Drug Detail:Feldene (Piroxicam [ peer-ox-i-kam ])
Drug Class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Highlights of Prescribing Information
FELDENE® (piroxicam) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1982
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (5.1)
- FELDENE is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (5.2)
Indications and Usage for Feldene
FELDENE is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated for
- Relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) (1)
- Relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (1)
Feldene Dosage and Administration
- Use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (2)
- OA and RA: 20 mg once daily (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
FELDENE (piroxicam) capsules: 10 mg and 20 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to piroxicam or any components of the drug product (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop (5.3)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure (5.4, 7)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of FELDENE in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure (5.5)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of FELDENE in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function (5.6)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs (5.7)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: FELDENE is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity) (5.8)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue FELDENE at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity (5.9)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): Discontinue and evaluate clinically (5.10)
- Fetal Toxicity: Limit use of NSAIDs, including FELDENE, between about 20 to 30 weeks in pregnancy due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction. Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy due to the risks of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (5.11, 8.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia (5.12, 7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >2% from clinical trials) are: nausea, constipation, flatulence, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, edema, rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pfizer Inc. at 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [SSRIs]/serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors [SNRIs]): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking FELDENE with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of FELDENE and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended (7)
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB), or Beta-Blockers: Concomitant use with FELDENE may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure (7)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with FELDENE in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function (7)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects (7)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use of FELDENE can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels (7)
Use In Specific Populations
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of FELDENE in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2022
Related/similar drugs
aspirin, prednisone, acetaminophen, tramadol, ibuprofen, meloxicam, naproxenFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Feldene
FELDENE is indicated:
- For relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Feldene Dosage and Administration
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of FELDENE and other treatment options before deciding to use FELDENE. Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
After observing the response to initial therapy with FELDENE, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs.
For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, the dosage is 20 mg given orally once per day. If desired, the daily dose may be divided. Because of the long half-life of FELDENE, steady-state blood levels are not reached for 7 to 12 days. Therefore, although the therapeutic effects of FELDENE are evident early in treatment, there is a progressive increase in response over several weeks and the effect of therapy should not be assessed for two weeks.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
FELDENE (piroxicam) capsules:
10 mg maroon and blue #322
20 mg maroon #323
4. Contraindications
FELDENE is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to piroxicam or any components of the drug product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)]
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)]
- In the setting of CABG surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as piroxicam, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including FELDENE, cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Elevations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (three or more times the upper limit of normal [ULN]) have been reported in approximately 1% of NSAID-treated patients in clinical trials. In addition, rare, sometimes fatal, cases of severe hepatic injury, including fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported.
Elevations of ALT or AST (less than three times ULN) may occur in up to 15% of patients treated with NSAIDs including piroxicam.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash), discontinue FELDENE immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including FELDENE, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of piroxicam may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of FELDENE in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If FELDENE is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Piroxicam has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to piroxicam and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, FELDENE is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]. When FELDENE is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including piroxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions, and to discontinue the use of FELDENE at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. FELDENE is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.10 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as FELDENE. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, discontinue FELDENE and evaluate the patient immediately.
5.12 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with FELDENE has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including FELDENE, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders, concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin), SSRIs, and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.13 Masking of Inflammation and Fever
The pharmacological activity of FELDENE in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
5.14 Laboratory Monitoring
Because serious GI bleeding, hepatotoxicity, and renal injury can occur without warning symptoms or signs, consider monitoring patients on long-term NSAID treatment with a complete blood count (CBC) and a chemistry profile periodically [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.6)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In patients taking FELDENE or other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse experiences occurring in approximately 1% to 10% of patients are:
Cardiovascular System: Edema
Digestive System: Anorexia, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
Nervous System: Dizziness, headache, vertigo
Skin and Appendages: Pruritus, rash
Special Senses: Tinnitus
Additional adverse experiences reported occasionally include:
Cardiovascular System: Palpitations
Digestive System: Stomatitis
Nervous System: Drowsiness
Special Senses: Blurred vision
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of FELDENE. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: Fever, infection, sepsis, anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death, flu-like syndrome, pain (colic), serum sickness
Cardiovascular System: Congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope, arrhythmia, exacerbation of angina, hypotension, myocardial infarction, vasculitis
Digestive System: Dyspepsia, elevated liver enzymes, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, ulcers (gastric/duodenal), dry mouth, esophagitis, gastritis, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice, melena, rectal bleeding, eructation, liver failure, pancreatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: Anemia, increased bleeding time, ecchymosis, eosinophilia, epistaxis, leukopenia, purpura, petechial rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia
Hypersensitivity: Positive ANA
Metabolic and Nutritional: Weight changes, Fluid retention, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
Nervous System: Anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, akathisia, convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis, mood alterations
Respiratory System: Asthma, dyspnea, respiratory depression, pneumonia
Skin and Appendages: Alopecia, bruising, desquamation, erythema, photosensitivity, sweat, angioedema, toxic epidermal necrosis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, onycholysis, Stevens Johnson Syndrome, urticaria, vesiculobullous reaction
Special Senses: Conjunctivitis, hearing impairment, swollen eyes
Urogenital System: Abnormal renal function, cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, hyperkalemia, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure, glomerulonephritis
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Female fertility decreased
7. Drug Interactions
See Table 1 for clinically significant drug interactions with piroxicam.
| Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis | |
|---|---|
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of FELDENE with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin), SSRIs, and SNRIs for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Concomitant use of FELDENE and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. FELDENE is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection. |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: |
|
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of piroxicam with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of FELDENE and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of piroxicam with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | The concomitant use of piroxicam with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of FELDENE and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of FELDENE and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed. In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration. |
| Highly Protein Bound Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | FELDENE is highly protein bound and, therefore, might be expected to displace other protein bound drugs. |
| Intervention: | Physicians should closely monitor patients for a change in dosage requirements when administering FELDENE to patients on other highly protein bound drugs. |
| Corticosteroids | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of corticosteroids with FELDENE may increase the risk of GI ulceration or bleeding. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of FELDENE with corticosteroids for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
FELDENE has not been investigated in pediatric patients. The safety and effectiveness of FELDENE have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.14)].
10. Overdosage
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdoses have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an acute NSAID overdose. There are no specific antidotes. It is advisable to contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222) to determine the latest recommendations because strategies for the management of overdose are continually evolving.
If gastric decontamination may be potentially beneficial to the patient, e.g., short time since ingestion or a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage), consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 grams to 100 grams in adults, 1 gram to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or an osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients.
The long plasma half-life of piroxicam should be considered when treating an overdose with piroxicam. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
11. Feldene Description
FELDENE (piroxicam) capsule is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, available as maroon and blue #322 10 mg capsules and maroon #323 20 mg capsules for oral administration. The chemical name is 4-hydroxyl-2-methyl-N-2-pyridinyl-2H-1,2,-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide 1,1-dioxide. The molecular weight is 331.35. Its molecular formula is C15H13N3O4S, and it has the following chemical structure.
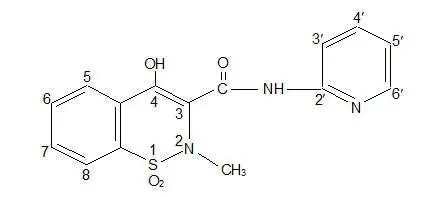
Piroxicam occurs as a white crystalline solid, sparingly soluble in water, dilute acid, and most organic solvents. It is slightly soluble in alcohol and in aqueous solutions. It exhibits a weakly acidic 4-hydroxy proton (pKa 5.1) and a weakly basic pyridyl nitrogen (pKa 1.8).
The inactive ingredients in FELDENE include: Blue 1, Red 3, lactose, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, starch.
12. Feldene - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Piroxicam has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of FELDENE, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Piroxicam is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin (PG) synthesis in vitro. Piroxicam concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because piroxicam is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic polymorphisms, such as the CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 polymorphisms. Limited data from two published reports showed that subjects with heterozygous CYP2C9*1/*2 (n=9), heterozygous CYP2C9*1/*3 (n=9), and homozygous CYP2C9*3/*3 (n=1) genotypes showed 1.7-, 1.7-, and 5.3-fold higher piroxicam systemic levels, respectively, than the subjects with CYP2C9*1/*1 (n=17, normal metabolizer genotype) following administration of a single oral dose. The mean elimination half-life values of piroxicam for subjects with CYP2C9*1/*3 (n=9) and CYP2C9*3/*3 (n=1) genotypes were 1.7- and 8.8-fold higher than subjects with CYP2C9*1/*1 (n=17). It is estimated that the frequency of the homozygous*3/*3 genotype is 0% to 1% in the population at large; however, frequencies as high as 5.7% have been reported in certain ethnic groups.
14. Clinical Studies
In controlled clinical trials, the effectiveness of FELDENE has been established for both acute exacerbations and long term management of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
The therapeutic effects of FELDENE are evident early in the treatment of both diseases with a progressive increase in response over several (8–12) weeks. Efficacy is seen in terms of pain relief and, when present, subsidence of inflammation.
Doses of 20 mg/day FELDENE display a therapeutic effect comparable to therapeutic doses of aspirin, with a lower incidence of minor gastrointestinal effects and tinnitus.
FELDENE has been administered concomitantly with fixed doses of gold and corticosteroids. The existence of a "steroid sparing" effect has not been adequately studied to date.
16. How is Feldene supplied
FELDENE® (piroxicam) 10 mg capsules are maroon and blue #322, supplied as:
| NDC Number | Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0069-3220-66 | bottles of 100 |
FELDENE® (piroxicam) 20 mg capsules are maroon #323, supplied as:
| NDC Number | Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0069-3230-66 | bottles of 100 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with FELDENE and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
| FELDENE
piroxicam capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| FELDENE
piroxicam capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc (134489525) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC | 829084545 | ANALYSIS(0069-3220, 0069-3230) , MANUFACTURE(0069-3220, 0069-3230) , API MANUFACTURE(0069-3220, 0069-3230) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC | 829084552 | ANALYSIS(0069-3220, 0069-3230) , MANUFACTURE(0069-3220, 0069-3230) , PACK(0069-3220, 0069-3230) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Inc | 943955690 | ANALYSIS(0069-3220, 0069-3230) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals | 985052076 | ANALYSIS(0069-3220, 0069-3230) , API MANUFACTURE(0069-3220, 0069-3230) | |








