficiency of Alpha1-PI (alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency). ARALAST NP increases antigenic and functional (anti-neutrophil elastase capacity, ANEC) serum levels and antigenic lung epithelial lining fluid levels of Alpha1-PI. (1)
The effect of augmentation therapy with any Alpha1-PI, including ARALAST NP, on pulmonary exacerbations and on the progression of emphysema in alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency has not been conclusively demonstrated in randomized, controlled clinical trials. (1)
Clinical data demonstrating the long-term effects of chronic augmentation and maintenance therapy of individuals with ARALAST NP or ARALAST are not available. (1)
ARALAST NP is not indicated as therapy for lung disease in patients in whom severe Alpha1-PI deficiency has not been established. (1)
Aralast NP Dosage and Administration
For Intravenous Use Only
- Recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg body weight administered once weekly by intravenous infusion. (2.1)
- Administer at a rate not to exceed 0.2 mL/kg body weight/minute, and as determined by the response and comfort of the patient. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Available as a lyophilized powder in single dose vials containing 0.5 gram or 1 gram of functional Alpha1-PI. (3)
Contraindications
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficient patients with antibodies against IgA. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions may occur in IgA deficient patients with antibodies against IgA. (5.1)
- May carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents such as viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent, despite manufacturing steps designed to minimize the risk of viral transmission. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction occurring in ≥5% of infusions in clinical studies were headache, musculoskeletal discomfort, vessel puncture site bruise, nausea, and rhinorrhea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. at 1-877-TAKEDA-7 (1-877-825-3327) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2023
Related/similar drugs
Glassia, Prolastin, Prolastin-C, alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor, ZemairaFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Aralast NP
ARALAST NP is an Alpha1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Alpha1-PI) indicated for chronic augmentation therapy in adults with clinically evident emphysema due to severe congenital deficiency of Alpha1-PI (alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency). ARALAST NP increases antigenic and functional (anti-neutrophil elastase capacity, ANEC) serum levels and antigenic lung epithelial lining fluid levels of Alpha1-PI.
The effect of augmentation therapy with any Alpha1-PI, including ARALAST NP, on pulmonary exacerbations and on the progression of emphysema in alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency has not been conclusively demonstrated in randomized, controlled clinical trials.
Clinical data demonstrating the long-term effects of chronic augmentation and maintenance therapy with ARALAST NP or ARALAST are not available.
ARALAST NP is not indicated as therapy for lung disease in patients in whom severe congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency has not been established.
2. Aralast NP Dosage and Administration
For Intravenous Use Only
2.1 Dosage
- Dose ranging studies using efficacy endpoints have not been performed.
- Administer 60 mg/kg body weight of ARALAST NP once weekly by intravenous infusion.
2.2 Reconstitution
- Use aseptic technique.
- Allow ARALAST NP and diluent to reach room temperature before reconstitution.
- Remove caps from the diluent and product vials.
- Swab the exposed stopper surfaces with alcohol.
- Remove cover from one end of the double-ended transfer needle. Insert the exposed end of the needle through the center of the stopper in the diluent vial.
- Remove plastic cap from the other end of the double-ended transfer needle now seated in the stopper of the diluent vial. To reduce any foaming, invert the vial of diluent and insert the exposed end of the needle through the center of the stopper in the product vial at an angle, making certain that the diluent vial is always above the product vial. The angle of insertion directs the flow of diluent against the side of the product vial. Refer to Figure 1 below. The vacuum in the vial is sufficient to allow transfer of all of the diluent.
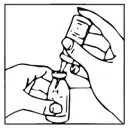
Figure 1
- Disconnect the two vials by removing the diluent vial from the transfer needle. This allows any remaining low pressure in the product vial to equalize. Next, remove the double-ended transfer needle from the product vial and discard the needle into the appropriate safety container.
- Let the vial stand until most of the contents is in solution, then GENTLY swirl until the powder is completely dissolved. Reconstitution requires no more than five minutes for a 0.5 gram vial and no more than 10 minutes for a 1 gram vial.
Note: Do not shake the content of the vial. Do not invert the vial until ready to withdraw content. - Reconstituted product is a colorless or slightly yellow to yellow-green solution.
- A few small visible particles may occasionally remain in the reconstituted product. These will be removed by the sterile 20 micron filter needle supplied with the product.
- Place the product vial on a stable flat surface.
- Open the blister pack of the 20 micron filter needle.
- Twist to remove the protective cap from the Luer adapter of the filter needle.
- Attach a single-use syringe (not provided) to the Luer adapter of the filter needle.
- Remove the protective cap from the filter needle and draw back plunger of the syringe to admit air into syringe. Insert the filter needle through the center of the stopper in product vial.
- Push the plunger to admit air in the product vial.
- Invert the system (product vial with syringe attached) so that product vial is on top.
- Withdraw the reconstituted product into the syringe.
- Remove the syringe from the filter needle and product vial. Remove filter needle from product vial and discard the needle into the appropriate sharps container.
2.3 Administration
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ARALAST NP is available as a lyophilized powder in single dose vials containing 0.5 gram or 1 gram of functional Alpha1-PI.
4. Contraindications
ARALAST NP is contraindicated in immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficient patients with antibodies against IgA, due to the risk of severe hypersensitivity.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
ARALAST NP may contain trace amounts of IgA. Patients with known antibodies to IgA, which can be present in patients with selective or severe IgA deficiency, have a greater risk of developing severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions. Closely follow the recommended infusion rate [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Monitor vital signs continuously and observe the patient carefully throughout the infusion. Discontinue the infusion if hypersensitivity symptoms occur and administer appropriate emergency treatment. Have epinephrine and other appropriate supportive therapy available for the treatment of any acute anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reaction.
5.2 Transmission of Infectious Agents
Because this product is made from human plasma, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, such as viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. This also applies to unknown or emerging viruses and other pathogens. The risk of transmitting an infectious agent has been minimized by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing for the presence of certain virus infections and by inactivating and removing certain viruses during the manufacturing process. Despite these measures, such products may still potentially transmit human pathogenic agents.
No seroconversions for hepatitis B or C (HBV or HCV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or any other known infectious agent were reported with the use of ARALAST NP during clinical studies.
All infections thought by a physician to possibly have been transmitted by this product should be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider to Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., at 1-877-TAKEDA-7 (1-877-825-3327) (in the U.S.).
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients following administration of ARALAST/ARALAST NP [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
No serious adverse reactions related to the use of ARALAST NP were reported in clinical trials.The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of infusions in clinical trials were headache, musculoskeletal discomfort, vessel puncture site bruise, nausea, and rhinorrhea.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of ARALAST NP was evaluated in a total of 38 subjects with severe congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency (pre-augmentation therapy serum levels of Alpha1-PI of less than 11 microM) in two clinical trials. The crossover trial was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, single-dose pharmacokinetic (PK) comparability trial conducted in 25 subjects with severe congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of ARALAST NP (test drug, 60 mg/kg body weight) as compared to ARALAST (reference drug, 60 mg/kg body weight), each infused at a rate of 0.2 mL/kg body weight/minute. The BAL trial was a multicenter, open-label, non-randomized trial in 13 subjects with severe congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency to determine the safety and effects of weekly augmentation therapy with ARALAST NP (60 mg/kg body weight/week) administered at a rate of 0.2 mL/kg body weight/minute in elevating Alpha1-PI levels in serum and epithelial lining fluid (ELF).
In both trials, there were no deaths and no serious adverse reactions associated with ARALAST NP or ARALAST administration. None of the subjects withdrew from the trial due to an adverse reaction. There was no reduction in infusion rate at 0.2 mL/kg body weight/min or infusion discontinuation/interruption due to an adverse reaction, except for one subject in the crossover trial who experienced pain at infusion site during ARALAST administration.
Table 1 summarizes the number of subjects, the total number of infusions, and the rate of adverse reactions (ARs) associated with ARALAST NP or ARALAST treatment for each clinical trial.
| Crossover Trial | Crossover Trial | BAL Trial | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARALAST NP | ARALAST | ARALAST NP | |
|
|||
| No. of subjects treated | 25 | 25 | 13 |
| No. of infusions | 25 | 25 | 104 |
| No. (%) of subjects with serious ARs | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| No. of serious ARs | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No. (%) of subjects with non-serious ARs | 12 (48%) | 13 (52%) | 4 (31%) |
| No. of non-serious ARs | 26 | 21 | 14 |
| No. (%) of Mild† ARs | 21 (81%) | 16 (76%) | 8 (57%) |
| No. (%) of Moderate‡ ARs | 5 (19%) | 5 (24%) | 5 (36%) |
| No. (%) of Severe§ ARs | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7%) |
The most common ARs (defined as adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of infusions) in each clinical trial are shown in Table 2.
| Crossover Trial (Number of Subjects = 25; Number of infusions per product = 25) | Crossover Trial (Number of Subjects = 25; Number of infusions per product = 25) | BAL Trial (Number of Subjects = 13; Number of infusions = 104) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction | ARALAST NP N (%)† | ARALAST N (%)† | ARALAST NP N (%)† |
|
|||
| Headache | 4 (16%) | 3 (12%) | 0 (0%) |
| Musculoskeletal discomfort | 4 (16%) | 2 (8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Vessel puncture site bruise | 2 (8%) | 4 (16%) | 0 (0%) |
| Lethargy | 0 (0%) | 2 (8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Nausea | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Rhinorrhea | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (6%) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ARALAST NP. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Vascular Disorders: Flushing
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Vomiting, Diarrhea
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Urticaria
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Myalgia
General and Administration Site Conditions: Injection site reaction, Fatigue, Malaise, Asthenia, Feeling abnormal
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ARALAST NP did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As for all patients, dosing for geriatric patients should be appropriate to their overall situation. Safety and effectiveness in patients over age 65 years of age have not been established.
11. Aralast NP Description
ARALAST NP contains approximately 2% Alpha1-PI with truncated C-terminal lysine (removal of Lys394), whereas ARALAST contains approximately 67% Alpha1-PI with the C-terminal lysine truncation.8 No known data suggest influence of these structural modifications on the functional activity and immunogenicity of Alpha1-PI.9
ARALAST NP is a sterile, lyophilized preparation of purified human alpha1-proteinase inhibitor (Alpha1-PI), also known as alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT).1 ARALAST NP is a similar product to ARALAST, containing the same active components of plasma Alpha1-PI with identical formulations.
ARALAST NP is prepared from large pools of human plasma by using the cold ethanol fractionation process, followed by purification steps including polyethylene glycol and zinc chloride precipitations and ion exchange chromatography.
To reduce the risk of viral transmission, the manufacturing process includes treatment with a solvent detergent (S/D) mixture [tri-n-butyl phosphate and polysorbate 80] to inactivate enveloped viral agents such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B (HBV), and hepatitis C (HCV). In addition, a nanofiltration step is incorporated into the manufacturing process to reduce the risk of transmission of enveloped and non-enveloped viral agents. Based on in vitro studies, the process used to produce ARALAST NP has been shown to inactivate and/or partition various viruses as shown in Table 3 below.
| Processing Step | Virus Log Reduction Factors HIV-1 | Virus Log Reduction Factors BVDV | Virus Log Reduction Factors PRV | Virus Log Reduction Factors HAV | Virus Log Reduction Factors MMV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A – Not applicable; study did not test for virus indicated. | |||||
| HIV–1: Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1; BVDV: Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus, model for Hepatitis C Virus and other lipid enveloped RNA viruses; PRV: Pseudorabies Virus, model for lipid-enveloped DNA viruses, to which Hepatitis B also belongs; HAV: Hepatitis A Virus; MMV: Mice Minute Virus, model for small non-lipid-enveloped DNA viruses | |||||
|
|||||
| Cold ethanol fractionation | 4.6 | 1.4 | 2.1 | 1.4 | ≤1.0* |
| Solvent Detergent-treatment | >5.8 | >6.0 | >5.5 | N/A | N/A |
| 15 N nanofiltration | >5.3 | >6.0 | >5.6 | >5.1 | 4.9 |
| Overall reduction factor | >15.7 | >13.4 | >13.2 | >6.5 | 4.9 |
The unreconstituted, lyophilized cake should be white or off-white to slightly yellow-green or yellow in color. When reconstituted as directed, the concentration of functionally active Alpha1-PI is ≥16 mg/mL and the specific activity is ≥0.55 mg active Alpha1-PI/mg total protein. The composition of the reconstituted product is as follows:
| Component | Quantity/mL |
|---|---|
|
|
| Elastase Inhibitory Activity | ≥400 mg Active Alpha1-PI/0.5 g vial *
≥800 mg Active Alpha1-PI/1 g vial † |
| Albumin | ≤5 mg/mL |
| Polyethylene Glycol | ≤112 mcg/mL |
| Polysorbate 80 | ≤50 mcg/mL |
| Sodium | ≤230 micromol/mL |
| Tri-n-butyl Phosphate | ≤1 mcg/mL |
| Zinc | ≤3 mg/L |
Each vial of ARALAST NP has the functional activity, as determined by inhibition of porcine pancreatic elastase, stated on the label. The formulation contains no preservative. The pH of the solution ranges from 7.2 to 7.8. Product must only be administered intravenously.
12. Aralast NP - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ARALAST NP administration is intended to inhibit serine proteases such as neutrophil elastase (NE), which is capable of degrading protein components of the alveolar walls and which is chronically present in the lung.
Alpha1-PI deficiency is an autosomal, co-dominant, hereditary disorder characterized by low serum and lung levels of Alpha1-PI.1,2,4,5 Severe forms of the deficiency are frequently associated with slowly progressive, moderate-to-severe panacinar emphysema that most often manifests in the third to fourth decades of life.1,2,3,5,6 However, an unknown percentage of individuals with severe Alpha1-PI deficiency are not diagnosed with or may never develop clinically evident emphysema during their lifetimes. Individuals with Alpha1-PI deficiency have little protection against NE released by neutrophils in their lower respiratory tract, resulting in a protease:protease inhibitor imbalance in the lung.2,7 This imbalance allows relatively unopposed destruction of the connective tissue framework of the lung parenchyma.7
There are a large number of phenotypic variants of this disorder.1,2,3 Individuals with the PiZZ variant typically have serum Alpha1-PI levels less than 35% of the average normal level.1,4 Individuals with the Pi(null)(null) variant have undetectable Alpha1-PI protein in their serum.1,2 Individuals with these low serum Alpha1-PI levels, i.e., less than 11 microM, have an increased risk of developing emphysema over their lifetimes. In addition, PiSZ individuals, whose serum Alpha1-PI levels range from approximately 9 to 23 microM,10 are considered to have moderately increased risk for developing emphysema, regardless of whether their serum Alpha1-PI levels are above or below 11 microM. The risk of accelerated development and progression of emphysema in individuals with severe Alpha1-PI deficiency is higher in smokers than in ex-smokers or non-smokers.2
Not all individuals with severe genetic variants of Alpha1-PI deficiency have emphysema. Augmentation therapy with Alpha1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Human) is indicated only in patients with severe congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency who have clinically evident emphysema.
Augmenting the levels of functional Alpha1-proteinase inhibitor by intravenous infusion is an approach to therapy for patients with Alpha1-PI deficiency. However, the efficacy of augmentation therapy in affecting the progression of emphysema has not been demonstrated in randomized, controlled clinical trials. The intended theoretical goal is to provide protection to the lower respiratory tract by correcting the imbalance between neutrophil elastase and protease inhibitors. Whether augmentation therapy with ARALAST NP actually protects the lower respiratory tract from progressive emphysematous changes has not been evaluated. Although the maintenance of blood serum levels of Alpha1-PI (antigenically measured) above 11 microM has been historically postulated to provide therapeutically relevant anti-neutrophil elastase protection, this has not been proven. Individuals with severe Alpha1-PI deficiency have been shown to have increased neutrophil and neutrophil elastase concentrations in lung epithelial lining fluid compared to normal PiMM individuals, and some PiSZ individuals with Alpha1-PI above 11 microM have emphysema attributed to Alpha1-PI deficiency. These observations underscore the uncertainty regarding the appropriate therapeutic target serum level of Alpha1-PI during augmentation therapy. The clinical benefit of increased blood levels of Alpha1-PI at the recommended dose has not been established.
The clinical efficacy of ARALAST NP in influencing the course of pulmonary emphysema or the frequency, duration, or severity of pulmonary exacerbations has not been demonstrated in randomized, controlled clinical trials.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Chronic augmentation therapy with a weekly dose of ARALAST NP at 60 mg/kg body weight to patients with Alpha1-PI deficiency increases the level of the deficient protein in plasma and in the epithelial lining fluid (ELF) as determined by antigenic assay. Normal individuals have plasma levels of Alpha1-PI greater than 20 microM. The clinical benefit of increased blood and ELF levels of Alpha1-PI at the recommended dose has not been demonstrated in adequately powered, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials for any Alpha1-PI product.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic comparability of ARALAST NP and the predecessor product ARALAST was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial in 25 subjects (median age: 59 years old; range: 20 to 75 years old) with severe Alpha1-PI deficiency who received a single infusion of 60 mg/kg body weight of each product. Figure 2 depicts the mean ± standard deviation (SD) plasma Alpha1-PI concentration-time profiles measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Table 4 summarizes the pharmacokinetic parameters of ARALAST NP and ARALAST.
Mean (± SD) Plasma Alpha1-PI Concentration-Time Profiles After a Single Intravenous Infusion of ARALAST NP and ARALAST (60 mg/kg) in Subjects with Congenital Alpha1-PI Deficiency
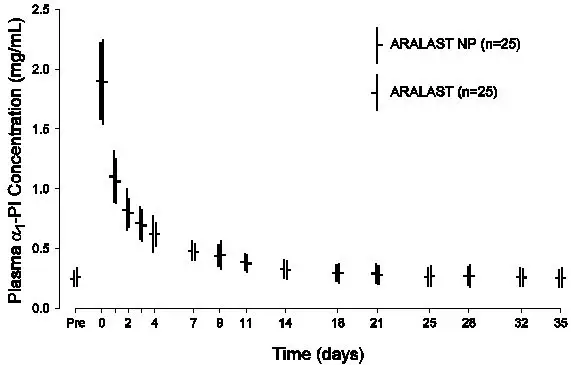
Figure 2
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | ARALAST NP Mean (± SD) | ARALAST Mean (± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax = Maximum increase in plasma Alpha1-PI concentration following infusion; AUC0-35d/dose = Area under the curve from time 0 to 35 days divided by dose; Half-life = terminal phase half-life determined using non-compartmental method. | ||
| Cmax | 1.6 (± 0.3) mg/mL | 1.7 (± 0.3) mg/mL |
| AUC0-35d/dose | 0.0837 (± 0.0212) day*kg/mL | 0.0897 (± 0.0204) day*kg/mL |
| Half-life | 4.7 (± 2.7) days | 4.8 (± 2.0) days |
The key pharmacokinetic parameter was AUC0-35d/dose. The 90% confidence interval (85.8% to 100.2%) for the geometric mean ratio of AUC0-35d/dose for ARALAST NP and ARALAST indicated that the 2 products are pharmacokinetically equivalent.
14. Clinical Studies
A clinical trial (ARALAST versus PROLASTIN trial) was conducted to compare the predecessor product ARALAST to a commercially available preparation of Alpha1-PI (PROLASTIN) in 28 subjects with congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency and emphysema, who had not received Alpha1-PI augmentation therapy within the preceding six months.
Subjects were randomized to receive either ARALAST or PROLASTIN, 60 mg/kg intravenously per week for 10 consecutive weeks. Following their first 10 weekly infusions, the subjects who were receiving PROLASTIN were switched to ARALAST while those who already were receiving ARALAST continued to receive it. Table 5 summarizes the mean serum antigenic and functional Alpha1-PI trough levels measured prior to infusion at steady state (Weeks 8 through 11).
| ARALAST Mean ± SD (Range of means) (No. of Subjects = 13) | PROLASTIN Mean ± SD (Range of means) (No. of Subjects = 13) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Antigenic Alpha1-PI | 15.3 ± 2.5 (14.7 to 15.5) microM | 16.9 ± 2.3 (16.2 to 17.2) microM |
| Functional Alpha1-PI | 15.3 ± 2.4 (14.8 to 15.6) microM | 15.7 ± 2.6 (14.4 to 16.4) microM |
Following weekly augmentation therapy with ARALAST or PROLASTIN, a gradual increase in peak and trough serum Alpha1-PI levels was noted, with stabilization after several weeks. The metabolic half-life of ARALAST was 5.9 days. Serum ANEC trough levels rose substantially in all subjects by Week 2, and by Week 3, serum ANEC trough levels exceeded 11 microM in the majority of subjects. With few exceptions, levels in both treatment groups remained above this level in individual subjects for the duration of the period Weeks 3 through 24. Although only five of fourteen subjects (35.7%) receiving ARALAST had BALs meeting acceptance criteria for analysis at both baseline and Week 7, a statistically significant increase in the antigenic level of Alpha1-PI in epithelial lining fluid (ELF) was observed. No statistically significant increase in the ANEC in the ELF was detected.
It was concluded that at a dose of 60 mg/kg administered intravenously once weekly, ARALAST and PROLASTIN had similar effects in maintaining target serum Alpha1-PI trough levels and increasing antigenic levels of Alpha1-PI in the ELF with maintenance augmentation therapy.
The pharmacokinetic comparability of ARALAST NP and the predecessor product ARALAST was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial in 25 subjects with severe Alpha1-PI deficiency [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
Another clinical trial (BAL TRIAL) was conducted to determine the effects of open-label, weekly intravenous augmentation therapy with 60 mg/kg ARALAST NP on ELF levels of Alpha1-PI, ANEC, and Alpha1-PI: human neutrophil elastase (HNE) complexes in subjects with severe, congenital Alpha1-PI deficiency. A total of 13 subjects completed 8 weekly infusions of ARALAST NP at a median dose of 63 (range: 58 to 67) mg/kg body weight at an infusion rate of 0.2 mL/kg/min. Of the 13 subjects, 12 had both baseline and post-treatment bronchoalveolar lavage samples. ARALAST NP augmentation therapy resulted in a significant increase (p<0.0001; n=12) in the mean plasma of antigenic Alpha1-PI levels, from a median baseline level of 4.0 (range: 3.1 to 6.3) microM to a median post-treatment level of 14.6 (range: 11.1 to 18.1) microM. Post-treatment values of plasma Alpha1-PI were above 11 microM in all 12 subjects. Median plasma functional Alpha1-PI (ANEC) levels also increased significantly (p<0.0001; n=12) from a median baseline level of 2.5 (range: 1.6 to 3.0) microM to a median post-treatment level of 11.4 (range: 7.8 to 16.9) microM. While antigenic Alpha1-PI levels in the ELF also increased significantly (p=0.0195; n=10) (Figure 3), only 4 out of 12 subjects were observed to have measurable ELF ANEC level in either or both lung lobes following 8 weekly infusions of ARALAST NP and the difference from baseline among these subjects did not reach statistical significance. Changes in the ELF analytes free and total human neutrophil elastase, Alpha1-PI:HNE complexes, IL-8, and TNF alpha were either not statistically significant, or could not be analyzed due to limited data.
Changes in ELF Alpha1-PI (AAT) Levels Following Intravenous Treatment with ARALAST NP (60 mg/kg/week) for 8 Weeks in Subjects with Severe Congenital Alpha1-PI Deficiency
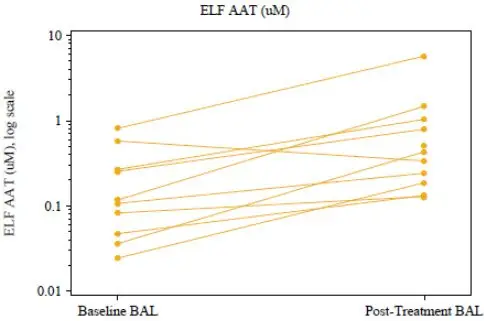
Figure 3
The clinical efficacy of ARALAST NP or any Alpha1-PI product in influencing the clinical course of pulmonary emphysema in Alpha1-PI deficiency has not been conclusively demonstrated in adequately powered, randomized, controlled clinical trials.
15. References
- Brantly M, Nukiwa T, Crystal RG. Molecular basis of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Med 1988 (Suppl 6A); 84:13–31.
- Crystal RG, Brantly ML, Hubbard RC, Curiel DT, et al. The alpha1-antitrypsin gene and its mutations: Clinical consequences and strategies for therapy. Chest 1989; 95:196–208.
- Crystal RG. α1-Antitrypsin deficiency: pathogenesis and treatment. Hospital Practice 1991; Feb.15:81–94.
- Hutchison DCS. Natural history of alpha-1-protease inhibitor deficiency. Am J Med 1988; 84(Suppl 6A):3–12.
- Hubbard RC, Crystal RG. Alpha-1-antitrypsin augmentation therapy for alpha-1- antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Med 1988; 84(Suppl 6A):52–62.
- Buist SA, Burrows B, Cohen A, et al. Guidelines for the approach to the patient with severe hereditary alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989; 140:1494–1497.
- Gadek JE, Fells GA, Zimmerman RL, et al. Antielastases of the human alveolar structures: Implications for the protease-antiprotease theory of emphysema. J Clin Invest 1981; 68:889–898.
- Kolarich D, et al. Biochemical, molecular characterization, and glycoproteomic analyses of α1-proteinase inhibitor products used for replacement therapy. Transfusion 2006; 46:1959–1977.
- Transcript of Blood Products Advisory Committee (BPAC) 85th Meeting; 3-4 Nov 2005.
- Turino GM, Barker AF, Brantly ML, et al: Clinical features of individuals with Pi*SZ phenotype of α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154: 1718–25, 1996.
17. Patient Counseling Information
- Inform patients of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions, including hives, generalized urticaria, chest tightness, dyspnea, wheezing, faintness, hypotension, and anaphylaxis. Advise patients to discontinue use of the product and contact their physician and/or seek immediate emergency care, depending on the severity of the reaction, if these symptoms occur.
- Inform patients that ARALAST NP is made from human plasma, therefore the possibility of transmitting infectious agents cannot be totally excluded. Explain that the risk of transmitting an infectious agent has been reduced by screening donors, testing plasma for certain virus infections, and a manufacturing process to inactivate and/or remove certain viruses.
- Inform patients that administration of ARALAST NP has been demonstrated to raise the levels of Alpha1-PI in the blood and in the lung, but that the effect of this augmentation on the frequency of pulmonary exacerbations and on the rate of progression of emphysema has not been established by clinical trials.
Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
U.S. License No. 1898
ARALAST NP® is a registered trademark of Baxalta Incorporated, a Takeda company.
TAKEDA® and the TAKEDA Logo® are registered trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
PROLASTIN® is a registered trademark of Grifols Therapeutics LLC.
| ARALAST
NP
alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor (human) kit |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| ARALAST
NP
alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor (human) kit |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. (039997266) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG | 300434670 | MANUFACTURE(0944-2814, 0944-2815) , LABEL(0944-2814, 0944-2815) , ANALYSIS(0944-2814, 0944-2815) , PACK(0944-2814, 0944-2815) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG | 300434676 | MANUFACTURE(0944-2814, 0944-2815) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG | 300434675 | MANUFACTURE(0944-2814, 0944-2815) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG | 300466733 | ANALYSIS(0944-2814, 0944-2815) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siegfried Hameln GmbH | 315869123 | ANALYSIS(64764-518, 64764-519) , MANUFACTURE(64764-518, 64764-519) | |