Drug Detail:Relafen (Nabumetone [ na-bue-me-tone ])
Drug Class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Relafen Description
Nabumetone is a naphthylalkanone designated chemically as 4-(6-methoxy-2-naphthalenyl)-2-butanone. It has the following structure: C15H16O2 M.W. 228.3
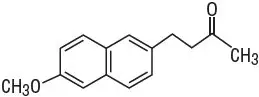
Nabumetone is a white to off-white crystalline substance. It is nonacidic and practically insoluble in water, but soluble in alcohol and most organic solvents. It has an n-octanol:phosphate buffer partition coefficient of 2,400 at pH 7.4.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains either 500 mg, 750 mg, or 1000 mg of nabumetone. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: povidone, croscarmellose, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, and colloidal silicon dioxide. The coating contains hydroxypropyl cellulose and hypromellose.
Relafen - Clinical Pharmacology
Nabumetone is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties in pharmacologic studies. As with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, its mode of action is not known; however, the ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis may be involved in the anti-inflammatory effect.
The parent compound is a prodrug, which undergoes hepatic biotransformation to the active component, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA), that is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis.
6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA)
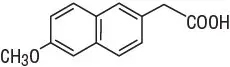
It is acidic and has an n-octanol:phosphate buffer partition coefficient of 0.5 at pH 7.4.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, approximately 80% of a radiolabeled dose of nabumetone is found in the urine, indicating that nabumetone is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Nabumetone itself is not detected in the plasma because, after absorption, it undergoes rapid biotransformation to the principal active metabolite, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA). Approximately 35% of a 1,000 mg oral dose of nabumetone is converted to 6MNA and 50% is converted into unidentified metabolites which are subsequently excreted in the urine. Following oral administration of nabumetone, 6MNA exhibits pharmacokinetic characteristics that generally follow a one-compartment model with first order input and first order elimination.
6MNA is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The free fraction is dependent on total concentration of 6MNA and is proportional to dose over the range of 1,000 mg to 2,000 mg. It is 0.2% to 0.3% at concentrations typically achieved following administration of 1,000 mg of nabumetone and is approximately 0.6% to 0.8% of the total concentrations at steady state following daily administration of 2,000 mg.
Steady-state plasma concentrations of 6MNA are slightly lower than predicted from single-dose data. This may result from the higher fraction of unbound 6MNA which undergoes greater hepatic clearance.
Coadministration of food increases the rate of absorption and subsequent appearance of 6MNA in the plasma but does not affect the extent of conversion of nabumetone into 6MNA. Peak plasma concentrations of 6MNA are increased by approximately one third.
Coadministration with an aluminum-containing antacid had no significant effect on the bioavailability of 6MNA.
| Abbreviation (units) | Young Adults Mean ± SD 1,000 mg n = 31 | Young Adults Mean ± SD 2,000 mg n = 12 | Elderly Mean ± SD 1,000 mg n = 27 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax (hr) | 3.0 (1.0 to 12.0) | 2.5 (1.0 to 8.0) | 4.0 (1.0 to 10.0) |
| t1/2 (hr) | 22.5 ± 3.7 | 26.2 ± 3.7 | 29.8 ± 8.1 |
| CLss/F (mL/min) | 26.1 ± 17.3 | 21.0 ± 4.0 | 18.6 ± 13.4 |
| Vdss/F (L) | 55.4 ± 26.4 | 53.4 ± 11.3 | 50.2 ± 25.3 |
The simulated curves in the graph below illustrate the range of active metabolite plasma concentrations that would be expected from 95% of patients following 1,000 mg to 2,000 mg doses to steady state. The cross-hatched area represents the expected overlap in plasma concentrations due to intersubject variation following oral administration of 1,000 mg to 2,000 mg of nabumetone.
Nabumetone Active Metabolite (6MNA) Plasma Concentrations at Steady State Following Once-Daily Dosing of Nabumetone 1,000 mg (n = 31) 2,000 mg (n = 12)
6MNA undergoes biotransformation in the liver, producing inactive metabolites that are eliminated as both free metabolites and conjugates. None of the known metabolites of 6MNA has been detected in plasma. Preliminary in vivo and in vitro studies suggest that unlike other NSAIDs, there is no evidence of enterohepatic recirculation of the active metabolite. Approximately 75% of a radiolabeled dose was recovered in urine in 48 hours. Approximately 80% was recovered in 168 hours. A further 9% appeared in the feces. In the first 48 hours, metabolites consisted of:
| - nabumetone, unchanged | not detectable |
| - 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6MNA), unchanged | < 1% |
| - 6MNA, conjugated | 11% |
| - 6-hydroxy-2-naphthylacetic acid (6HNA), unchanged | 5% |
| - 6HNA, conjugated | 7% |
| - 4-(6-hydroxy-2-naphthyl)-butan-2-ol, conjugated | 9% |
| - O-desmethyl-nabumetone, conjugated | 7% |
| - unidentified minor metabolites | 34% |
| Total % Dose: | 73% |
Following oral administration of dosages of 1,000 mg to 2,000 mg to steady state, the mean plasma clearance of 6MNA is 20 to 30 mL/min and the elimination half-life is approximately 24 hours.
Related/similar drugs
aspirin, prednisone, ibuprofen, meloxicam, naproxen, Cymbalta, hydroxychloroquineCLINICAL TRIALS
Patient Exposure in Clinical Trials of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
In clinical trials with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients, most patients responded to nabumetone in doses of 1,000 mg/day administered nightly; total daily dosages up to 2,000 mg were used. In open-labeled studies, 1,490 patients were permitted dosage increases and were followed for approximately 1 year (mode). Twenty percent of patients (n = 294) were withdrawn for lack of effectiveness during the first year of these open-labeled studies. The following table provides patient-exposure to doses used in the U.S. clinical trials:
| Dose of Nabumetone | Number of Patients | Mean/Mode Duration of Treatment (yr) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | RA | OA | RA | |
| 500 mg | 17 | 6 | 0.4/- | 0.2/- |
| 1,000 mg | 917 | 701 | 1.2/1 | 1.4/1 |
| 1,500 mg | 645 | 224 | 2.3/1 | 1.7/1 |
| 2,000 mg | 15 | 100 | 0.6/1 | 1.3/1 |
As with other NSAIDs, the lowest dose should be sought for each patient. Patients weighing under 50 kg may be less likely to require dosages beyond 1,000 mg; therefore, after observing the response to initial therapy, the dose should be adjusted to meet individual patients' requirements.
Indications and Usage for Relafen
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of nabumetone tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use nabumetone tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
Nabumetone tablets are indicated for relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Contraindications
Nabumetone tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to nabumetone or product excipients.
Nabumetone tablets should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
Nabumetone tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS).
Warnings
Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reaction information was derived from blinded-controlled and open-labeled clinical trials and from worldwide marketing experience. In the description below, rates of the more common events (greater than 1%) and many of the less common events (less than 1%) represent results of U.S. clinical studies.
Of the 1,677 patients who received nabumetone during U.S. clinical trials, 1,524 were treated for at least 1 month, 1,327 for at least 3 months, 929 for at least a year, and 750 for at least 2 years. More than 300 patients have been treated for 5 years or longer.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were related to the gastrointestinal tract and included diarrhea, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain.
Overdosage
Symptoms following acute NSAIDs overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following a NSAIDs overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 g/kg in children), and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated in patients seen within 4 hours of ingestion with symptoms or following a large overdose (5 to 10 times the usual dose). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
There have been overdoses of up to 25 grams of nabumetone reported with no long-term sequelae following standard emergency treatment (i.e., activated charcoal, gastric lavage, IV H2-blockers, etc.).
Relafen Dosage and Administration
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of nabumetone tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use nabumetone tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
After observing the response to initial therapy with nabumetone tablets, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs.
How is Relafen supplied
RELAFEN Nabumetone tablets USP, 500 mg are white, coated, modified capsule-shaped tablets, debossed with "HT" on one side and "500" on the other. They are available in bottles of: 30 tablets - NDC 73684-100-30.
RELAFEN Nabumetone tablets USP, 750 mg are white, coated, modified capsule-shaped tablets, debossed with "HT" on one side and "750" on the other. They are available in bottles of: 30 tablets - NDC 73684-101-30.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Rev. 03/2020 | |||
| Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) | ||||
| What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti- inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|||
| NSAIDs should only be used: | ||||
|
||||
| What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain. |
||||
| Who should not take NSAIDs? Do not take NSAIDs:
|
||||
Before taking NSAIDS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti- inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
|
||||
|
|
|||
| Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | ||||
|
|
|||
If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away. These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.
|
||||
Other information about NSAIDs
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals. |
||||
| Manufactured for: Blucrest Pharmaceuticals, LLC. Hazlet, NJ 07730. For further information please visit: www.blucrestpharma.com |
||||
| RELAFEN
nabumetone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| RELAFEN
nabumetone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BLUCREST PHARMACEUTICALS LLC (117424533) |






