Drug Detail:Serevent diskus (Salmeterol (inhalation) [ sal-mee-ter-all ])
Drug Class: Adrenergic bronchodilators
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SEREVENT DISKUS (salmeterol xinafoate inhalation powder), for oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1994
WARNING: ASTHMA-RELATED DEATH
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- •
- Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA), such as salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without inhaled corticosteroids [ICS]) increase the risk of asthma-related death. A U.S. trial showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol (13 deaths out of 13,176 subjects treated for 28 weeks on salmeterol versus 3 out of 13,179 subjects on placebo). When LABA are used in fixed-dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared with ICS alone. (5.1)
- •
- Prescribe SEREVENT DISKUS only as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are inadequately controlled on an ICS. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or medium-dose ICS. (1.1, 5.1)
- •
- Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for Serevent Diskus
SEREVENT DISKUS is a LABA indicated for:
- •
- Treatment of asthma in patients aged 4 years and older with an ICS. (1.1)
- •
- Prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB) in patients aged 4 years and older. (1.2)
- •
- Maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). (1.3)
Important limitation of use: Not indicated for relief of acute bronchospasm. (1.1, 1.3)
Serevent Diskus Dosage and Administration
- •
- For oral inhalation only. (2)
- •
- Treatment of asthma in patients aged 4 years and older: 1 inhalation twice daily in addition to concomitant treatment with an ICS. (2.1)
- •
- EIB: 1 inhalation at least 30 minutes before exercise. (2.2)
- •
- Maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with COPD: 1 inhalation twice daily. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Inhalation powder: Inhaler containing salmeterol (50 mcg) as a powder formulation for oral inhalation. (3)
Contraindications
- •
- Asthma: Without concomitant use of an ICS. (4)
- •
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or acute episodes of asthma or COPD requiring intensive measures. (4)
- •
- Severe hypersensitivity to milk proteins or demonstrated hypersensitivity to salmeterol or any of the excipients. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- •
- LABA as monotherapy (without ICS) for asthma increase the risk of asthma-related death and asthma-related hospitalizations. Prescribe for asthma only as concomitant therapy with an inhaled corticosteroid. (5.1)
- •
- Do not initiate in acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD. Do not use to treat acute symptoms. (5.2)
- •
- Not a substitute for corticosteroids. Patients with asthma must take a concomitant ICS. (5.3)
- •
- Do not use in combination with an additional medicine containing a LABA because of risk of overdose. (5.4)
- •
- If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, discontinue SEREVENT DISKUS and institute alternative therapy. (5.5)
- •
- Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular or central nervous system disorders because of beta-adrenergic stimulation. (5.6)
- •
- Use with caution in patients with convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, and ketoacidosis. (5.9)
- •
- Be alert to hypokalemia and hyperglycemia. (5.10)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) are:
- •
- Asthma: Headache, influenza, nasal/sinus congestion, pharyngitis, rhinitis, tracheitis/bronchitis. (6.1)
- •
- COPD: Cough, headache, musculoskeletal pain, throat irritation, viral respiratory infection. (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1-888-825-5249 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- •
- Strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, ketoconazole): Use not recommended. May increase risk of cardiovascular effects. (7.1)
- •
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants: Use with extreme caution. May potentiate effect of salmeterol on vascular system. (7.2)
- •
- Beta-blockers: Use with caution. May block bronchodilatory effects of beta-agonists and produce severe bronchospasm. (7.3)
- •
- Diuretics: Use with caution. Electrocardiographic changes and/or hypokalemia associated with non–potassium-sparing diuretics may worsen with concomitant beta-agonists. (7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
Hepatic impairment: Monitor patients for signs of increased drug exposure. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 2/2022
Related/similar drugs
Dupixent, Xolair, albuterol, montelukast, Symbicort, Singulair, Breo ElliptaFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: ASTHMA-RELATED DEATH
Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA), such as salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without inhaled corticosteroids [ICS]) increase the risk of asthma-related death. Data from a large placebo-controlled U.S. trial that compared the safety of salmeterol with placebo added to usual asthma therapy showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol (13 deaths out of 13,176 subjects treated for 28 weeks on salmeterol versus 3 deaths out of 13,179 subjects on placebo). Use of background ICS was not required in this study. When LABA are used in fixed-dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared with ICS alone.
Use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma as monotherapy without a concomitant ICS is contraindicated. Use SEREVENT DISKUS only as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are inadequately controlled on an ICS. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or medium-dose ICS.
Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. For pediatric and adolescent patients with asthma who require addition of a LABA to an ICS, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA should ordinarily be used to ensure adherence with both drugs. In cases where use of an ICS and a LABA is clinically indicated, appropriate steps must be taken to ensure adherence with both treatment components. If adherence cannot be assured, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA is recommended.
1. Indications and Usage for Serevent Diskus
1.1 Treatment of Asthma
SEREVENT DISKUS is indicated for the treatment of asthma and in the prevention of bronchospasm only as concomitant therapy with an ICS in patients aged 4 years and older with reversible obstructive airway disease, including patients with symptoms of nocturnal asthma. LABA, such as salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without ICS) increase the risk of asthma-related death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma without concomitant use of an ICS is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. Use SEREVENT DISKUS only as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are inadequately controlled on an ICS. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or medium-dose ICS.
Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. For pediatric and adolescent patients with asthma who require addition of a LABA to an ICS, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA should ordinarily be used to ensure adherence with both drugs. In cases where use of a separate ICS and a LABA is clinically indicated, appropriate steps must be taken to ensure adherence with both treatment components. If adherence cannot be assured, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA is recommended.
Important Limitation of Use
SEREVENT DISKUS is NOT indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
1.2 Prevention of Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
SEREVENT DISKUS is also indicated for prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB) in patients aged 4 years and older. Use of SEREVENT DISKUS as a single agent for the prevention of EIB may be clinically indicated in patients who do not have persistent asthma. In patients with persistent asthma, use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the prevention of EIB may be clinically indicated, but the treatment of asthma should include an ICS.
1.3 Maintenance Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
SEREVENT DISKUS is indicated for the long-term twice-daily administration in the maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (including emphysema and chronic bronchitis).
Important Limitation of Use
SEREVENT DISKUS is NOT indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
2. Serevent Diskus Dosage and Administration
SEREVENT DISKUS should be administered by the orally inhaled route only.
More frequent administration or a greater number of inhalations (more than 1 inhalation twice daily) is not recommended as some patients are more likely to experience adverse effects. Patients using SEREVENT DISKUS should not use additional LABA for any reason. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.6).]
2.1 Asthma
LABA, such as salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without ICS) increase the risk of asthma-related death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Because of this risk, use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma without concomitant use of an ICS is contraindicated. Use SEREVENT DISKUS only as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are inadequately controlled on an ICS. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or medium-dose ICS.
Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. For patients with asthma younger than 18 years who require addition of a LABA to an ICS, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA should ordinarily be used to ensure adherence with both drugs. In cases where use of a separate ICS and a LABA is clinically indicated, appropriate steps must be taken to ensure adherence with both treatment components. If adherence cannot be assured, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA is recommended.
For bronchodilatation and prevention of symptoms of asthma, including the symptoms of nocturnal asthma, the usual dosage for adults and children aged 4 years and older is 1 inhalation (50 mcg) twice daily, approximately 12 hours apart. If a previously effective dosage regimen fails to provide the usual response, medical advice should be sought immediately as this is often a sign of destabilization of asthma. Under these circumstances, the therapeutic regimen should be reevaluated. If symptoms arise in the period between doses, an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist should be taken for immediate relief.
2.2 Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
Use of SEREVENT DISKUS as a single agent for the prevention of EIB may be clinically indicated in patients who do not have persistent asthma. In patients with persistent asthma, use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the prevention of EIB may be clinically indicated, but the treatment of asthma should include an ICS. One inhalation of SEREVENT DISKUS at least 30 minutes before exercise has been shown to protect patients against EIB. When used intermittently as needed for prevention of EIB, this protection may last up to 9 hours in adults and adolescents and up to 12 hours in patients aged 4 to 11 years. Additional doses of SEREVENT should not be used for 12 hours after the administration of this drug. Patients who are receiving SEREVENT DISKUS twice daily should not use additional SEREVENT for prevention of EIB.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Inhalation powder: Inhaler containing a foil blister strip of powder formulation for oral inhalation. The strip contains salmeterol 50 mcg per blister.
4. Contraindications
Use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma without concomitant use of an ICS is contraindicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The use of SEREVENT DISKUS is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- •
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or other acute episodes of asthma or COPD where intensive measures are required [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Severe hypersensitivity to milk proteins or demonstrated hypersensitivity to salmeterol or any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Adverse Reactions (6.3), Description (11)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Asthma-Related Death
LABA, such as salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without ICS) increase the risk of asthma-related death. When LABA are used in fixed-dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared with ICS alone.
Use of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma without concomitant use of an ICS is contraindicated. Use SEREVENT DISKUS only as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are inadequately controlled on an ICS. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or medium-dose ICS.
Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. For pediatric and adolescent patients with asthma who require addition of a LABA to an ICS, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA should ordinarily be used to ensure adherence with both drugs. In cases where use of a separate ICS and a LABA is clinically indicated, appropriate steps must be taken to ensure adherence with both treatment components. If adherence cannot be assured, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA is recommended.
The Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART) was a large 28-week placebo-controlled U.S. trial comparing the safety of salmeterol (SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol) with placebo, each added to usual asthma therapy, that showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Given the similar basic mechanisms of action of beta2-agonists, the findings seen in the SMART trial are considered a class effect.
A 16-week clinical trial performed in the United Kingdom, the Salmeterol Nationwide Surveillance (SNS) trial, showed results similar to the SMART trial. In the SNS trial, the rate of asthma-related death was numerically, though not statistically significantly, greater in subjects with asthma treated with salmeterol (42 mcg twice daily) than those treated with albuterol (180 mcg 4 times daily) added to usual asthma therapy.
The SNS and SMART trials enrolled subjects with asthma. Available data do not suggest an increased risk of death with use of LABA in patients with COPD.
5.2 Deterioration of Disease and Acute Episodes
SEREVENT DISKUS should not be initiated in patients during rapidly deteriorating or potentially life-threatening episodes of asthma or COPD. SEREVENT DISKUS has not been studied in subjects with acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD. The initiation of SEREVENT DISKUS in this setting is not appropriate.
Serious acute respiratory events, including fatalities, have been reported when salmeterol has been initiated in patients with significantly worsening or acutely deteriorating asthma. In most cases, these have occurred in patients with severe asthma (e.g., patients with a history of corticosteroid dependence, low pulmonary function, intubation, mechanical ventilation, frequent hospitalizations, previous life-threatening acute asthma exacerbations) and in some patients with acutely deteriorating asthma (e.g., patients with significantly increasing symptoms; increasing need for inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists; decreasing response to usual medications; increasing need for systemic corticosteroids; recent emergency room visits; deteriorating lung function). However, these events have occurred in a few patients with less severe asthma as well. It was not possible from these reports to determine whether salmeterol contributed to these events.
Increasing use of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists is a marker of deteriorating asthma. In this situation, the patient requires immediate reevaluation with reassessment of the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for adding additional ICS or initiating systemic corticosteroids. Patients should not use more than 1 inhalation twice daily of SEREVENT DISKUS.
SEREVENT DISKUS should not be used for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. An inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist, not SEREVENT DISKUS, should be used to relieve acute symptoms such as shortness of breath. When prescribing SEREVENT DISKUS, the healthcare provider should also prescribe an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist (e.g., albuterol) for treatment of acute symptoms.
When beginning treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS, patients who have been taking oral or inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists on a regular basis (e.g., 4 times a day) should be instructed to discontinue the regular use of these drugs.
5.3 SEREVENT DISKUS is Not a Substitute for Corticosteroids
There are no data demonstrating that SEREVENT DISKUS has a clinical anti-inflammatory effect such as that associated with corticosteroids. When initiating and throughout treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS in patients receiving oral or ICS for treatment of asthma, patients must continue taking a suitable dosage of corticosteroids to maintain clinical stability even if they feel better as a result of initiating SEREVENT DISKUS. Any change in corticosteroid dosage should be made ONLY after clinical evaluation.
5.4 Excessive Use of SEREVENT DISKUS and Use with Other Long-acting Beta2-agonists
SEREVENT DISKUS should not be used more often than recommended, at higher doses than recommended, or in conjunction with other medicines containing LABA, as an overdose may result. Clinically significant cardiovascular effects and fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs. Patients using SEREVENT DISKUS should not use another medicine containing a LABA (e.g., formoterol fumarate, arformoterol tartrate, indacaterol) for any reason.
5.5 Paradoxical Bronchospasm and Upper Airway Symptoms
As with other inhaled medicines, SEREVENT DISKUS can produce paradoxical bronchospasm, which may be life threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs following dosing with SEREVENT DISKUS, it should be treated immediately with an inhaled, short-acting bronchodilator; SEREVENT DISKUS should be discontinued immediately; and alternative therapy should be instituted. Upper airway symptoms of laryngeal spasm, irritation, or swelling, such as stridor and choking, have been reported in patients receiving SEREVENT DISKUS.
5.6 Cardiovascular and Central Nervous System Effects
Excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation has been associated with seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, and insomnia [see Overdosage (10)]. Therefore, SEREVENT DISKUS, like all products containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension.
Salmeterol can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of salmeterol at recommended doses, if they occur, the drug may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Large doses of inhaled or oral salmeterol (12 to 20 times the recommended dose) have been associated with clinically significant prolongation of the QTc interval, which has the potential for producing ventricular arrhythmias. Fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs.
5.7 Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, hypotension), including anaphylaxis, may occur after administration of SEREVENT DISKUS. There have been reports of anaphylactic reactions in patients with severe milk protein allergy after inhalation of powder products containing lactose; therefore, patients with severe milk protein allergy should not use SEREVENT DISKUS [see Contraindications (4)].
5.8 Drug Interactions with Strong Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
The use of strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, ketoconazole, telithromycin) with SEREVENT DISKUS is not recommended because increased cardiovascular adverse effects may occur [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.9 Coexisting Conditions
SEREVENT DISKUS, like all medicines containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with convulsive disorders or thyrotoxicosis and in those who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines. Doses of the related beta2-adrenoceptor agonist albuterol, when administered intravenously, have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis.
5.10 Hypokalemia and Hyperglycemia
Beta-adrenergic agonist medicines may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Clinically significant and dose-related changes in blood glucose and/or serum potassium were seen infrequently during clinical trials with SEREVENT DISKUS at recommended doses.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
LABA, including salmeterol, the active ingredient in SEREVENT DISKUS, as monotherapy (without ICS) increase the risk of asthma-related death. Data from a large 28-week placebo-controlled U.S. trial that compared the safety of salmeterol or placebo added to usual asthma therapy showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol. Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience in Asthma
Adult and Adolescent Subjects Aged 12 Years and Older
Two multicenter, 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trials evaluated twice-daily doses of SEREVENT DISKUS in subjects aged 12 years and older with asthma. Table 1 reports the incidence of adverse reactions in these 2 trials.
| a Table 1 includes all events (whether considered drug-related or nondrug-related by the investigator) that occurred at a rate of ≥3% in the group receiving SEREVENT DISKUS and were more common than in the placebo group. | |||
|
Adverse Event |
Percent of Subjects |
||
|
SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg Twice Daily (n = 149) |
Albuterol Inhalation Aerosol 180 mcg 4 Times Daily (n = 150) |
Placebo (n = 152) |
|
|
Ear, nose, and throat | |||
|
Nasal/sinus congestion, pallor |
9 |
8 |
6 |
|
Rhinitis |
5 |
4 |
4 |
|
Neurological | |||
|
Headache |
13 |
12 |
9 |
|
Respiratory | |||
|
Asthma |
3 |
<1 |
1 |
|
Tracheitis/bronchitis |
7 |
3 |
4 |
|
Influenza |
5 |
5 |
2 |
Pharyngitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and cough occurred at ≥3% but were more common in the placebo group. However, throat irritation has been described at rates exceeding that of placebo in other controlled clinical trials.
Additional Adverse Reactions: Other adverse reactions not previously listed, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, that were reported more frequently by subjects with asthma treated with SEREVENT DISKUS compared with subjects treated with placebo include the following: contact dermatitis, eczema, localized aches and pains, nausea, oral mucosal abnormality, pain in joint, paresthesia, pyrexia of unknown origin, sinus headache, and sleep disturbance.
Pediatric Subjects Aged 4 to 11 Years
Two multicenter, 12-week, controlled trials have evaluated twice-daily doses of SEREVENT DISKUS in subjects aged 4 to 11 years with asthma. Table 2 includes all events (whether considered drug-related or nondrug-related by the investigator) that occurred at a rate of ≥3% in the group receiving SEREVENT DISKUS and were more common than in the placebo group.
|
Adverse Event |
Percent of Subjects |
||
|
SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg Twice Daily (n = 211) |
Albuterol Inhalation Aerosol 200 mcg 4 Times Daily (n = 115) |
Placebo (n = 215) |
|
|
Ear, nose, and throat | |||
|
Ear signs and symptoms |
4 |
9 |
3 |
|
Pharyngitis |
6 |
3 |
3 |
|
Neurological | |||
|
Headache |
17 |
20 |
14 |
|
Respiratory | |||
|
Asthma |
4 |
<1 |
2 |
|
Skin | |||
|
Skin rashes |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
Urticaria |
3 |
2 |
0 |
The following events were reported at an incidence of >1% in the salmeterol group and with a higher incidence than in the albuterol and placebo groups: gastrointestinal signs and symptoms, lower respiratory signs and symptoms, photodermatitis, and arthralgia and articular rheumatism.
In clinical trials evaluating concurrent therapy of salmeterol with ICS, adverse events were consistent with those previously reported for salmeterol, or with events that would be expected with the use of ICS.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Elevation of hepatic enzymes was reported in ≥1% of subjects in clinical trials. The elevations were transient and did not lead to discontinuation from the trials. In addition, there were no clinically relevant changes noted in glucose or potassium.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Two multicenter, 24-week, placebo-controlled U.S. trials evaluated twice-daily doses of SEREVENT DISKUS in subjects with COPD. For presentation (Table 3), the placebo data from a third trial, identical in design, subject entrance criteria, and overall conduct but comparing fluticasone propionate with placebo, were integrated with the placebo data from these 2 trials (total N = 341 for salmeterol and 576 for placebo).
| a Table 3 includes all events (whether considered drug-related or nondrug-related by the investigator) that occurred at a rate of ≥3% in the group receiving SEREVENT DISKUS and were more common than in the placebo group. | ||
|
Adverse Event |
Percent of Subjects |
|
|
SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg Twice Daily (n = 341) |
Placebo (n = 576) |
|
|
Cardiovascular | ||
|
Hypertension |
4 |
2 |
|
Ear, nose, and throat | ||
|
Throat irritation |
7 |
6 |
|
Nasal congestion/blockage |
4 |
3 |
|
Sinusitis |
4 |
2 |
|
Ear signs and symptoms |
3 |
1 |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||
|
Nausea and vomiting |
3 |
3 |
|
Lower respiratory | ||
|
Cough |
5 |
4 |
|
Rhinitis |
4 |
2 |
|
Viral respiratory infection |
5 |
4 |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||
|
Musculoskeletal pain |
12 |
10 |
|
Muscle cramps and spasms |
3 |
1 |
|
Neurological | ||
|
Headache |
14 |
11 |
|
Dizziness |
4 |
2 |
|
Average duration of exposure (days) |
138.5 |
128.9 |
Additional Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions occurring in the group receiving SEREVENT DISKUS that occurred at a frequency of ≥1% and were more common than in the placebo group were as follows: anxiety; arthralgia and articular rheumatism; bone and skeletal pain; candidiasis mouth/throat; dental discomfort and pain; dyspeptic symptoms; edema and swelling; gastrointestinal infections; hyperglycemia; hyposalivation; keratitis and conjunctivitis; lower respiratory signs and symptoms; migraines; muscle pain; muscle stiffness, tightness, and rigidity; musculoskeletal inflammation; pain; and skin rashes.
Adverse reactions to salmeterol are similar in nature to those seen with other selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonists, e.g., tachycardia; palpitations; immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm; headache; tremor; nervousness; and paradoxical bronchospasm.
Laboratory Abnormalities
There were no clinically relevant changes in these trials. Specifically, no changes in potassium were noted.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of salmeterol. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or causal connection to salmeterol or a combination of these factors.
In extensive U.S. and worldwide postmarketing experience with salmeterol, serious exacerbations of asthma, including some that have been fatal, have been reported. In most cases, these have occurred in patients with severe asthma and/or in some patients in whom asthma has been acutely deteriorating [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], but they have also occurred in a few patients with less severe asthma. It was not possible from these reports to determine whether salmeterol contributed to these events.
Cardiovascular
Arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystoles) and anaphylaxis.
Non-Site Specific
Very rare anaphylactic reaction in patients with severe milk protein allergy.
Respiratory
Reports of upper airway symptoms of laryngeal spasm, irritation, or swelling such as stridor or choking; oropharyngeal irritation.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4
Salmeterol is a substrate of CYP3A4. The use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, ketoconazole, telithromycin) with SEREVENT DISKUS is not recommended because increased cardiovascular adverse effects may occur.
In a drug interaction trial in 20 healthy subjects, coadministration of inhaled salmeterol (50 mcg twice daily) and oral ketoconazole (400 mg once daily) for 7 days resulted in greater systemic exposure to salmeterol (AUC increased 16-fold and Cmax increased 1.4-fold). Three (3) subjects were withdrawn due to beta2-agonist side effects (2 with prolonged QTc and 1 with palpitations and sinus tachycardia). Although there was no statistical effect on the mean QTc, coadministration of salmeterol and ketoconazole was associated with more frequent increases in QTc duration compared with salmeterol and placebo administration.
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants
SEREVENT DISKUS should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of salmeterol on the vascular system may be potentiated by these agents.
7.3 Beta-adrenergic Receptor Blocking Agents
Beta-blockers not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as salmeterol, but may also produce severe bronchospasm in patients with asthma or COPD. Therefore, patients with asthma or COPD should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents for these patients; cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
7.4 Non–Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
The ECG changes and/or hypokalemia that may result from the administration of non–potassium-sparing diuretics (such as loop or thiazide diuretics) can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists, especially when the recommended dose of the beta-agonist is exceeded. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of SEREVENT DISKUS with non–potassium-sparing diuretics.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The available data from published epidemiological studies and case reports with use of SEREVENT DISKUS in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). Beta‑agonists may interfere with uterine contractility. There are clinical considerations in pregnant women with asthma (see Clinical Considerations).
Oral administration of salmeterol to pregnant rabbits caused teratogenicity characteristic of beta‑adrenoceptor stimulation at maternal doses approximately 50 times the maximum recommended human daily inhaled dose (MRHDID) on an AUC basis. These adverse effects generally occurred at large multiples of the MRHDID when salmeterol was administered by the oral route to achieve high systemic exposures. No such effects occurred at an oral salmeterol dose approximately 20 times the MRHDID (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryofetal Risk: In women with poorly or moderately controlled asthma, there is an increased risk of pre-eclampsia in the mother and prematurity, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in the neonate. Severe asthma during pregnancy has been associated with maternal mortality, fetal mortality, or both. Pregnant women with asthma should be closely monitored and medication adjusted as necessary to maintain optimal asthma control.
Labor and Delivery: There are no adequate and well-controlled human studies that have evaluated the effects of SEREVENT DISKUS during labor and delivery. Because of the potential for beta-agonist interference with uterine contractility, use of SEREVENT DISKUS during labor should be restricted to those patients in whom the benefits clearly outweigh the risks.
Data
Human Data: While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from epidemiological studies and case reports have not established an association with SEREVENT DISKUS use during pregnancy and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The available studies have methodologic limitations, including retrospective data collection and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data: In 3 embryofetal development studies, pregnant rabbits received oral administration of salmeterol at doses ranging from 100 to 10,000 mcg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. In pregnant Dutch rabbits administered salmeterol doses approximately 50 times the MRHDID (on an AUC basis at maternal oral doses of 1,000 mcg/kg/day and higher), fetal toxic effects were observed characteristically resulting from beta‑adrenoceptor stimulation. These included precocious eyelid openings, cleft palate, sternebral fusion, limb and paw flexures, and delayed ossification of the frontal cranial bones. No such effects occurred at a salmeterol dose approximately 20 times the MRHDID (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 600 mcg/kg/day). New Zealand White rabbits were less sensitive since only delayed ossification of the frontal cranial bones was seen at a salmeterol dose approximately 2,000 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal oral dose of 10,000 mcg/kg/day).
In 2 embryofetal development studies, pregnant rats received salmeterol by oral administration at doses ranging from 100 to 10,000 mcg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Salmeterol produced no maternal toxicity or embryofetal effects at doses up to 973 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal oral doses up to 10,000 mcg/kg/day).
In a peri- and post-natal development study in pregnant rats dosed by the oral route from late gestation through delivery and lactation, salmeterol at a dose 973 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis with a maternal oral dose of 10,000 mcg/kg/day) was fetotoxic and decreased the fertility of survivors.
Salmeterol xinafoate crossed the placenta following oral administration to mice and rats.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of salmeterol in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Salmeterol is detected in rat milk (see Data). Salmeterol concentrations in human plasma after inhaled therapeutic doses are low and therefore concentrations in human breast milk are likely to be low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for SEREVENT DISKUS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from SEREVENT DISKUS or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data: Oral administration of salmeterol at a dose of 10,000 mcg/kg/day to lactating rats resulted in measurable levels in milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Available data from controlled clinical trials suggest that LABA used as monotherapy increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. For pediatric and adolescent patients with asthma who require addition of a LABA to an ICS, a fixed-dose combination product containing both an ICS and a LABA should ordinarily be used to ensure adherence with both drugs [see Indications and Usage (1.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The safety and efficacy of SEREVENT DISKUS in adolescents (aged 12 years and older) have been established based on adequate and well-controlled trials conducted in adults and adolescents [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. A large 28-week placebo-controlled U.S. trial comparing salmeterol (SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol) and placebo, each added to usual asthma therapy, showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Post hoc analyses in pediatric subjects aged 12 to 18 years were also performed. Pediatric subjects accounted for approximately 12% of subjects in each treatment arm. Respiratory-related death or life-threatening experience occurred at a similar rate in the salmeterol group (0.12% [2/1,653]) and the placebo group (0.12% [2/1,622]; relative risk: 1.0 [95% CI: 0.1, 7.2]). All-cause hospitalization, however, was increased in the salmeterol group (2% [35/1,653]) versus the placebo group (less than 1% [16/1,622]; relative risk: 2.1 [95% CI: 1.1, 3.7]).
The safety and efficacy of SEREVENT DISKUS have been evaluated in over 2,500 subjects aged 4 to 11 years with asthma, 346 of whom were administered SEREVENT DISKUS for 1 year. Based on available data, no adjustment of dosage of SEREVENT DISKUS in pediatric patients is warranted for either asthma or EIB.
In 2 randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trials of 12 weeks’ duration, SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg was administered to 211 pediatric subjects with asthma who did and who did not receive concurrent ICS. The efficacy of SEREVENT DISKUS was demonstrated over the 12-week treatment period with respect to peak expiratory flow (PEF) and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1). SEREVENT DISKUS was effective in demographic subgroups (gender and age) of the population.
In 2 randomized trials in children aged 4 to 11 years with asthma and EIB, a single 50-mcg dose of SEREVENT DISKUS prevented EIB when dosed 30 minutes prior to exercise, with protection lasting up to 11.5 hours in repeat testing following this single dose in many subjects.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of adult and adolescent subjects with asthma who received SEREVENT DISKUS in chronic dosing clinical trials, 209 were aged 65 years and older. Of the total number of subjects with COPD who received SEREVENT DISKUS in chronic dosing clinical trials, 167 were aged 65 years and older and 45 were aged 75 years and older. No apparent differences in the safety of SEREVENT DISKUS were observed when geriatric subjects were compared with younger subjects in clinical trials. As with other beta2-agonists, however, special caution should be observed when using SEREVENT DISKUS in geriatric patients who have concomitant cardiovascular disease that could be adversely affected by beta-agonists. Data from the trials in subjects with COPD suggested a greater effect on FEV1 of SEREVENT DISKUS in subjects younger than 65 years, as compared with subjects aged 65 years and older. However, based on available data, no adjustment of dosage of SEREVENT DISKUS in geriatric patients is warranted.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Formal pharmacokinetic studies using SEREVENT DISKUS have not been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment. Since salmeterol is predominantly cleared by hepatic metabolism, impairment of liver function may lead to accumulation of salmeterol in plasma. Therefore, patients with hepatic disease should be closely monitored.
10. Overdosage
The expected signs and symptoms with overdosage of SEREVENT DISKUS are those of excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation and/or occurrence or exaggeration of any of the signs and symptoms of beta-adrenergic stimulation (e.g., seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, muscle cramps, dry mouth, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, insomnia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis). Overdosage with SEREVENT DISKUS can lead to clinically significant prolongation of the QTc interval, which can produce ventricular arrhythmias.
As with all inhaled sympathomimetic medicines, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with an overdose of SEREVENT DISKUS.
Treatment consists of discontinuation of SEREVENT DISKUS together with appropriate symptomatic therapy. The judicious use of a cardioselective beta-receptor blocker may be considered, bearing in mind that such medication can produce bronchospasm. There is insufficient evidence to determine if dialysis is beneficial for overdosage of SEREVENT DISKUS. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in cases of overdosage.
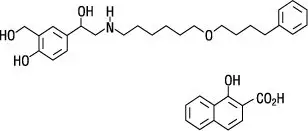
11. Serevent Diskus Description
The active component of SEREVENT DISKUS is salmeterol xinafoate, a beta2-adrenergic bronchodilator. Salmeterol xinafoate is the racemic form of the 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid salt of salmeterol. It has the chemical name 4-hydroxy-α1-[[[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino]methyl]-1,3-benzenedimethanol, 1-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxylate and the following chemical structure:
Salmeterol xinafoate is a white powder with a molecular weight of 603.8, and the empirical formula is C25H37NO4•C11H8O3. It is freely soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol, chloroform, and isopropanol; and sparingly soluble in water.
SEREVENT DISKUS is a teal green plastic inhaler containing a foil blister strip. Each blister on the strip contains a white powder mix of micronized salmeterol xinafoate salt (72.5 mcg, equivalent to 50 mcg of salmeterol base) in 12.5 mg of formulation containing lactose monohydrate (which contains milk proteins). After the inhaler is activated, the powder is dispersed into the airstream created by the patient inhaling through the mouthpiece.
Under standardized in vitro test conditions, SEREVENT DISKUS delivers 47 mcg of salmeterol base per blister when tested at a flow rate of 60 L/min for 2 seconds.
In adult subjects with obstructive lung disease and severely compromised lung function (mean FEV1 20% to 30% of predicted), mean peak inspiratory flow (PIF) through the DISKUS inhaler was 82.4 L/min (range: 46.1 to 115.3 L/min).
The actual amount of drug delivered to the lung will depend on patient factors, such as inspiratory flow profile.
12. Serevent Diskus - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Salmeterol is a selective LABA. In vitro studies show salmeterol to be at least 50 times more selective for beta2-adrenoceptors than albuterol. Although beta2-adrenoceptors are the predominant adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle and beta1-adrenoceptors are the predominant receptors in the heart, there are also beta2-adrenoceptors in the human heart comprising 10% to 50% of the total beta-adrenoceptors. The precise function of these receptors has not been established, but their presence raises the possibility that even selective beta2-agonists may have cardiac effects.
The pharmacologic effects of beta2-adrenoceptor agonist drugs, including salmeterol, are at least in part attributable to stimulation of intracellular adenyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Increased cyclic AMP levels cause relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and inhibition of release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from cells, especially from mast cells.
In vitro tests show that salmeterol is a potent and long-lasting inhibitor of the release of mast cell mediators, such as histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandin D2, from human lung. Salmeterol inhibits histamine-induced plasma protein extravasation and inhibits platelet-activating factor–induced eosinophil accumulation in the lungs of guinea pigs when administered by the inhaled route. In humans, single doses of salmeterol administered via inhalation aerosol attenuate allergen-induced bronchial hyper-responsiveness.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Inhaled salmeterol, like other beta-adrenergic agonist drugs, can produce dose-related cardiovascular effects and effects on blood glucose and/or serum potassium [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.10)]. The cardiovascular effects (heart rate, blood pressure) associated with salmeterol inhalation aerosol occur with similar frequency, and are of similar type and severity, as those noted following albuterol administration.
The effects of rising inhaled doses of salmeterol and standard inhaled doses of albuterol were studied in volunteers and in subjects with asthma. Salmeterol doses up to 84 mcg administered as inhalation aerosol resulted in heart rate increases of 3 to 16 beats/min, about the same as albuterol dosed at 180 mcg by inhalation aerosol (4 to 10 beats/min). Adult and adolescent subjects receiving 50-mcg doses of salmeterol inhalation powder (n = 60) underwent continuous electrocardiographic monitoring during two 12-hour periods after the first dose and after 1 month of therapy, and no clinically significant dysrhythmias were noted. Also, pediatric patients receiving 50-mcg doses of salmeterol inhalation powder (n = 67) underwent continuous electrocardiographic monitoring during two 12-hour periods after the first dose and after 3 months of therapy, and no clinically significant dysrhythmias were noted.
In 24-week clinical studies in patients with COPD, the incidence of clinically significant abnormalities on the predose ECGs at Weeks 12 and 24 in patients who received salmeterol 50 mcg was not different compared with placebo.
No effect of treatment with salmeterol 50 mcg was observed on pulse rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a subset of patients with COPD who underwent 12-hour serial vital sign measurements after the first dose (n = 91) and after 12 weeks of therapy (n = 74). Median changes from baseline in pulse rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressure were similar for patients receiving either salmeterol or placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Concomitant Use of SEREVENT DISKUS with Other Respiratory Medications
Short-acting Beta2-agonists: In two 12-week repetitive-dose clinical trials in adult and adolescent subjects with asthma (N = 149), the mean daily need for additional beta2-agonist in subjects using SEREVENT DISKUS was approximately 1½ inhalations/day. Twenty-six percent (26%) of the subjects in these trials used between 8 and 24 inhalations of short-acting beta-agonist per day on 1 or more occasions. Nine percent (9%) of the subjects in these trials averaged over 4 inhalations/day over the course of the 12-week trials. No increase in frequency of cardiovascular events was observed among the 3 subjects who averaged 8 to 11 inhalations/day; however, the safety of concomitant use of more than 8 inhalations/day of short-acting beta2-agonist with SEREVENT DISKUS has not been established. In 29 subjects who experienced worsening of asthma while receiving SEREVENT DISKUS during these trials, albuterol therapy administered via either nebulizer or inhalation aerosol (1 dose in most cases) led to improvement in FEV1 and no increase in occurrence of cardiovascular adverse events.
In 2 clinical trials in subjects with COPD, the mean daily need for additional beta2-agonist for subjects using SEREVENT DISKUS was approximately 4 inhalations/day. Twenty-four percent (24%) of subjects using SEREVENT DISKUS averaged 6 or more inhalations of albuterol per day over the course of the 24-week trials. No increase in frequency of cardiovascular adverse reactions was observed among subjects who averaged 6 or more inhalations per day.
Methylxanthines: The concurrent use of intravenously or orally administered methylxanthines (e.g., aminophylline, theophylline) by subjects receiving salmeterol has not been completely evaluated. In 1 clinical trial in subjects with asthma, 87 subjects receiving SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol 42 mcg twice daily concurrently with a theophylline product had adverse event rates similar to those in 71 subjects receiving SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol without theophylline. Resting heart rates were slightly higher in the subjects on theophylline but were little affected by therapy with SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol.
In 2 clinical trials in subjects with COPD, 39 subjects receiving SEREVENT DISKUS concurrently with a theophylline product had adverse event rates similar to those in 302 subjects receiving SEREVENT DISKUS without theophylline. Based on the available data, the concomitant administration of methylxanthines with SEREVENT DISKUS did not alter the observed adverse event profile.
Cromoglycate: In clinical trials, inhaled cromolyn sodium did not alter the safety profile of salmeterol when administered concurrently.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Salmeterol xinafoate, an ionic salt, dissociates in solution so that the salmeterol and 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (xinafoate) moieties are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated independently. Salmeterol acts locally in the lung; therefore, plasma levels do not predict therapeutic effect.
Absorption
Because of the small therapeutic dose, systemic levels of salmeterol are low or undetectable after inhalation of recommended doses (50 mcg of salmeterol inhalation powder twice daily). Following chronic administration of an inhaled dose of 50 mcg of salmeterol inhalation powder twice daily, salmeterol was detected in plasma within 5 to 45 minutes in 7 subjects with asthma; plasma concentrations were very low, with mean peak concentrations of 167 pg/mL at 20 minutes and no accumulation with repeated doses.
Distribution
The percentage of salmeterol bound to human plasma proteins averages 96% in vitro over the concentration range of 8 to 7,722 ng of salmeterol base per milliliter, much higher concentrations than those achieved following therapeutic doses of salmeterol.
Metabolism
Salmeterol base is extensively metabolized by hydroxylation, with subsequent elimination predominantly in the feces. No significant amount of unchanged salmeterol base was detected in either urine or feces.
An in vitro study using human liver microsomes showed that salmeterol is extensively metabolized to α-hydroxysalmeterol (aliphatic oxidation) by CYP3A4. Ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, essentially completely inhibited the formation of α-hydroxysalmeterol in vitro.
Elimination
In 2 healthy adult subjects who received 1 mg of radiolabeled salmeterol (as salmeterol xinafoate) orally, approximately 25% and 60% of the radiolabeled salmeterol was eliminated in urine and feces, respectively, over a period of 7 days. The terminal elimination half-life was about 5.5 hours (1 volunteer only).
The xinafoate moiety has no apparent pharmacologic activity. The xinafoate moiety is highly protein bound (>99%) and has a long elimination half-life of 11 days.
Drug Interaction Studies
Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Ketoconazole: In a placebo-controlled crossover drug interaction trial in 20 healthy male and female subjects, coadministration of salmeterol (50 mcg twice daily) and the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (400 mg once daily) for 7 days resulted in a significant increase in plasma salmeterol exposure as determined by a 16-fold increase in AUC (ratio with and without ketoconazole 15.76 [90% CI: 10.66, 23.31]) mainly due to increased bioavailability of the swallowed portion of the dose. Peak plasma salmeterol concentrations were increased by 1.4-fold (90% CI: 1.23, 1.68). Three (3) out of 20 subjects (15%) were withdrawn from salmeterol and ketoconazole coadministration due to beta-agonist–mediated systemic effects (2 with QTc prolongation and 1 with palpitations and sinus tachycardia). Coadministration of salmeterol and ketoconazole did not result in a clinically significant effect on mean heart rate, mean blood potassium, or mean blood glucose. Although there was no statistical effect on the mean QTc, coadministration of salmeterol and ketoconazole was associated with more frequent increases in QTc duration compared with salmeterol and placebo administration.
Erythromycin: In a repeat-dose trial in 13 healthy subjects, concomitant administration of erythromycin (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) and salmeterol inhalation aerosol resulted in a 40% increase in salmeterol Cmax at steady state (ratio with and without erythromycin 1.4 [90% CI: 0.96, 2.03], P = 0.12), a 3.6-beat/min increase in heart rate ([95% CI: 0.19, 7.03], P<0.04), a 5.8-msec increase in QTc interval ([95% CI: -6.14, 17.77], P = 0.34), and no change in plasma potassium.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an 18-month carcinogenicity study in CD-mice, salmeterol at oral doses of 1,400 mcg/kg and above (approximately 20 times the MRHDID for adults and children based on comparison of the plasma AUCs) caused a dose-related increase in the incidence of smooth muscle hyperplasia, cystic glandular hyperplasia, leiomyomas of the uterus, and ovarian cysts. No tumors were seen at 200 mcg/kg (approximately 3 times the MRHDID for adults and children based on comparison of the AUCs).
In a 24-month oral and inhalation carcinogenicity study in Sprague Dawley rats, salmeterol caused a dose-related increase in the incidence of mesovarian leiomyomas and ovarian cysts at doses of 680 mcg/kg and above (approximately 66 and 35 times the MRHDID for adults and children, respectively, on a mcg/m2 basis). No tumors were seen at 210 mcg/kg (approximately 20 and 10 times the MRHDID for adults and children, respectively, on a mcg/m2 basis). These findings in rodents are similar to those reported previously for other beta-adrenergic agonist drugs. The relevance of these findings to human use is unknown.
Salmeterol produced no detectable or reproducible increases in microbial and mammalian gene mutation in vitro. No clastogenic activity occurred in vitro in human lymphocytes or in vivo in a rat micronucleus test.
Fertility and reproductive performance were unaffected in male and female rats at oral doses up to 2,000 mcg/kg (approximately 195 times the MRHDID for adults on a mcg/m2 basis).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Preclinical
Studies in laboratory animals (minipigs, rodents, and dogs) have demonstrated the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death (with histologic evidence of myocardial necrosis) when beta-agonists and methylxanthines are administered concurrently. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Asthma
The initial trials supporting the approval of SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of asthma did not require the regular use of ICS. However, for the treatment of asthma, SEREVENT DISKUS is currently indicated only as concomitant therapy with an ICS [see Indications and Usage (1.1)].
Adult and Adolescent Subjects Aged 12 Years and Older
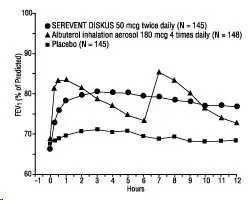
In 2 randomized double-blind trials, SEREVENT DISKUS was compared with albuterol inhalation aerosol and placebo in adolescent and adult subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma (protocol defined as 50% to 80% predicted FEV1, actual mean of 67.7% at baseline), including subjects who did and who did not receive concurrent ICS. The efficacy of SEREVENT DISKUS was demonstrated over the 12-week period with no change in effectiveness over this time period (Figure 1). There were no gender- or age-related differences in safety or efficacy. No development of tachyphylaxis to the bronchodilator effect was noted in these trials. FEV1 measurements (mean change from baseline) from these two 12-week trials are shown in Figure 1 for both the first and last treatment days.
Figure 1. Serial 12-Hour FEV1 from Two 12-Week Clinical Trials in Subjects with Asthma
First Treatment Day
Last Treatment Day (Week 12)
Table 4 shows the treatment effects seen during daily treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS for 12 weeks in adolescent and adult subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma.
| a Statistically superior to placebo and albuterol (P<0.001). b Statistically superior to placebo (P<0.001). |
||||
|
Parameter |
Time |
SEREVENT DISKUS |
Albuterol Inhalation Aerosol |
Placebo |
|
No. of randomized subjects |
149 |
148 |
152 |
|
|
Mean AM peak expiratory flow (L/min) |
Baseline 12 weeks |
395 |
394 |
394 |
|
427a |
394 |
396 |
||
|
Mean % days with no asthma symptoms |
Baseline 12 weeks |
13 |
12 |
14 |
|
33 |
21 |
20 |
||
|
Mean % nights with no awakenings |
Baseline 12 weeks |
63 |
68 |
70 |
|
85a |
71 |
73 |
||
|
Rescue medications (mean no. of inhalations per day) |
Baseline 12 weeks |
4.3 |
4.3 |
4.2 |
|
1.6b |
2.2 |
3.3 |
||
|
Asthma exacerbations (%) |
15 |
16 |
14 |
|
Maintenance of efficacy for periods up to 1 year has been documented.
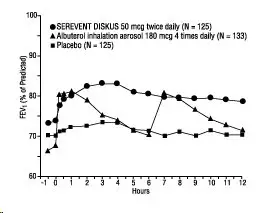
SEREVENT DISKUS and SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol were compared with placebo in 2 additional randomized double-blind clinical trials in adolescent and adult subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma. SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg and SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol 42 mcg, both administered twice daily, produced significant improvements in pulmonary function compared with placebo over the 12-week period. While no statistically significant differences were observed between the active treatments for any of the efficacy assessments or safety evaluations performed, there were some efficacy measures on which the metered-dose inhaler appeared to provide better results. Similar findings were noted in 2 randomized, single-dose, crossover comparisons of SEREVENT DISKUS and SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol for the prevention of EIB. Therefore, while SEREVENT DISKUS was comparable to SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol in clinical trials in mild-to-moderate subjects with asthma, it should not be assumed that they will produce clinically equivalent outcomes in all subjects.
Subjects on Concomitant Inhaled Corticosteroids: In 4 clinical trials in adult and adolescent subjects with asthma (N = 1,922), the effect of adding SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol to ICS therapy was evaluated over a 24-week treatment period. The trials compared the addition of salmeterol therapy to an increase (at least doubling) of the ICS dose.
Two randomized, double-blind, controlled, parallel-group clinical trials (N = 997) enrolled subjects (aged 18 to 82 years) with persistent asthma who were previously maintained but not adequately controlled on ICS therapy. During the 2-week run-in period, all subjects were switched to beclomethasone dipropionate (BDP) 168 mcg twice daily. Subjects still not adequately controlled were randomized to either the addition of SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol 42 mcg twice daily or an increase of BDP to 336 mcg twice daily. As compared with the doubled dose of BDP, the addition of SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in pulmonary function and asthma symptoms, and statistically significantly greater reduction in supplemental albuterol use. The percent of subjects who experienced asthma exacerbations overall was not different between groups (i.e., 16.2% in the group receiving SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol versus 17.9% in the higher-dose beclomethasone dipropionate group).
Two randomized, double-blind, controlled, parallel-group clinical trials (N = 925) enrolled subjects (aged 12 to 78 years) with persistent asthma who were previously maintained but not adequately controlled on prior asthma therapy. During the 2- to 4-week run-in period, all subjects were switched to fluticasone propionate 88 mcg twice daily. Subjects still not adequately controlled were randomized to either the addition of SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol 42 mcg twice daily or an increase of fluticasone propionate to 220 mcg twice daily. As compared with the increased (2.5 times) dose of fluticasone propionate, the addition of SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in pulmonary function and asthma symptoms, and statistically significantly greater reductions in supplemental albuterol use. Fewer subjects receiving SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol experienced asthma exacerbations than those receiving the higher dose of fluticasone propionate (8.8% versus 13.8%).
Table 5 shows the treatment effects seen during daily treatment with SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol for 24 weeks in adolescent and adult subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma.
Onset of Action: During the initial treatment day in several multiple-dose clinical trials with SEREVENT DISKUS in subjects with asthma, the median time to onset of clinically significant bronchodilatation (≥15% improvement in FEV1) ranged from 30 to 48 minutes after a 50-mcg dose.
One hour after a single dose of 50 mcg of SEREVENT DISKUS, the majority of subjects had ≥15% improvement in FEV1. Maximum improvement in FEV1 generally occurred within 180 minutes, and clinically significant improvement continued for 12 hours in most subjects.
Pediatric Subjects
In a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial (N = 449), 50 mcg of SEREVENT DISKUS was administered twice daily to pediatric subjects with asthma who did and who did not receive concurrent ICS. The efficacy of salmeterol inhalation powder was demonstrated over the 12-week treatment period with respect to periodic serial PEF (36% to 39% postdose increase from baseline) and FEV1 (32% to 33% postdose increase from baseline). Salmeterol was effective in demographic subgroup analyses (gender and age) and was effective when coadministered with other inhaled asthma medications such as short-acting bronchodilators and ICS. A second randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (N = 207) with 50 mcg of salmeterol inhalation powder via an alternate device supported the findings of the trial with the DISKUS.
Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial
The SMART trial was a randomized double-blind trial that enrolled LABA-naive subjects with asthma (average age of 39 years; 71% Caucasian, 18% African American, 8% Hispanic) to assess the safety of salmeterol (SEREVENT Inhalation Aerosol) 42 mcg twice daily over 28 weeks compared with placebo when added to usual asthma therapy.
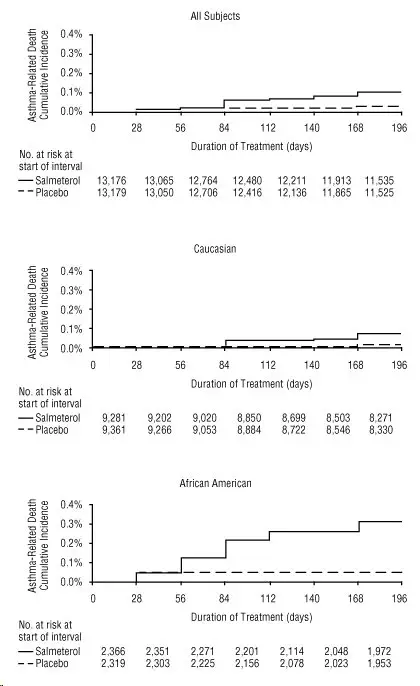
A planned interim analysis was conducted when approximately half of the intended number of subjects had been enrolled (N = 26,355), which led to premature termination of the trial. The results of the interim analysis showed that subjects receiving salmeterol were at increased risk for fatal asthma events (Table 5 and Figure 2). In the total population, a higher rate of asthma-related death occurred in subjects treated with salmeterol than those treated with placebo (0.10% versus 0.02%, relative risk: 4.37 [95% CI: 1.25, 15.34]).
Post hoc subpopulation analyses were performed. In Caucasians, asthma-related death occurred at a higher rate in subjects treated with salmeterol than in subjects treated with placebo (0.07% versus 0.01%, relative risk: 5.82 [95% CI: 0.70, 48.37]). In African Americans also, asthma-related death occurred at a higher rate in subjects treated with salmeterol than those treated with placebo (0.31% versus 0.04%, relative risk: 7.26 [95% CI: 0.89, 58.94]). Although the relative risks of asthma-related death were similar in Caucasians and African Americans, the estimate of excess deaths in subjects treated with salmeterol was greater in African Americans because there was a higher overall rate of asthma-related death in African American subjects (Table 5).
Post hoc analyses in pediatric subjects aged 12 to 18 years were also performed. Pediatric subjects accounted for approximately 12% of subjects in each treatment arm. Respiratory-related death or life-threatening experience occurred at a similar rate in the salmeterol group (0.12% [2/1,653]) and the placebo group (0.12% [2/1,622]; relative risk: 1.0 [95% CI: 0.1, 7.2]). All-cause hospitalization, however, was increased in the salmeterol group (2% [35/1,653]) versus the placebo group (less than 1% [16/1,622]; relative risk: 2.1 [95% CI: 1.1, 3.7]).
The data from the SMART trial were not adequate to determine whether concurrent use of ICS or other long-term asthma control therapy mitigated the risk of asthma-related death.
| a Life-table 28-week estimate, adjusted according to the subjects’ actual lengths of exposure to study treatment to account for early withdrawal of subjects from the study. b Relative risk is the ratio of the rate of asthma-related death in the salmeterol group and the rate in the placebo group. The relative risk indicates how many more times likely an asthma-related death occurred in the salmeterol group than in the placebo group in a 28-week treatment period. c Estimate of the number of additional asthma-related deaths in subjects treated with salmeterol in SMART, assuming 10,000 subjects received salmeterol for a 28-week treatment period. Estimate calculated as the difference between the salmeterol and placebo groups in the rates of asthma-related death multiplied by 10,000. d The Total Population includes the following ethnic origins listed on the case report form: Caucasian, African American, Hispanic, Asian, and “Other.” In addition, the Total Population includes those subjects whose ethnic origin was not reported. The results for Caucasian and African American subpopulations are shown above. No asthma-related deaths occurred in the Hispanic (salmeterol n = 996, placebo n = 999), Asian (salmeterol n = 173, placebo n = 149), or “Other” (salmeterol n = 230, placebo n = 224) subpopulations. One asthma-related death occurred in the placebo group in the subpopulation whose ethnic origin was not reported (salmeterol n = 130, placebo n = 127). |
|||||||||
|
Salmeterol n (%a) |
Placebo n (%a) |
Relative Riskb (95% Confidence Interval) |
Excess Deaths Expressed per 10,000 Subjectsc (95% Confidence Interval) |
||||||
|
Total Populationd | |||||||||
|
Salmeterol: n = 13,176 |
13 (0.10%) |
4.37 (1.25, 15.34) |
8 (3, 13) |
||||||
|
Placebo: n = 13,179 |
3 (0.02%) | ||||||||
|
Caucasian | |||||||||
|
Salmeterol: n = 9,281 |
6 (0.07%) |
5.82 (0.70, 48.37) |
6 (1, 10) |
||||||
|
Placebo: n = 9,361 |
1 (0.01%) | ||||||||
|
African American | |||||||||
|
Salmeterol: n = 2,366 |
7 (0.31%) |
7.26 (0.89, 58.94) |
27 (8, 46) |
||||||
|
Placebo: n = 2,319 |
1 (0.04%) | ||||||||
Figure 2. Cumulative Incidence of Asthma-Related Deaths in the 28-Week Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART), by Duration of Treatment
14.2 Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
In 2 randomized, single-dose, crossover trials in adolescents and adults with EIB (N = 52), 50 mcg of SEREVENT DISKUS prevented EIB when dosed 30 minutes prior to exercise. For some subjects, this protective effect against EIB was still apparent up to 8.5 hours following a single dose (Table 6).
|
SEREVENT DISKUS (N = 52) |
Placebo (N = 52) |
||||
|
n |
% Total |
n |
% Total |
||
|
0.5-Hour postdose exercise challenge |
% Fall in FEV1 | ||||
|
<10% |
31 |
60 |
15 |
29 |
|
|
≥10%, <20% |
11 |
21 |
3 |
6 |
|
|
≥20% |
10 |
19 |
34 |
65 |
|
|
Mean maximal % fall in FEV1 (SE) |
-11% (1.9) |
-25% (1.8) |
|||
|
8.5-Hour postdose exercise challenge |
% Fall in FEV1 | ||||
|
<10% |
26 |
50 |
12 |
23 |
|
|
≥10%, <20% |
12 |
23 |
7 |
13 |
|
|
≥20% |
14 |
27 |
33 |
63 |
|
|
Mean maximal % fall in FEV1 (SE) |
-16% (2.0) |
-27% (1.5) |
|||
In 2 randomized trials in children aged 4 to 11 years with asthma and EIB (N = 50), a single 50-mcg dose of SEREVENT DISKUS prevented EIB when dosed 30 minutes prior to exercise, with protection lasting up to 11.5 hours in repeat testing following this single dose in many subjects.
14.3 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
In 2 clinical trials evaluating twice-daily treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg (n = 336) compared with placebo (n = 366) in subjects with chronic bronchitis with airflow limitation, with or without emphysema, improvements in pulmonary function endpoints were greater with salmeterol 50 mcg than with placebo. Treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS did not result in significant improvements in secondary endpoints assessing COPD symptoms in either clinical trial. Both trials were randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trials of 24 weeks’ duration and were identical in design, subject entrance criteria, and overall conduct.
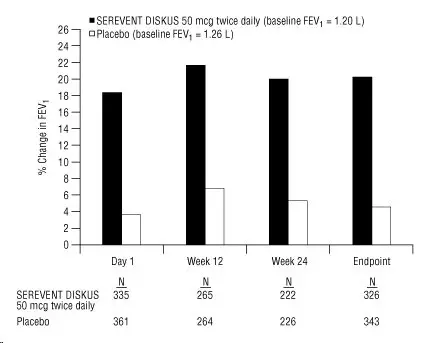
Figure 3 displays the integrated 2-hour postdose FEV1 results from the 2 clinical trials. The percent change in FEV1 refers to the change from baseline, defined as the predose value on Treatment Day 1. To account for subject withdrawals during the trial, Endpoint (last evaluable FEV1) data are provided. Subjects receiving SEREVENT DISKUS 50 mcg had significantly greater improvements in 2-hour postdose FEV1 at Endpoint (216 mL, 20%) compared with placebo (43 mL, 5%). Improvement was apparent on the first day of treatment and maintained throughout the 24 weeks of treatment.
Figure 3. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in Postdose FEV1 Integrated Data from 2 Trials of Subjects with Chronic Bronchitis and Airflow Limitation
Onset of Action and Duration of Effect
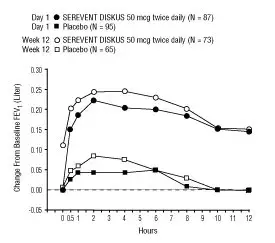
The onset of action and duration of effect of SEREVENT DISKUS were evaluated in a subset of subjects (n = 87) from 1 of the 2 clinical trials discussed above. Following the first 50-mcg dose, significant improvement in pulmonary function (mean FEV1 increase of 12% or more and at least 200 mL) occurred at 2 hours. The mean time to peak bronchodilator effect was 4.75 hours. As seen in Figure 4, evidence of bronchodilatation was seen throughout the 12-hour period. Figure 4 also demonstrates that the bronchodilating effect after 12 weeks of treatment was similar to that observed after the first dose. The mean time to peak bronchodilator effect after 12 weeks of treatment was 3.27 hours.
Figure 4. Serial 12-Hour FEV1 on the First Day and at Week 12 of Treatment
16. How is Serevent Diskus supplied
SEREVENT DISKUS is supplied as a disposable teal green plastic inhaler containing a foil blister strip with 60 blisters. The inhaler is packaged in a plastic-coated, moisture-protective foil pouch (NDC 0173-0521-00).
Store at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C); excursions permitted from 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in a dry place away from direct heat or sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
SEREVENT DISKUS should be stored inside the unopened moisture-protective foil pouch and only removed from the pouch immediately before initial use. Discard SEREVENT DISKUS 6 weeks after opening the foil pouch or when the counter reads “0” (after all blisters have been used), whichever comes first. The inhaler is not reusable. Do not attempt to take the inhaler apart.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Asthma-Related Death
Inform patients that salmeterol when used alone increases the risk of asthma-related death and may increase the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. Inform patients that SEREVENT DISKUS should not be the only therapy for the treatment of asthma and must only be used as additional therapy when ICS do not adequately control asthma symptoms. Inform patients that when SEREVENT DISKUS is added to their treatment regimen they must continue to use their ICS.
Not for Acute Symptoms
Inform patients that SEREVENT DISKUS is not meant to relieve acute asthma symptoms or exacerbations of COPD and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Advise patients to treat acute symptoms with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist such as albuterol. Provide patients with such medication and instruct them in how it should be used.
Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of the following:
- •
- Decreasing effectiveness of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists
- •
- Need for more inhalations than usual of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists
- •
- Significant decrease in lung function as outlined by the physician
Tell patients they should not stop therapy with SEREVENT DISKUS without physician/provider guidance since symptoms may recur after discontinuation.
Not a Substitute for Corticosteroids
Advise all patients with asthma that they must also continue regular maintenance treatment with an ICS if they are taking SEREVENT DISKUS.
SEREVENT DISKUS should not be used as a substitute for oral or inhaled corticosteroids. The dosage of these medications should not be changed and they should not be stopped without consulting the physician, even if the patient feels better after initiating treatment with SEREVENT DISKUS.
Do Not Use Additional Long-acting Beta2-agonists
Instruct patients not to use other LABA.
Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, hypotension), including anaphylaxis, may occur after administration of SEREVENT DISKUS. Patients should discontinue SEREVENT DISKUS if such reactions occur. There have been reports of anaphylactic reactions in patients with severe milk protein allergy after inhalation of powder products containing lactose; therefore, patients with severe milk protein allergy should not take SEREVENT DISKUS.
Risks Associated with Beta-agonist Therapy
Inform patients of adverse effects associated with beta2-agonists, such as palpitations, chest pain, rapid heart rate, tremor, or nervousness.
Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
Patients using SEREVENT DISKUS for the treatment of EIB should not use additional doses for 12 hours. Patients who are receiving SEREVENT DISKUS twice daily should not use additional SEREVENT for prevention of EIB.
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
GlaxoSmithKline
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
©2022 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
SRD:16PI
|
MEDICATION GUIDE SEREVENT DISKUS (SER uh vent DISK us) (salmeterol xinafoate inhalation powder) for oral inhalation use |
|
What is the most important information I should know about SEREVENT DISKUS? SEREVENT DISKUS can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
What is SEREVENT DISKUS?
|
|
Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS:
|
|
Before using SEREVENT DISKUS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. SEREVENT DISKUS and certain other medicines may interact with each other. This may cause serious side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take antifungal or anti-HIV medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
How should I use SEREVENT DISKUS? Read the step-by-step instructions for using SEREVENT DISKUS at the end of this Medication Guide.
|
|
What are the possible side effects of SEREVENT DISKUS? SEREVENT DISKUS can cause serious side effects, including:
ο increased blood pressure ο chest pain ο a fast or irregular heartbeat, awareness of heartbeat
ο tremor ο nervousness
ο rash ο swelling of your face, mouth, and tongue ο hives ο breathing problems
Common side effects of SEREVENT DISKUS include: Asthma: • headache • nasal congestion • bronchitis • throat irritation • runny nose • flu COPD: • headache • musculoskeletal pain • throat irritation • cough • respiratory infection These are not all the possible side effects of SEREVENT DISKUS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store SEREVENT DISKUS?
Keep SEREVENT DISKUS and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of SEREVENT DISKUS. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SEREVENT DISKUS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SEREVENT DISKUS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about SEREVENT DISKUS that was written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in SEREVENT DISKUS? Active ingredient: salmeterol xinafoate Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate (contains milk proteins) For more information about SEREVENT DISKUS, call 1-888-825-5249. Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies. GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709 ©2018 GSK group of companies or its licensor. SRD:7MG |
|
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0173-0521-00
Serevent Diskus
(salmeterol xinafoate inhalation powder)
50 mcg
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Each blister contains 50 mcg of salmeterol base with lactose monohydrate.
Federal Law requires the dispensing of SEREVENT DISKUS with the Medication Guide inside the carton.
See prescribing information for dosing information.
Rx only
gsk
1 DISKUS Inhalation Device Containing 1 Foil Strip of 60 Blisters
Made in Singapore
©2020 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
- 62000000049404 Rev. 4/20
| SEREVENT
DISKUS
salmeterol xinafoate powder, metered |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - GlaxoSmithKline LLC (167380711) |