Drug Detail:Pyrukynd (Mitapivat)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous metabolic agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
PYRUKYND® (mitapivat) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
Indications and Usage for Pyrukynd
PYRUKYND is a pyruvate kinase activator indicated for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency. (1)
Pyrukynd Dosage and Administration
- Starting dosage: 5 mg orally twice daily with or without food. (2.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for dose titration and taper schedule. (2.1, 2.3)
- The tablet should be swallowed whole. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 5 mg, 20 mg, and 50 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Acute Hemolysis: Avoid abrupt interruption or abrupt discontinuation of PYRUKYND to minimize the risk of acute hemolysis. A gradual reduction in dosing rather than abrupt cessation is recommended when possible. (5.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions including laboratory abnormalities (≥ 10%) in patients with PK deficiency were estrone decreased (males), increased urate, back pain, estradiol decreased (males), and arthralgia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Agios Pharmaceuticals at 1-833-228-8474 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers: Avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
- Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Do not titrate PYRUKYND beyond 20 mg twice daily. (7.1)
- Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Consider alternatives that are not moderate inducers. If there are no alternatives, adjust PYRUKYND dosage. (7.1)
- Sensitive CYP3A, CYP2B6, CYP2C substrates including hormonal contraceptives: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index. (7.2)
- UGT1A1 Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index. (7.2)
- P-gp Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use of PYRUKYND in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Pyrukynd
PYRUKYND is indicated for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency.
2. Pyrukynd Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
PYRUKYND is taken with or without food and swallowed whole. Do not split, crush, chew, or dissolve the tablets.
The starting dosage for PYRUKYND is 5 mg orally twice daily. To gradually increase hemoglobin (Hb), titrate PYRUKYND from 5 mg twice daily to 20 mg twice daily, and then to the maximum recommended dose of 50 mg twice daily, with these dose increases occurring every 4 weeks (see Table 1). Assess Hb and transfusion requirement before increasing to the next dose level, as some patients may reach and maintain normal Hb at 5 mg twice daily or 20 mg twice daily.
Discontinue PYRUKYND if no benefit has been observed by 24 weeks, based on the hemoglobin and hemolysis laboratory results and transfusion requirements.
| Duration | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Week 1 through Week 4 | 5 mg twice daily |
| Week 5 through Week 8 | If Hb is below normal range or patient has required a transfusion within the last 8 weeks:
|
| Week 9 through Week 12 | If Hb is below normal range or patient has required a transfusion within the last 8 weeks:
|
| Maintenance | If Hb decreases, consider up-titration to the maximum of 50 mg twice daily as per the above schedule. |
2.2 Missed Dose
If a dose of PYRUKYND is missed by 4 hours or less, administer the dose as soon as possible. If a dose of PYRUKYND is missed by more than 4 hours, do not administer a replacement dose, and wait until the next scheduled dose. Subsequently, return to the normal dosing schedule.
2.3 Interruption or Discontinuation
To reduce the risk of acute hemolysis, avoid abrupt interruption or abrupt discontinuation of PYRUKYND when possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Taper the dose to gradually discontinue the medication (see Table 2). Monitor patients for signs of acute hemolysis and worsening of anemia.
| Current Dose | Dose Taper Schedule | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1-7 | Day 8-14 | Day 15 | |
| Abbreviations: N/A = not applicable. | |||
| 5 mg twice daily | 5 mg once daily | Discontinue | N/A |
| 20 mg twice daily | 20 mg once daily | 5 mg once daily | Discontinue |
| 50 mg twice daily | 50 mg once daily | 20 mg once daily | Discontinue |
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use of PYRUKYND in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Special Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.6 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions and Hemoglobin Levels Above Normal
If a dose reduction is required because of an adverse reaction or tolerability, or for Hb above normal, the dose may be reduced to the next lower dose level, 20 mg twice daily or 5 mg twice daily.
If a patient needs to discontinue PYRUKYND, the dose taper schedule (Table 2) should be followed. In situations where the risk to the patient due to the adverse reaction or Hb above normal is greater than the risk of acute hemolysis due to sudden withdrawal of the drug, treatment may be stopped without taper and patients should be monitored for signs of acute hemolysis.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- 5 mg tablets: round, blue, film-coated tablets with "M5" printed on one side.
- 20 mg tablets: round, blue, film-coated tablets with "M20" printed on one side.
- 50 mg tablets: oblong, blue, film-coated tablets with "M50" printed on one side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Acute Hemolysis with Abrupt Treatment Interruption
Acute hemolysis with subsequent anemia has been observed following abrupt interruption or discontinuation of PYRUKYND in a dose-ranging study. Avoid abruptly discontinuing PYRUKYND. Gradually taper the dose of PYRUKYND to discontinue treatment if possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.6)]. When discontinuing treatment, monitor patients for signs of acute hemolysis and anemia including jaundice, scleral icterus, dark urine, dizziness, confusion, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reaction is described elsewhere in labeling:
- Acute Hemolysis with Abrupt Treatment Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 155 patients received PYRUKYND, 79% of whom were exposed for longer than 24 weeks. PYRUKYND was administered up to 50 mg orally twice daily in 67 patients with PK deficiency in the ACTIVATE trial (N=40) and the ACTIVATE-T trial (N=27) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
ACTIVATE Trial
In the ACTIVATE trial patients with PK deficiency who were not regularly transfused received PYRUKYND in incremental doses up to 50 mg twice daily (N=40) or placebo (N=39).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 10% of patients receiving PYRUKYND in the ACTIVATE Trial, including atrial fibrillation, gastroenteritis, rib fracture, and musculoskeletal pain, which each occurred in 1 patient.
In the ACTIVATE trial, the most common adverse reactions including laboratory abnormalities (≥ 10%) in patients with PK deficiency were estrone decreased (males), increased urate, back pain, estradiol decreased (males), and arthralgia.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in the ACTIVATE trial.
| Adverse Reactions | PYRUKYND (N=40) | Placebo (N=39) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) |
|
| Grades: Per the CTCAE definition. Grouped Term Definitions |
||||
|
||||
| Back pain* | 15% | 0 | 8% | 0 |
| Arthralgia† | 10% | 0 | 5% | 0 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia‡ | 8% | 5% | 3% | 0 |
| Gastroenteritis | 8% | 3% | 0 | 0 |
| Hot flush§ | 8% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 8% | 0 | 5% | 0 |
| Hypertension | 5% | 5% | 0 | 0 |
| Arrhythmia¶ | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Breast discomfort | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Constipation | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dry mouth# | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Paresthesia | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Laboratory abnormalities of PYRUKYND included increased urate (15%).
Variations in Reproductive Hormones
In ACTIVATE, increases in serum testosterone and decreases in serum estrone and estradiol were observed in men receiving PYRUKYND (Table 4). These changes in hormones persisted throughout the study period. In patients who discontinued PYRUKYND and had follow-up hormone measurements, the hormone changes returned close to the baseline levels 28 days after discontinuing PYRUKYND. In female patients, sex hormone analysis was limited due to physiologic variations in hormones during the menstrual cycle and the use of hormonal contraceptives.
| ACTIVATE | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | PYRUKYND (16 males) n (%) | Placebo (15 males) n (%) |
|
||
| Reproductive hormone analyses* | ||
| Estrone decreased (males) | 9 (56.3) | 0 |
| Estradiol decreased (males) | 2 (12.5) | 1 (6.7) |
| Blood testosterone increased (males) | 1 (6.3) | 1 (6.7) |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on PYRUKYND
| Strong CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| Strong CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| Moderate CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
7.2 Effect of PYRUKYND on Other Drugs
| CYP3A Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| CYP2B6 and CYP2C Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| UGT1A1 Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| P-gp Substrates | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of PYRUKYND did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Mitapivat undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism. Moderate and severe hepatic impairment is expected to increase the systemic exposure of mitapivat. Avoid use of PYRUKYND in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Pyrukynd Description
The active ingredient of PYRUKYND is mitapivat, a pyruvate kinase activator, present as mitapivat sulfate. The chemical name of mitapivat sulfate is 8-quinolinesulfonamide, N-[4-[[4- (cyclopropylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl]phenyl]-, sulfate, hydrate (2:1:3). The chemical structure of mitapivat sulfate is:
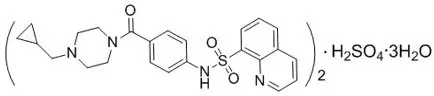
The molecular formula is (C24H26N4SO3)2 ∙ H2SO4 ∙ 3H2O, and the molecular weight is 1053.23 for mitapivat sulfate. Mitapivat sulfate is a white to off-white solid and is slightly soluble in water.
PYRUKYND is available as 5 mg, 20 mg, and 50 mg tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 5 mg, 20 mg, or 50 mg mitapivat free base, provided as 5.85 mg, 23.4 mg, or 58.5 mg, respectively, of the sulfate hydrate salt, and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablet film coating contains the inactive ingredients FD&C Blue No. 2, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. The tablets are imprinted with black ink containing the inactive ingredients ammonium hydroxide, ferrosoferric oxide, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze.
12. Pyrukynd - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mitapivat is a pyruvate kinase activator that acts by allosterically binding to the pyruvate kinase tetramer and increasing pyruvate kinase (PK) activity. The red blood cell (RBC) form of pyruvate kinase (PK-R) is mutated in PK deficiency, which leads to reduced adenosine triphosphate (ATP), shortened RBC lifespan, and chronic hemolysis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Mitapivat decreases 2,3 diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) and increases ATP in healthy volunteers.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mitapivat exposure increased in an approximately dose proportional manner over the clinically relevant dose range of 5 mg to 50 mg twice daily.
The population pharmacokinetic model simulated Cmax, Ctrough, AUC0-12 and accumulation ratio of mitapivat at recommended dosages are listed in the table below.
| Mitapivat Dosage | Cmax
(ng/mL) | Ctrough
(ng/mL) | AUC0-12
(ng*h/mL) | Accumulation Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| 5 mg twice daily | 101.2 (17%) | 10.1 (74%) | 450.4 (28%) | 1.2 |
| 20 mg twice daily | 389.9 (18%) | 32.3 (77%) | 1623.8 (28%) | 1.1 |
| 50 mg twice daily | 935.2 (18%) | 62.1 (80%) | 3591.4 (28%) | 1.0 |
14. Clinical Studies
Patients with PK Deficiency
Patients Not Regularly Transfused
The efficacy of PYRUKYND was evaluated in ACTIVATE, a multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study (NCT03548220) of 80 adults with PK deficiency who were not regularly transfused, defined as having had no more than 4 transfusions in the 52- week period prior to treatment and no transfusions in the 3-month period prior to treatment. Patients were included if they had documented presence of at least 2 variant alleles in the pyruvate kinase liver and red blood cell (PKLR) gene, of which at least 1 was a missense variant, and Hb less than or equal to 10 g/dL. Patients who were homozygous for the c.1436G>A (p.R479H) variant or had 2 non-missense variants (without the presence of another missense variant) in the PKLR gene were excluded because these patients did not achieve Hb response (change from baseline in Hb ≥1.5 g/dL at >50% assessments) in the dose-ranging study. Randomization was stratified by average screening Hb (<8.5 vs ≥8.5 g/dL) and PKLR gene variant category (missense/missense vs. missense/non-missense).
Among the 80 patients with PK deficiency, 40 patients were randomized to PYRUKYND. Following a period of dose titration up to 50 mg twice daily, patients continued a fixed dose of PYRUKYND for 12 weeks. Eighty-eight percent of patients were maintained on 50 mg twice daily.
The median duration of treatment with PYRUKYND was 24.1 weeks (range 23.6 to 27.4 weeks). Overall, 30 (75%) patients were exposed to PYRUKYND for >24 weeks and <28 weeks. Among the 80 randomized patients, the median age was 33 years (range 18 to 78) and 40% were male; race was reported in 88% of patients: 75% were White, 10% Asian, 1.3% Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander and 1.3% were other races. The median baseline hemoglobin was 8.5 g/dL (range: 6.4 to 10.2 g/dL). There were 55 patients (69%) with the missense/missense PKLR gene variant category, and 25 patients (31%) with the missense/non-missense PKLR gene variant category. There were 58 patients (73%) who had a history of splenectomy. Complications and comorbidities associated with PK deficiency included iron overload with a median baseline ferritin of 479 ng/mL (range: 21 to 5890 ng/mL), chelation therapy use in the year before the first dose of study treatment in 15 patients (19%), decreased bone mineral density in 64 patients (80%) who had a baseline femoral neck T-score or lumbar spine T-score <-1.0, and history of cholecystectomy in 58 patients (73%).
Efficacy was based upon Hb response, defined as a ≥1.5 g/dL increase in Hb from baseline sustained at 2 or more scheduled assessments (Weeks 16, 20, and 24) during the fixed dose period without transfusions. The efficacy results, including changes in markers of hemolysis are shown in Table 6.
| Endpoint | PYRUKYND N=40 | Placebo N=40 | Difference*, †
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval, Hb: hemoglobin, LDH: lactate dehydrogenase, LS Mean Change: least square mean change from baseline, SD: standard deviation | |||
|
|||
| Hb Response, n (%) | 16 (40%) | 0 | 39 (24, 55) <0.0001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | |||
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 8.6 (1.0) | 8.5 (0.8) | |
| LS Mean Change (95% CI) | 1.7 (1.3, 2.1) | -0.1 (-0.6, 0.3) | 1.8 (1.2, 2.4) |
| <0.0001 | |||
| Indirect bilirubin (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 4.8 (3.6) | 5.2 (3.6) | |
| LS Mean Change (95% CI) | -1.2 (-1.7, -0.7) | 0.3 (-0.2, 0.8) | -1.5 (-2.2, -0.9) |
| <0.0001 | |||
| Reticulocyte (fraction of 1) | |||
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 0.37 (0.24) | 0.40 (0.22) | |
| LS Mean Change (95% CI) | -0.10 (-0.13, -0.07) | 0 (-0.02, 0.03) | -0.10 (-0.14, -0.06) |
| <0.0001 | |||
| LDH (U/L) | |||
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 348 (276) | 260 (140) | |
| LS Mean Change (95% CI) | -92 (-124, -60) | -21 (-53, 11) | -71 (-116, -26) |
| 0.003 | |||
| Haptoglobin (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 8.2 (10.7) | 8.3 (13.8) | |
| LS Mean Change (95% CI) | 16.9 (8.8, 25.1) | 1.2 (-7.0, 9.4) | 15.8 (4.3, 27.3) |
| 0.008 | |||
In ACTIVATE, the LS Mean change from baseline with PYRUKYND compared to placebo was -0.4 (standard error [SE] 0.1) for jaundice (scale: 0-4), -1.1 (SE 0.4) for tiredness (scale: 0-10), and -0.3 (SE 0.3) for shortness of breath (scale: 0-10), assessed with the daily Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency Diary (PKDD) where lower scores represent less sign/symptom severity.
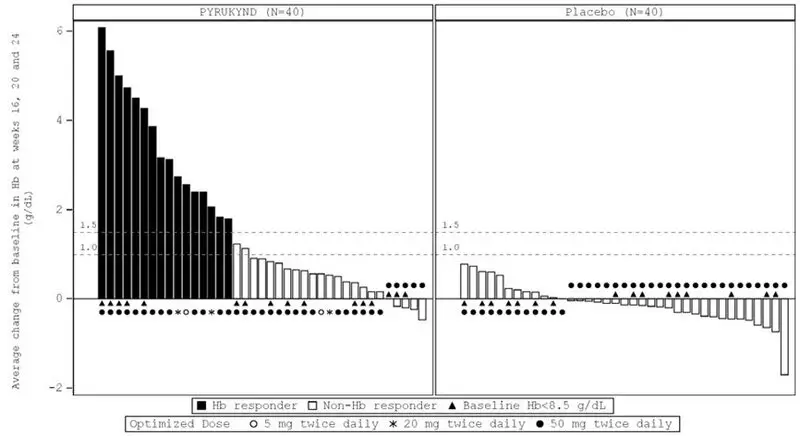
In ACTIVATE, the majority of PYRUKYND-treated patients experienced an increase in Hb, while the majority of patients in the placebo arm experienced a decrease in Hb as measured by average change from baseline at weeks 16, 20, and 24 (Figure 1).
|
| Figure 1: Average Change at Weeks 16, 20, and 24 from Baseline in Hemoglobin (Hb) by Patient - All Randomized Patients (ACTIVATE)* |
|
|
| CI: confidence interval, Hb: hemoglobin, LS: least square |
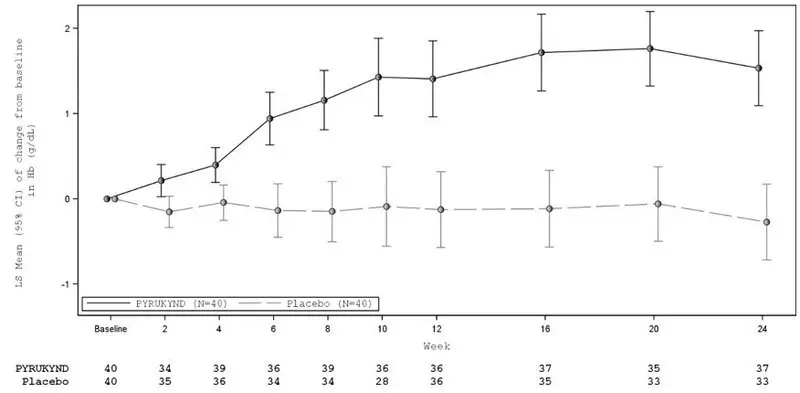
| Figure 2: LS Mean Change from Baseline in Hemoglobin Over Time - All Randomized Patients (ACTIVATE) |
|
|
Fifteen of the 16 patients with a Hb response in ACTIVATE continued in a long-term extension study and were evaluable for maintenance of response. Thirteen maintained increases in Hb concentration from baseline above the response threshold of ≥1.5 g/dL at the last available Hb assessment without requiring any transfusions. The median duration of response for the 16 patients with Hb response was 6.9 months (range: 3.3, 18.4+).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| PATIENT INFORMATION PYRUKYND (pye roo' kind) (mitapivat) tablets, for oral use |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 2/2022 | |||
| What is PYRUKYND?
PYRUKYND is a prescription medicine used to treat low red blood cell counts caused by the early breakdown of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia) in adults with pyruvate kinase deficiency (PK Deficiency). It is not known if PYRUKYND is safe and effective in children. |
||||
Before taking PYRUKYND, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
PYRUKYND and certain other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. PYRUKYND may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how PYRUKYND works. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
||||
How should I take PYRUKYND?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of PYRUKYND? PYRUKYND may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
| The most common side effects of PYRUKYND include: | ||||
|
|
|||
| These are not all of the possible side effects of PYRUKYND. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
How should I store PYRUKYND?
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of PYRUKYND.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use PYRUKYND for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give PYRUKYND to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about PYRUKYND that is written for healthcare professionals. |
||||
| What are the ingredients in PYRUKYND?
Active ingredient: mitapivat Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablet film coating contains: FD&C Blue No. 2, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. The tablets printed with black ink contains: ammonium hydroxide, ferrosoferric oxide, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze. Manufactured for and Distributed by: Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Cambridge, MA 02139 PYRUKYND® is a trademark of Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. © 2022 Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. For more information, visit www.pyrukynd.com or call 1-833-228-8474. |
||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| PYRUKYND
mitapivat kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (011567735) |
| Registrant - Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (011567735) |