Drug Detail:Endari (Glutamine [ gloo-ta-meen ])
Drug Class: Nutraceutical products
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ENDARI (L-glutamine oral powder )
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Indications and Usage for Endari
ENDARI is an amino acid indicated to reduce the acute complications of sickle cell disease in adult and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older. (1)
Endari Dosage and Administration
- 5 grams to 15 grams orally, twice daily based on body weight. (2)
- Each dose of Endari should be mixed in 8 oz. (240 mL) of cold or room temperature beverage or 4 oz. to 6 oz. of food before ingestion. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Oral Powder: 5 grams of L-glutamine powder per paper-foil-plastic laminate packet. (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 10%) are constipation, nausea, headache, abdominal pain, cough, pain in extremity, back pain, and chest pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Emmaus Medical, Inc. at 1-877-420-6493 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Endari
Endari is indicated to reduce the acute complications of sickle cell disease in adult and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older.
2. Endari Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage
Administer Endari orally, twice per day at the dose based on body weight according to Table 1.
| Weight in kilograms | Weight in pounds | Per dose in grams | Per day in grams | Packets per dose | Packets per day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| less than 30 | less than 66 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| 30 to 65 | 66 to 143 | 10 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| greater than 65 | greater than 143 | 15 | 30 | 3 | 6 |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Oral powder: 5 grams of L–glutamine as a white crystalline powder in paper-foil-plastic laminate packets
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to Endari in 187 patients, including 136 exposed for 6 months and 109 exposed for ≥1 year. Endari was studied in 2 placebo-controlled clinical trials (a phase 3 study, n=230 and a phase 2 study, n=70). In these trials, patients with sickle cell anemia or sickle β0-thalassemia were randomized to receive Endari (n=187) or placebo (n=111) orally twice daily for 48 weeks followed by 3 weeks of tapering. Both studies included pediatric and adult patients (5-58 years of age) and 54% were female. The majority of patients were black (97.3%), had a diagnosis of sickle cell anemia (89.9%) and were receiving hydroxyurea at baseline (63.4%).
Treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions was reported in 2.7% (n=5) of patients receiving Endari. These adverse reactions included one case each of hypersplenism, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, burning sensation, and hot flash.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in both treatment groups, more frequently in the placebo group, and were consistent with the underlying disease.
Three deaths (3/187=1.6%) occurred during the study in the Endari treatment group as compared to none in the placebo treatment group. None of the deaths were considered to be related to Endari treatment. Adverse reactions occurring in greater than 10% of patients treated with Endari are shown in Table 2 below.
| Adverse reaction | Endari N = 187 (%) | Placebo N = 111 (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Constipation | 21 | 18 |
| Nausea | 19 | 14 |
| Headache | 18 | 15 |
| Abdominal Pain* | 17 | 16 |
| Cough | 16 | 14 |
| Pain in extremity | 13 | 7 |
| Back pain | 12 | 5 |
| Chest pain | 12 | 8 |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Endari have been established in pediatric patients 5 years and older. Use of Endari is supported by evidence from 2 placebo-controlled studies in adult and pediatric patients with sickle cell disease. The clinical studies enrolled 110 pediatric patients in the following age groups: 46 children (5 years up to less than 12 years) and 64 adolescents (12 years to less than 17 years).
The safety and effectiveness of Endari in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease younger than 5 years old has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Endari did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10. Overdosage
Single oral doses of L-glutamine at about 20 g/kg to 22 g/kg, 8 g/kg to 11 g/kg, and 19 g/kg were lethal in mice, rats, and rabbits, respectively. Supportive measures should be undertaken in the event of overdose of Endari.
11. Endari Description
Endari (L-glutamine) is an amino acid. L-glutamine is designated chemically as (S)-2-aminoglutaramic acid, L-glutamic acid 5-amide, or (S)-2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid. The molecular formula is C5H10N2O3 with the molecular weight of 146.15 g/mol and the following structural formula:
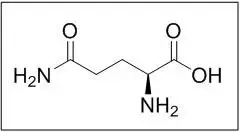
Endari is formulated as a white crystalline powder and is packaged as 5 grams in a paper-foil-plastic laminate packet for oral administration.
12. Endari - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of the amino acid L-glutamine in treating sickle cell disease (SCD) is not fully understood. Oxidative stress phenomena are involved in the pathophysiology of SCD. Sickle red blood cells (RBCs) are more susceptible to oxidative damage than normal RBCs, which may contribute to the chronic hemolysis and vaso-occlusive events associated with SCD. The pyridine nucleotides, NAD+ and its reduced form NADH, play roles in regulating and preventing oxidative damage in RBCs. L-glutamine may improve the NAD redox potential in sickle RBCs through increasing the availability of reduced glutathione.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In vivo analyses demonstrated that L-glutamine supplementation improved NAD redox potential.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of L-glutamine has been studied in healthy subjects and a variety of disease states. Relevant results from published literature are summarized below.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of L-glutamine.
L-glutamine was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay, nor clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay in mammalian (Chinese Hamster Lung CHL/IU) cells.
Animal reproduction studies and its potential for impairment of fertility have not been conducted with L-glutamine . It is also not known whether L-glutamine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or whether it can affect reproductive capacity.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of Endari in sickle cell disease was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center clinical trial entitled "A Phase III Safety and Efficacy Study of L-Glutamine to Treat Sickle Cell Disease or Sickle βo-thalassemia" [NCT01179217] (see Table 3).
The clinical trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of Endari in 230 patients (5 to 58 years of age) with sickle cell anemia or sickle β0-thalassemia who had 2 or more painful crises within 12 months prior to enrollment. Eligible patients stabilized on hydroxyurea for at least 3 months continued their therapy throughout the study. The trial excluded patients who had received blood products within 3 weeks, had renal insufficiency or uncontrolled liver disease, or were pregnant (or planning pregnancy) or lactating. Study patients received Endari or placebo for a treatment duration of 48 weeks followed by 3 weeks of tapering.
Efficacy was demonstrated by a reduction in the number of sickle cell crises through Week 48 and prior to the start of tapering among patients that received Endari compared to patients who received placebo. This clinical benefit was observed irrespective of hydroxyurea use. A sickle cell crisis was defined as a visit to an emergency room/medical facility for sickle cell disease-related pain which was treated with a parenterally administered narcotic or parenterally administered ketorolac. In addition, the occurrence of chest syndrome, priapism, and splenic sequestration were considered sickle cell crises. Treatment with Endari also resulted in fewer hospitalizations due to sickle cell pain at Week 48, fewer cumulative days in hospital and a lower incidence of acute chest syndrome.
| Event | Endari (n = 152) | Placebo (n = 78) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Median number of sickle cell crises (min,max)* | 3 (0, 15) | 4 (0, 15) |
| Median number of hospitalizations for sickle cell pain (min, max)* | 2 (0, 14) | 3 (0, 13) |
| Median cumulative days hospitalized (min, max)* | 6.5 (0, 94) | 11 (0, 187) |
| Median time (days) to first sickle cell crisis (95% CI)*,† | 84 (62, 109) | 54 (31, 73) |
| Patients with occurrences of acute chest syndrome (%)* | 13 (8.6%) | 18 (23.1%) |
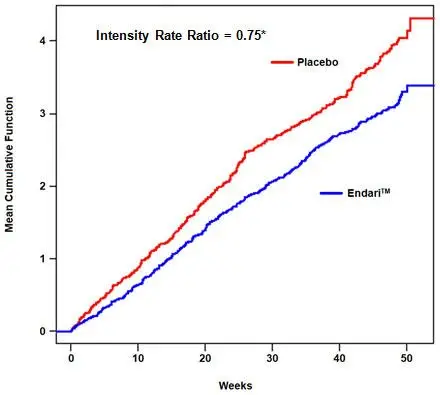
The recurrent crisis event time analysis (Figure 1) yielded an intensity rate ratio (IRR) value of 0.75 with 95% CI= (0.62, 0.90) and (0.55, 1.01) based on unstratified models using the Andersen-Gill and Lin, Wei, Yang and Ying methods, respectively in favor of Endari, suggesting that over the entire 48-week period, the average cumulative crisis count was reduced by 25% from the Endari group over the placebo group.
| Figure 1. Recurrent Event Time for Sickle Cell Crises by Treatment Group | |
|
|
|
| *Andersen-Gill: 95% CI (0.62, 0.90); Lin-Wei-Yang-Ying: 95% CI (0.55, 1.01) | |
16. How is Endari supplied
Endari is supplied in paper-foil-plastic laminate packets containing 5 grams of L-glutamine white crystalline powder.
- Carton of 60 packets: NDC 42457-420-60
| ENDARI
glutamine powder, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Emmaus Medical, Inc. (784073434) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ajinomoto do Brazil Industria e Comercio de Almentos Ltda. | 914653634 | API MANUFACTURE(42457-420) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon, Inc. | 053217022 | PACK(42457-420) | |