Drug Detail:Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir [ soe-fos-bue-vir ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antivirals
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SOVALDI® (sofosbuvir) tablets, for oral use
SOVALDI® (sofosbuvir) oral pellets
Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION IN PATIENTS COINFECTED WITH HCV AND HBV
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 08/2019 |
| Dosage and Administration | |
| Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 3 Years of Age and Older with Genotype 2 or 3 HCV (2.3) | 08/2019 |
| Preparation and Administration of Oral Pellets (2.4) | 08/2019 |
Indications and Usage for Sovaldi
SOVALDI is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult patients with genotype 1, 2, 3 or 4 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis as a component of a combination antiviral treatment regimen. (1)
- Pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with genotype 2 or 3 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis in combination with ribavirin. (1)
Sovaldi Dosage and Administration
- Testing Prior to the Initiation of Therapy: Test all patients for HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti-HBc. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage in adults: One 400 mg tablet taken once daily with or without food. (2.2)
- Recommended dosage in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older: Recommended dosage of SOVALDI in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with genotype 2 or 3 HCV using SOVALDI tablets or oral pellets is based on weight. Refer to Table 3 of the full prescribing information for specific dosing guidelines based on body weight. (2.3)
- HCV/HIV-1 coinfection: For adult and pediatric patients with HCV/HIV-1 coinfection, follow the dosage recommendations in the tables below, respectively. (2.2, 2.3)
- Recommended adult treatment regimen and duration: (2.2)
| Adult Patient Population | Regimen and Duration | |
|---|---|---|
| Genotype 1 or 4 | Treatment-naïve without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + peginterferon alfa + ribavirin 12 weeks |
| Genotype 2 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin 12 weeks |
| Genotype 3 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin 24 weeks |
- SOVALDI in combination with ribavirin for 24 weeks can be considered for adult patients with genotype 1 infection who are interferon ineligible. (2.2)
- Should be used in combination with ribavirin for treatment of HCV in adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation for up to 48 weeks or until liver transplantation, whichever occurs first. (2.2)
- Recommended treatment regimen and duration for pediatric patients 3 years of age and older: (2.3, 2.4)
| Pediatric Patient Population 3 Years of Age and Older | Regimen and Duration | |
|---|---|---|
| Genotype 2 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin 12 weeks |
| Genotype 3 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin 24 weeks |
- A dosage recommendation cannot be made for patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease. (2.7, 8.6)
- Instructions for Use should be followed for preparation and administration of SOVALDI oral pellets. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 400 mg and 200 mg of sofosbuvir. (3)
- Oral Pellets: 200 mg and 150 mg of sofosbuvir. (3)
Contraindications
- When used in combination with peginterferon alfa/ribavirin or ribavirin alone, all contraindications to peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin also apply to SOVALDI combination therapy. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation: Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection before initiation of HCV treatment. Monitor HCV/HBV coinfected patients for HBV reactivation and hepatitis flare during HCV treatment and post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated. (5.1)
- Bradycardia with amiodarone coadministration: Serious symptomatic bradycardia may occur in patients taking amiodarone with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen, particularly in patients also receiving beta blockers, or those with underlying cardiac comorbidities and/or advanced liver disease. Coadministration of amiodarone with SOVALDI is not recommended. In patients without alternative, viable treatment options, cardiac monitoring is recommended. (5.2, 6.2, 7.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse events (incidence greater than or equal to 20%, all grades) observed with SOVALDI in combination with ribavirin were fatigue and headache. The most common adverse events observed with SOVALDI in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin were fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia and anemia. (6.1). The most common adverse events observed with SOVALDI in combination with ribavirin oral solution in pediatric patients was decreased appetite. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Coadministration of amiodarone with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen may result in serious symptomatic bradycardia. (5.2, 6.2, 7.1)
- Drugs that are intestinal P-gp inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John's wort) may alter the concentrations of sofosbuvir. (5.3, 7, 12.3)
- Consult the full prescribing information prior to use for potential drug-drug interactions. (5.2, 5.3, 7, 12.3)
- Clearance of HCV infection with direct acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact safe and effective use of concomitant medications. Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (INR or blood glucose) and dose adjustments of certain concomitant medications may be necessary. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Patients with HCV/HIV-1 coinfection: Safety and efficacy have been studied. (14.4)
- Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation: Safety and efficacy have been studied. (8.8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2020
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION IN PATIENTS COINFECTED WITH HCV AND HBV
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection before initiating treatment with SOVALDI. HBV reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct acting antivirals and were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Monitor HCV/HBV coinfected patients for hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment and post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2. Sovaldi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to the Initiation of Therapy
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection by measuring hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) before initiating HCV treatment with SOVALDI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of SOVALDI is one 400 mg tablet, taken orally, once daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Administer SOVALDI in combination with ribavirin or in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of HCV. The recommended treatment regimen and duration for SOVALDI combination therapy is provided in Table 1.
For patients with HCV/HIV-1 coinfection, follow the dosage recommendations in Table 1. Refer to Drug Interactions (7) for dosage recommendations for concomitant HIV-1 antiviral drugs.
| Patient Population | Treatment Regimen and Duration | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Genotype 1 or 4 | Treatment-naïve without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + peginterferon alfa* + ribavirin† 12 weeks |
| Genotype 2 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced‡ without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin† 12 weeks |
| Genotype 3 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced‡ without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin† 24 weeks |
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 3 Years of Age and Older with Genotype 2 or 3 HCV
The recommended treatment regimen, duration, and recommended dosage for SOVALDI combination therapy is provided in Table 2 and Table 3. Table 4 provides the weight-based dosage of ribavirin when used in combination with SOVALDI for pediatric patients. For patients with HCV/HIV-1 coinfection, follow the dosage recommendations in Table 3 and Table 4. Refer to Drug Interactions (7) for dosage recommendations for concomitant HIV-1 antiviral drugs. In pediatric patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation, administer SOVALDI in combination with ribavirin for up to 48 weeks or until the time of liver transplantation, whichever occurs first, to prevent post-transplant HCV reinfection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
| Patient Population | Treatment Regimen and Duration | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Genotype 2 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced* without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin† 12 weeks |
| Genotype 3 | Treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced* without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) | SOVALDI + ribavirin† 24 weeks |
The recommended dosage of SOVALDI in pediatric patients 3 years and older with genotype 2 or 3 HCV using SOVALDI tablets or oral pellets (with or without food) is based on weight (Table 3), and is to be taken orally once daily in combination with ribavirin [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.5)]. SOVALDI pellets can be taken by pediatric patients who cannot swallow the tablet formulation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
| Body Weight (kg) | Dosing of SOVALDI Tablets or Oral Pellets | SOVALDI Daily Dose |
|---|---|---|
| at least 35 | one 400 mg tablet once daily or two 200 mg tablets once daily or two 200 mg packets of pellets once daily | 400 mg per day |
| 17 to less than 35 | one 200 mg tablet once daily or one 200 mg packet of pellets once daily | 200 mg per day |
| less than 17 | one 150 mg packet of pellets once daily | 150 mg per day |
| Body Weight (kg) | Oral Ribavirin Daily Dosage* |
|---|---|
|
|
| less than 47 | 15 mg per kg per day (divided dose AM and PM) |
| 47–49 | 600 mg per day (1 × 200 mg AM, 2 × 200 mg PM) |
| 50–65 | 800 mg per day (2 × 200 mg AM, 2 × 200 mg PM) |
| 66–80 | 1000 mg per day (2 × 200 mg AM, 3 × 200 mg PM) |
| greater than 80 | 1200 mg per day (3 × 200 mg AM, 3 × 200 mg PM) |
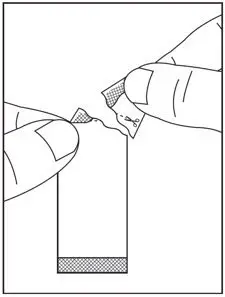
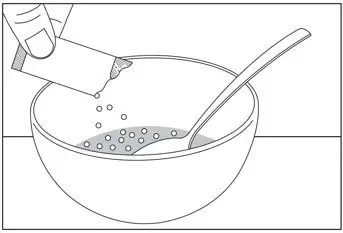
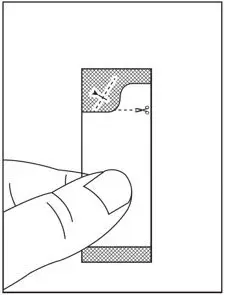
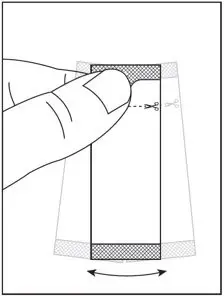
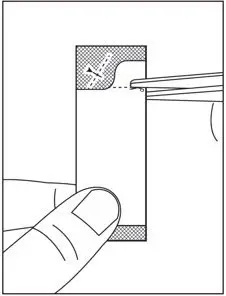
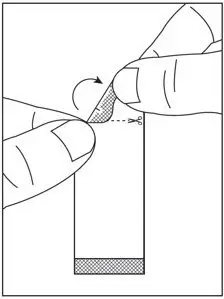
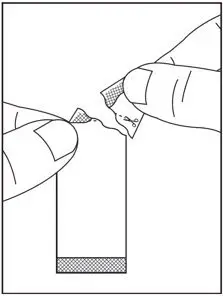
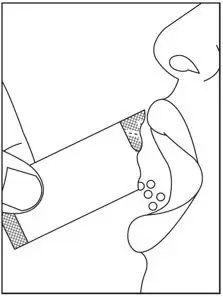
2.4 Preparation and Administration of Oral Pellets
See the SOVALDI oral pellets full Instructions for Use for details on the preparation and administration of SOVALDI pellets.
Do not chew SOVALDI pellets. If SOVALDI pellets are administered with food, sprinkle the pellets on one or more spoonfuls of non-acidic soft food at or below room temperature. Examples of non-acidic foods include pudding, chocolate syrup, mashed potato, and ice cream. Take SOVALDI pellets within 30 minutes of gently mixing with food and swallow the entire contents without chewing to avoid a bitter aftertaste.
2.5 Dosage Modification
Dosage reduction of SOVALDI is not recommended.
If a patient has a serious adverse reaction potentially related to peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin, the peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin dosage should be reduced or discontinued, if appropriate, until the adverse reaction abates or decreases in severity. Refer to the peginterferon alfa and ribavirin prescribing information for additional information about how to reduce and/or discontinue the peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin dosage.
2.6 Discontinuation of Dosing
If the other agents used in combination with SOVALDI are permanently discontinued, SOVALDI should also be discontinued.
2.7 Severe Renal Impairment and End Stage Renal Disease
No dosage recommendation can be given for patients with severe renal impairment (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate [eGFR] less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2) or with end stage renal disease (ESRD) due to higher exposures (up to 20-fold) of the predominant sofosbuvir metabolite [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
SOVALDI is available as tablets or pellets for oral use. Each dosage form is available in two dose strengths.
- 400 mg Tablets: 400 mg sofosbuvir: yellow, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablet debossed with "GSI" on one side and "7977" on the other side.
- 200 mg Tablets: 200 mg sofosbuvir: yellow, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet debossed with "GSI" on one side and "200" on the other side.
- 200 mg Pellets: 200 mg sofosbuvir: white to off-white pellets in unit-dose packets.
- 150 mg Pellets: 150 mg sofosbuvir: white to off-white pellets in unit-dose packets.
4. Contraindications
When SOVALDI is used in combination with ribavirin or peginterferon alfa/ribavirin, the contraindications applicable to those agents are applicable to combination therapies. Refer to the prescribing information of peginterferon alfa and ribavirin for a list of their contraindications.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Patients Coinfected with HCV and HBV
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct acting antivirals, and who were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Cases have been reported in patients who are HBsAg positive and also in patients with serologic evidence of resolved HBV infection (i.e., HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive). HBV reactivation has also been reported in patients receiving certain immunosuppressant or chemotherapeutic agents; the risk of HBV reactivation associated with treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals may be increased in these patients.
HBV reactivation is characterized as an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA level. In patients with resolved HBV infection, reappearance of HBsAg can occur. Reactivation of HBV replication may be accompanied by hepatitis, i.e., increases in aminotransferase levels and, in severe cases, increases in bilirubin levels, liver failure, and death can occur.
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti-HBc before initiating HCV treatment with SOVALDI. In patients with serologic evidence of HBV infection, monitor for clinical and laboratory signs of hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment with SOVALDI and during post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated.
5.2 Serious Symptomatic Bradycardia When Coadministered with Amiodarone
Postmarketing cases of symptomatic bradycardia and cases requiring pacemaker intervention have been reported when amiodarone is coadministered with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen. A fatal cardiac arrest was reported in a patient taking amiodarone who was coadministered a sofosbuvir-containing regimen (HARVONI [ledipasvir/sofosbuvir]). Bradycardia has generally occurred within hours to days, but cases have been observed up to 2 weeks after initiating HCV treatment. Patients also taking beta blockers, or those with underlying cardiac comorbidities and/or advanced liver disease may be at increased risk for symptomatic bradycardia with coadministration of amiodarone. Bradycardia generally resolved after discontinuation of HCV treatment. The mechanism for this effect is unknown.
Coadministration of amiodarone with SOVALDI is not recommended. For patients taking amiodarone who have no other alternative, viable treatment options and who will be coadministered SOVALDI:
- Counsel patients about the risk of serious symptomatic bradycardia
- Cardiac monitoring in an in-patient setting for the first 48 hours of coadministration is recommended, after which outpatient or self-monitoring of the heart rate should occur on a daily basis through at least the first 2 weeks of treatment.
Patients who are taking SOVALDI who need to start amiodarone therapy due to no other alternative, viable treatment options should undergo similar cardiac monitoring as outlined above.
Due to amiodarone's long half-life, patients discontinuing amiodarone just prior to starting SOVALDI should also undergo similar cardiac monitoring as outlined above.
Patients who develop signs or symptoms of bradycardia should seek medical evaluation immediately. Symptoms may include near-fainting or fainting, dizziness or lightheadedness, malaise, weakness, excessive tiredness, shortness of breath, chest pains, confusion or memory problems [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.3 Risk of Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Use with P-gp Inducers
Drugs that are P-gp inducers in the intestine (e.g., rifampin, St. John's wort) may significantly decrease sofosbuvir plasma concentrations and may lead to a reduced therapeutic effect of SOVALDI. The use of rifampin and St. John's wort with SOVALDI is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Risks Associated with Combination Treatment
Because SOVALDI is used in combination with other antiviral drugs for treatment of HCV infection, consult the prescribing information for these drugs used in combination with SOVALDI. Warnings and Precautions related to these drugs also apply to their use in SOVALDI combination treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Symptomatic Bradycardia When Coadministered with Amiodarone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
When SOVALDI is administered with ribavirin or peginterferon alfa/ribavirin, refer to the respective prescribing information for a description of adverse reactions associated with their use.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Subjects
The safety assessment of SOVALDI was based on pooled Phase 3 clinical trial data (both controlled and uncontrolled) including:
- 650 subjects who received SOVALDI + ribavirin (RBV) combination therapy for 12 weeks,
- 98 subjects who received SOVALDI + ribavirin combination therapy for 16 weeks,
- 250 subjects who received SOVALDI + ribavirin combination therapy for 24 weeks,
- 327 subjects who received SOVALDI + peginterferon (Peg-IFN) alfa + ribavirin combination therapy for 12 weeks,
- 243 subjects who received peginterferon alfa + ribavirin for 24 weeks, and
- 71 subjects who received placebo (PBO) for 12 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The proportion of subjects who permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 4% for subjects receiving placebo, 1% for subjects receiving SOVALDI + ribavirin for 12 weeks, less than 1% for subjects receiving SOVALDI + ribavirin for 24 weeks, 11% for subjects receiving peginterferon alfa + ribavirin for 24 weeks and 2% for subjects receiving SOVALDI + peginterferon alfa + ribavirin for 12 weeks.
Adverse events observed in at least 15% of subjects in the Phase 3 clinical trials outlined above are provided in Table 5. A side-by-side tabulation is displayed to simplify presentation; direct comparison across trials should not be made due to differing trial designs.
The most common adverse events (at least 20%) for SOVALDI + ribavirin combination therapy were fatigue and headache. The most common adverse events (at least 20%) for SOVALDI + peginterferon alfa + ribavirin combination therapy were fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia and anemia.
| Interferon-free Regimens | Interferon-containing Regimens | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBO 12 weeks | SOVALDI + RBV*
12 weeks | SOVALDI + RBV*
24 weeks | Peg-IFN alfa + RBV†
24 weeks | SOVALDI + Peg-IFN alfa + RBV*
12 weeks |
|
| N=71 | N=650 | N=250 | N=243 | N=327 | |
|
|||||
| Fatigue | 24% | 38% | 30% | 55% | 59% |
| Headache | 20% | 24% | 30% | 44% | 36% |
| Nausea | 18% | 22% | 13% | 29% | 34% |
| Insomnia | 4% | 15% | 16% | 29% | 25% |
| Pruritus | 8% | 11% | 27% | 17% | 17% |
| Anemia | 0% | 10% | 6% | 12% | 21% |
| Asthenia | 3% | 6% | 21% | 3% | 5% |
| Rash | 8% | 8% | 9% | 18% | 18% |
| Decreased Appetite | 10% | 6% | 6% | 18% | 18% |
| Chills | 1% | 2% | 2% | 18% | 17% |
| Influenza Like Illness | 3% | 3% | 6% | 18% | 16% |
| Pyrexia | 0% | 4% | 4% | 14% | 18% |
| Diarrhea | 6% | 9% | 12% | 17% | 12% |
| Neutropenia | 0% | <1% | <1% | 12% | 17% |
| Myalgia | 0% | 6% | 9% | 16% | 14% |
| Irritability | 1% | 10% | 10% | 16% | 13% |
With the exception of anemia and neutropenia, the majority of events presented in Table 5 occurred at severity of grade 1 in SOVALDI-containing regimens.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of SOVALDI. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Sofosbuvir is a substrate of drug transporter P-gp and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) while the predominant circulating metabolite GS-331007 is not. Drugs that are P-gp inducers in the intestine (e.g., rifampin or St. John's wort) may decrease sofosbuvir plasma concentration, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of SOVALDI, and thus concomitant use with SOVALDI is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Clearance of HCV infection with direct acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact the safe and effective use of concomitant medications. For example, altered blood glucose control resulting in serious symptomatic hypoglycemia has been reported in diabetic patients in postmarketing case reports and published epidemiological studies. Management of hypoglycemia in these cases required either discontinuation or dose modification of concomitant medications used for diabetes treatment.
Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (e.g. International Normalized Ratio [INR] in patients taking warfarin, blood glucose levels in diabetic patients) or drug concentrations of concomitant medications such as cytochrome P450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g. certain immunosuppressants) is recommended to ensure safe and effective use. Dose adjustments of concomitant medications may be necessary.
Information on potential drug interactions with SOVALDI is summarized in Table 7. The table is not all-inclusive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Antiarrhythmics:
amiodarone | Effect on amiodarone and sofosbuvir concentrations unknown | Coadministration of amiodarone with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen may result in serious symptomatic bradycardia. The mechanism of this effect is unknown. Coadministration of amiodarone with SOVALDI is not recommended; if coadministration is required, cardiac monitoring is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
| Anticonvulsants:
Carbamazepine phenytoin phenobarbital oxcarbazepine | ↓ sofosbuvir ↓ GS-331007 | Coadministration of SOVALDI with carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital or oxcarbazepine is expected to decrease the concentration of sofosbuvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of SOVALDI. Coadministration is not recommended. |
| Antimycobacterials:
Rifabutin rifampin rifapentine | ↓ sofosbuvir ↓ GS-331007 | Coadministration of SOVALDI with rifabutin or rifapentine is expected to decrease the concentration of sofosbuvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of SOVALDI. Coadministration is not recommended. Coadministration of SOVALDI with rifampin, an intestinal P-gp inducer, is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Herbal Supplements:
St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | ↓ sofosbuvir ↓ GS-331007 | Coadministration of SOVALDI with St. John's wort, an intestinal P-gp inducer, is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| HIV Protease Inhibitors:
tipranavir/ritonavir | ↓ sofosbuvir ↓ GS-331007 | Coadministration of SOVALDI with tipranavir/ritonavir is expected to decrease the concentration of sofosbuvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of SOVALDI. Coadministration is not recommended. |
7.2 Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with SOVALDI
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with SOVALDI, no clinically significant drug interactions have been either observed or are expected when SOVALDI is combined with the following drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]: cyclosporine, darunavir/ritonavir, efavirenz, emtricitabine, methadone, oral contraceptives, raltegravir, rilpivirine, tacrolimus, or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
If SOVALDI is administered with ribavirin or peginterferon and ribavirin, the information for ribavirin and peginterferon with regard to pregnancy testing, contraception, and infertility also applies to these combination regimens. Refer to ribavirin and/or peginterferon prescribing information for additional information.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of SOVALDI in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with genotype 2 and 3 infection have been established. SOVALDI was evaluated in an open-label clinical trial (Study 1112), which included 106 subjects (31 genotype 2; 75 genotype 3) 3 years of age and older. The safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy were comparable to that observed in adults [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.5)].
The safety and efficacy of SOVALDI in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older with compensated cirrhosis is supported by comparable sofosbuvir and GS-331007 exposures between: 1) adults and pediatric patients without cirrhosis and 2) adults without cirrhosis and adults with compensated cirrhosis. Thus, similar efficacy would be expected for pediatric patients with compensated cirrhosis as adults with compensated cirrhosis.
The safety and efficacy of SOVALDI have not been established in pediatric patients less than 3 years of age with HCV genotype 2 or 3. The safety and efficacy of SOVALDI have not been established in pediatric patients with HCV genotype 1 or 4.
8.5 Geriatric Use
SOVALDI was administered to 90 subjects aged 65 and over. The response rates observed for subjects over 65 years of age were similar to that of younger subjects across treatment groups. No dosage adjustment of SOVALDI is warranted in geriatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of SOVALDI is required for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. The safety and efficacy of SOVALDI have not been established in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2) or ESRD requiring hemodialysis. No dosage recommendation can be given for patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Refer also to ribavirin and peginterferon alfa prescribing information for patients with CrCl less than 50 mL/min.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of SOVALDI is required for patients with mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B or C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Safety and efficacy of SOVALDI have not been established in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. See peginterferon alfa prescribing information for contraindication in hepatic decompensation.
8.8 Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Awaiting Liver Transplantation
SOVALDI was studied in HCV-infected adult subjects with hepatocellular carcinoma prior to undergoing liver transplantation in an open-label clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of SOVALDI and ribavirin administered pre-transplant to prevent post-transplant HCV reinfection. The primary endpoint of the trial was post-transplant virologic response (pTVR) defined as HCV RNA less than lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) at 12 weeks post-transplant. HCV-infected subjects, regardless of genotype, with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) meeting the MILAN criteria (defined as the presence of a tumor 5 cm or less in diameter in patients with single hepatocellular carcinomas and no more than three tumor nodules, each 3 cm or less in diameter in patients with multiple tumors and no extrahepatic manifestations of the cancer or evidence of vascular invasion of tumor) received 400 mg SOVALDI and weight-based 1000–1200 mg ribavirin daily for 24–48 weeks or until the time of liver transplantation, whichever occurred first. An interim analysis was conducted on 61 subjects who received SOVALDI and ribavirin; 45 subjects had HCV genotype 1; 44 subjects had a baseline CPT score less than 7 and all subjects had a baseline unadjusted MELD score up to 14. Of these 61 subjects, 41 subjects underwent liver transplantation following up to 48 weeks of treatment with SOVALDI and ribavirin; 37 had HCV RNA less than LLOQ at the time of transplantation. Of the 37 subjects, the post-transplant virologic response (pTVR) rate is 64% (23/36) in the 36 evaluable subjects who have reached the 12 week post-transplant time point. The safety profile of SOVALDI and ribavirin in HCV-infected subjects prior to liver transplantation was comparable to that observed in subjects treated with SOVALDI and ribavirin in Phase 3 clinical trials.
10. Overdosage
The highest documented dosage of sofosbuvir was a single dose of sofosbuvir 1200 mg (three times the recommended dosage) administered to 59 healthy subjects. In that trial, there were no untoward effects observed at this dosage level, and adverse events were similar in frequency and severity to those reported in the placebo and sofosbuvir 400 mg treatment groups. The effects of higher dosages are not known.
No specific antidote is available for overdose with SOVALDI. If overdose occurs, the patient must be monitored for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with SOVALDI consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. A 4-hour hemodialysis session removed 18% of the administered dose.
11. Sovaldi Description
SOVALDI (sofosbuvir) is a nucleotide analog inhibitor of HCV NS5B polymerase.
The IUPAC name for sofosbuvir is (S)-isopropyl 2-((S)-(((2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)-(phenoxy)phosphorylamino)propanoate. It has a molecular formula of C22H29FN3O9P and a molecular weight of 529.45. It has the following structural formula:
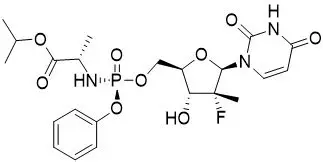
Sofosbuvir is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a solubility of ≥ 2 mg/mL across the pH range of 2–7.7 at 37 °C and is slightly soluble in water.
SOVALDI tablets, 200 mg or 400 mg, are for oral administration. Each tablet contains 200 mg or 400 mg of sofosbuvir. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
SOVALDI pellets, 150 mg or 200 mg, are for oral administration, supplied as white to off-white pellets in unit-dose packets. Each unit-dose packet contains 150 mg or 200 mg of sofosbuvir. The pellets include the following inactive ingredients: amino methacrylate copolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium stearyl fumarate, stearic acid, and talc.
12. Sovaldi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sofosbuvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent against the hepatitis C virus [see Microbiology (12.4)].
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Description of Clinical Trials
The safety and efficacy of SOVALDI was evaluated in five Phase 3 trials in a total of 1724 HCV mono-infected subjects with genotypes 1 to 6 chronic hepatitis C virus, one Phase 3 trial in 223 HCV/HIV-1 coinfected subjects with genotype 1, 2 or 3 HCV, and one trial in 106 pediatric subjects 3 years of age and older with genotype 2 or 3 HCV, as summarized in Table 11 [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3, 14.4, and 14.5)].
| Trial | Population | Study Arms (Number of Subjects Treated) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| NEUTRINO *
(NCT01641640) | Treatment naïve (TN) (GT1, 4, 5 or 6) | SOVALDI+Peg-IFN alfa+RBV 12 weeks (327) |
| FISSION *
(NCT01497366) | TN (GT2 or 3) | SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks (256) Peg-IFN alfa+RBV 24 weeks (243) |
| POSITRON †
(NCT01542788) | Interferon intolerant, ineligible or unwilling subjects (GT2 or 3) | SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks (207) Placebo 12 weeks (71) |
| FUSION †
(NCT01604850) | Previous interferon relapsers or nonresponders (GT2 or 3) | SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks (103) SOVALDI+RBV 16 Weeks (98) |
| VALENCE †
(NCT01682720) | TN or previous interferon relapsers or nonresponders (GT2 or 3) | SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks for GT2 (73) SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks for GT3 (11) SOVALDI+RBV 24 Weeks for GT3 (250) Placebo for 12 weeks (85) |
| PHOTON-1 *
(NCT01667731) |
| SOVALDI+RBV 24 Weeks for GT1 (114) SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks for GT2 or 3 TN (68) SOVALDI+RBV 24 Weeks for GT2 or 3 previous interferon relapsers or nonresponders (41) |
| 1112 (NCT02175758)* | GT2 or GT3 pediatric subjects 3 years of age and older | SOVALDI+RBV 12 Weeks for GT2 (31) SOVALDI+RBV 24 Weeks for GT3 (75) |
Subjects in the adult trials did not have cirrhosis or had compensated cirrhosis. SOVALDI was administered at a dose of 400 mg once daily. The ribavirin (RBV) dosage for adult subjects was weight-based at 1000–1200 mg daily administered in two divided doses when used in combination with SOVALDI, and the peginterferon alfa 2a dosage, where applicable, was 180 micrograms per week. Treatment duration was fixed in each trial and was not guided by subjects' HCV RNA levels (no response guided algorithm). Plasma HCV RNA values were measured during the clinical trials using the COBAS TaqMan HCV test (version 2.0), for use with the High Pure System. The assay had a lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 25 IU per mL. Sustained virologic response (SVR12) was the primary endpoint which was defined as HCV RNA less than LLOQ at 12 weeks after the end of treatment.
14.4 Clinical Trials in Adult Subjects Coinfected with HCV and HIV-1 ─ Photon-1 (Study 0123)
SOVALDI was studied in an open-label clinical trial (Study PHOTON-1) evaluating the safety and efficacy of 12 or 24 weeks of treatment with SOVALDI and ribavirin in adult subjects with genotype 1, 2 or 3 chronic hepatitis C coinfected with HIV-1. Genotype 2 and 3 subjects were either HCV treatment-naïve or experienced, whereas genotype 1 subjects were all treatment-naïve. Subjects received 400 mg SOVALDI and weight-based ribavirin (1000 mg for subjects weighing less than 75 kg or 1200 mg for subjects weighing at least 75 kg) daily for 12 or 24 weeks based on genotype and prior treatment history. Subjects were either not on antiretroviral therapy with a CD4+ cell count greater than 500 cells/mm3 or had virologically suppressed HIV-1 with a CD4+ cell count greater than 200 cells/mm3. Efficacy data 12 weeks post treatment are available for 210 subjects (see Table 22).
| HCV genotype 1 | HCV genotype 2 | HCV genotype 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOVALDI + RBV 24 weeks TN (N=114) | SOVALDI + RBV 12 weeks TN (N=26) | SOVALDI + RBV 24 weeks TE (N=13) |
|
| TN = Treatment-naïve; TE = Treatment-experienced | |||
|
|||
| Overall | 76% (87/114) | 88% (23/26) | 92% (12/13) |
| Outcome for subjects without SVR12 | |||
| On-treatment virologic failure | 1% (1/114) | 4% (1/26) | 0/13 |
| Relapse† | 22% (25/113) | 0/25 | 8% (1/13) |
| Other‡ | 1% (1/114) | 8% (2/26) | 0/13 |
In subjects with HCV genotype 1 infection, the SVR12 rate was 82% (74/90) in subjects with genotype 1a infection and 54% (13/24) in subjects with genotype 1b infection, with relapse accounting for the majority of treatment failures. SVR12 rates in subjects with HCV genotype 1 infection were 80% (24/30) in subjects with baseline IL28B C/C allele and 75% (62/83) in subjects with baseline IL28B non-C/C alleles.
In the 223 HCV subjects with HIV-1 coinfection, the percentage of CD4+ cells did not change during treatment. Median CD4+ cell count decreases of 85 cells/mm3 and 84 cells/mm3 were observed at the end of treatment with SOVALDI + ribavirin for 12 or 24 weeks, respectively. HIV-1 rebound during SOVALDI + ribavirin treatment occurred in 2 subjects (0.9%) on antiretroviral therapy.
14.5 Clinical Trial in Pediatrics (Study 1112)
The efficacy of SOVALDI in HCV-infected pediatric subjects 3 years of age and older was evaluated in 106 subjects with HCV genotype 2 (N = 31) or genotype 3 (N = 75) in a Phase 2, open label clinical trial. Subjects with HCV genotype 2 or 3 infection in the trial were treated with SOVALDI and weight-based ribavirin for 12 or 24 weeks, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 03/2020 | |||
| Patient Information | ||||
| SOVALDI® (soh-VAHL-dee) (sofosbuvir) tablets | SOVALDI® (soh-VAHL-dee) (sofosbuvir) oral pellets |
|||
| Important: SOVALDI is used in combination with other antiviral medicines. When taking SOVALDI with ribavirin or in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin you should also read those Medication Guides. The information in this Patient Information Leaflet talks about SOVALDI when it is used with ribavirin and in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin. | ||||
| What is the most important information I should know about SOVALDI? SOVALDI can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
| What is SOVALDI?
SOVALDI is a prescription medicine used with other antiviral medicines to treat adults with chronic (lasting a long time) hepatitis C virus (HCV):
It is not known if SOVALDI is safe and effective in children under 3 years of age with HCV genotype 2 or 3 infection, or with HCV genotype 1 or 4 infection. It is not known if SOVALDI is safe and effective in people who have had a liver transplant. |
||||
Before taking SOVALDI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
|
||||
How should I take SOVALDI?
|
||||
| How should I give SOVALDI oral pellets to my child? See the detailed Instructions for Use for information about how to give or take a dose of SOVALDI oral pellets.
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of SOVALDI? SOVALDI can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|
||
| The most common side effects of SOVALDI when used in combination with ribavirin include: | ||||
|
| |||
| The most common side effects of SOVALDI when used in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin include: | ||||
|
|
|
||
| These are not all the possible side effects of SOVALDI. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
How should I store SOVALDI?
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SOVALDI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use SOVALDI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SOVALDI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about SOVALDI that is written for health professionals. For more information, call 1-800-445-3235 or go to www.SOVALDI.com. |
||||
| What are the ingredients in SOVALDI? Active ingredient: sofosbuvir Inactive ingredients, Tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film-coat contains polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. Inactive ingredients, Oral Pellets: amino methacrylate copolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium stearyl fumarate, stearic acid, and talc. Gilead Sciences, Inc., Foster City, CA 94404 For more information, call 1-800-445-3235 or go to www.SOVALDI.com. SOVALDI is a trademark of Gilead Sciences, Inc., or its related companies. All other trademarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners. ©2020 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved. 204671-GS-010 |
||||
| SOVALDI
sofosbuvir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOVALDI
sofosbuvir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOVALDI
sofosbuvir pellet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOVALDI
sofosbuvir pellet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| F.I.S. FABBRICA ITALIANA SINTETICI S.P.A. | 431189117 | API MANUFACTURE(61958-1501, 61958-1503, 61958-1504, 61958-1505) | |