Drug Detail:Tivdak (Tisotumab vedotin-tftv)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TIVDAK® (tisotumab vedotin-tftv) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
WARNING: OCULAR TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- TIVDAK caused changes in the corneal epithelium and conjunctiva resulting in changes in vision, including severe vision loss, and corneal ulceration. (5.1)
- Conduct an ophthalmic exam at baseline, prior to each dose, and as clinically indicated. (2.2, 5.1)
-
Adhere to premedication and required eye care before, during, and after infusion. (2.2)
-
Withhold TIVDAK until improvement and resume, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue, based on severity. (2.3, 5.1)
Recent Major Changes
Dosage and Administration (2.3) 7/2023
Warnings and Precautions (5.5) 7/2023
Indications and Usage for Tivdak
TIVDAK is a tissue factor-directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate indicated for the treatment of adult patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer with disease progression on or after chemotherapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. (14.1)
Tivdak Dosage and Administration
- For intravenous infusion only. Do not administer TIVDAK as an intravenous push or bolus. Do not mix with, or administer as an infusion with, other medicinal products. (2.4)
- The recommended dose of TIVDAK is 2 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 200 mg) given as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
For Injection: 40 mg as a lyophilized cake or powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Peripheral neuropathy: Monitor patients for new or worsening peripheral neuropathy. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on severity. (2.3, 5.2)
- Hemorrhage: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on severity. (2.3, 5.3).
- Pneumonitis: Severe, life-threatening or fatal pneumonitis may occur. Withhold TIVDAK for persistent or recurrent Grade 2 pneumonitis and consider dose reduction. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK for Grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis. (2.3, 5.4)
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including events of fatal or life-threatening Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), can occur in patients treated with TIVDAK. Immediately withhold TIVDAK for suspected severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including SJS. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK for confirmed Grade 3 or 4 severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including SJS. (2.3, 5.5).
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: TIVDAK can cause fetal harm. Advise of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were hemoglobin decreased, fatigue, lymphocytes decreased, nausea, peripheral neuropathy, alopecia, epistaxis, conjunctival adverse reactions, hemorrhage, leukocytes decreased, creatinine increased, dry eye, prothrombin international normalized ratio increased, activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged, diarrhea, and rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Seagen Inc. at 1-855-4SEAGEN or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Closely monitor for TIVDAK adverse reactions. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Moderate or severe hepatic impairment: Exposure to MMAE and adverse reactions are increased. Avoid use. (8.6)
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2023
Related/similar drugs
Keytruda, Avastin, carboplatin, fluorouracil, pembrolizumab, cisplatinFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: OCULAR TOXICITY
- TIVDAK caused changes in the corneal epithelium and conjunctiva resulting in changes in vision, including severe vision loss, and corneal ulceration. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Conduct an ophthalmic exam at baseline, prior to each dose, and as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
Adhere to premedication and required eye care before, during, and after infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
-
Withhold TIVDAK until improvement and resume, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue, based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Tivdak
TIVDAK® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer with disease progression on or after chemotherapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
2. Tivdak Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of TIVDAK is 2 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 200 mg for patients ≥100 kg) administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
2.2 Premedication and Required Eye Care
Adhere to the following recommendations to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
Ophthalmic exam: Conduct an ophthalmic exam including visual acuity and slit lamp exam at baseline, prior to each dose, and as clinically indicated.
-
Topical corticosteroid eye drops: The initial prescription and all renewals of any corticosteroid medication should be made only after examination with a slit lamp. Administer first drop in each eye prior to each infusion. Instruct patients to continue to administer eye drops in each eye as prescribed for 72 hours after each infusion.
-
Topical ocular vasoconstrictor drops: Administer in each eye immediately prior to each infusion.
-
Cold packs: Use cooling eye pads during the infusion of TIVDAK.
-
Topical lubricating eye drops: Instruct patients to administer for the duration of therapy and for 30 days after the last dose of TIVDAK.
-
Contact lenses: Advise patients to avoid wearing contact lenses unless advised by their eye care provider for the entire duration of therapy.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended TIVDAK dose reduction schedule is provided in Table 1.
| * Permanently discontinue in patients who cannot tolerate 0.9 mg/kg | |
| TIVDAK Dose Level | |
| Starting dose | 2 mg/kg |
| First dose reduction | 1.3 mg/kg |
| Second dose reduction | 0.9 mg/kg* |
The recommended dose modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| * Refer patients to an eye care provider promptly for an assessment of new or worsening ocular symptoms. | |||
| Adverse Reaction | Severity | Occurrence | TIVDAK Dose Modification |
| Keratitis* [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Superficial punctate keratitis (SPK) | Any | Monitor. |
| Confluent superficial keratitis | First occurrence | Withhold dose until SPK or normal, then resume treatment at the next lower dose level. | |
| Second occurrence | Permanently discontinue. | ||
| Ulcerative keratitis or perforation | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Conjunctival ulceration* [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any ulceration | First occurrence | Withhold dose until complete conjunctival re-epithelialization, then resume treatment at the next lower dose level. |
| Second occurrence | Permanently discontinue. | ||
| Conjunctival or corneal scarring or symblepharon* [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any scarring or symblepharon | Any | Permanently discontinue. |
| Conjunctivitis and other ocular adverse reactions* [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 1 | Any | Monitor. |
| Grade 2 | First occurrence | Withhold dose until Grade ≤1, then resume treatment at the same dose. | |
| Second occurrence | Withhold dose until Grade ≤1, then resume treatment at the next lower dose level. If no resolution to Grade ≤1, permanently discontinue. | ||
| Third occurrence | Permanently discontinue. | ||
| Grade 3 or 4 | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 2 | Any (initial or worsening of pre-existing condition) | Withhold dose until Grade ≤1, then resume treatment at the next lower dose level. |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Any grade pulmonary or CNS | Any | Permanently discontinue. |
| Grade 2 in any other location | Any | Withhold until resolved, then resume treatment at the same dose. | |
| Grade 3 in any other location | First occurrence | Withhold dose until resolved, then resume treatment at the same dose. | |
| Second occurrence | Permanently discontinue. | ||
| Grade 4 in any other location | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | Grade 2 | Any | Withhold dose until Grade ≤1 for persistent or recurrent pneumonitis, consider resuming treatment at next lower dose level. |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS))
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | Suspected (any grade) | Any | Immediately withhold dose and consult a specialist to confirm the diagnosis. |
| Confirmed Grade 3 or 4 | Any | Permanently discontinue. | |
2.4 Instructions for Preparation and Administration
- Administer TIVDAK as an intravenous infusion only.
- TIVDAK is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures1.
- DO NOT mix TIVDAK as an intravenous push or bolus.
- DO NOT mix TIVDAK with, or administer as an infusion with, other medicinal products.
Use appropriate aseptic technique for reconstitution and preparation of dosing solutions. Prior to administration, the TIVDAK vial is reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP. The reconstituted solution is subsequently diluted in an intravenous infusion bag containing one of the following: 5% Dextrose Injection USP, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or Lactated Ringer’s Injection, USP.
Reconstitution in Single-dose Vial
- Calculate the recommended dose based on the patient’s weight to determine the number of vials needed.
- Reconstitute each 40 mg vial with 4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, resulting in 10 mg/mL TIVDAK.
- Slowly swirl each vial until the contents are completely dissolved. Allow the reconstituted vial(s) to settle. DO NOT SHAKE THE VIAL. Do not expose to direct sunlight.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. The reconstituted solution should be clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to brownish-yellow and free of visible particles. Discard any vial with visible particles or discoloration.
- Based upon the calculated dose amount, the reconstituted solution from the vial(s) should be added to the infusion bag immediately. This product does not contain a preservative. If not used immediately, reconstituted vials may be stored for up to 24 hours in refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36 °F to 46 °F) or at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for up to a maximum of 8 hours prior to dilution. DO NOT FREEZE. Do not expose to direct sunlight. Discard unused vials with reconstituted solution beyond the recommended storage time.
Dilution in Infusion Bag
- Withdraw the calculated dose amount of reconstituted solution from the vial(s) and transfer into an infusion bag.
- Dilute TIVDAK with one of the following: 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP. The infusion bag size should allow enough diluent to achieve a final concentration of 0.7 mg/mL to 2.4 mg/mL TIVDAK.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. DO NOT SHAKE THE BAG. Do not expose to direct sunlight.
- Visually inspect the infusion bag for any particulate matter or discoloration prior to use. The reconstituted solution should be clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to brownish-yellow and free of visible particles. Discard the infusion bag if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Discard any unused portion left in the single-dose vials.
Administration
- Confirm administration of steroid and vasoconstrictor eye drops [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Apply cold packs fully over the eyes following administration of the vasoconstrictor eye drops and leave on during the infusion. Change cold packs as needed throughout infusion to ensure eye area remains cold [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Immediately administer the infusion over 30 minutes through an intravenous line containing a 0.2 µm in-line filter.
- If the infusion is not administered immediately, store the diluted TIVDAK solution in refrigeration as specified in Table 3. Discard if storage time exceeds these limits. DO NOT FREEZE. Once removed from refrigeration, complete administration of the diluted infusion solution of TIVDAK within 4 hours (including infusion time).
| Diluent Used to Prepare Solution for Infusion | Diluted TIVDAK Solution Storage Conditions (Including Infusion Time) |
| 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP | Up to 18 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) |
| 5% Dextrose Injection, USP | Up to 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) |
| Lactated Ringer’s Injection, USP | Up to 12 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
For Injection: 40 mg of tisotumab vedotin-tftv as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Ocular Adverse Reactions
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 60% of patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common ocular adverse reactions were conjunctival adverse reactions (40%), dry eye (29%), corneal adverse reactions (21%), and blepharitis (8%). Grade 3 ocular adverse reactions occurred in 3.8% of patients, including severe ulcerative keratitis in 3.2% of patients. One patient experienced ulcerative keratitis with perforation requiring corneal transplantation. Cases of symblepharon were reported in patients with other tumor types treated with TIVDAK at the recommended dose.
The median time to onset of the first ocular adverse reaction was 1.2 months (range, 0 – 6.5). Of the patients who experienced ocular events, 55% had complete resolution and 30% had partial improvement (defined as a decrease in severity by one or more grades from the worst grade) at last follow up. Ocular adverse reactions led to discontinuation of TIVDAK in 6% of patients with cervical cancer.
In innovaTV 204, 4% of patients experienced visual acuity changes to 20/50 or worse including 1% of patients who experienced a visual acuity change to 20/200. Of the patients who experienced decreased visual acuity to 20/50 or worse, 75% resolved, including the patient who experienced decreased visual acuity to 20/200.
Refer patients to an eye care provider for an ophthalmic exam including visual acuity and slit lamp exam at baseline, prior to each dose, and as clinically indicated. Adhere to premedication and required eye care to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Promptly refer patients to an eye care provider for any new or worsening ocular signs and symptoms.
Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 42% of patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials; 8% of patients experienced Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy adverse reactions included peripheral neuropathy (20%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (11%), peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy (5%), motor neuropathy (3%), muscular weakness (3%), and demyelinating peripheral polyneuropathy (1%). One patient with another tumor type treated with TIVDAK at the recommended dose developed Guillain-Barre syndrome.
The median time to onset of peripheral neuropathy was 2.4 months (range, 0-11.3). Of the patients who experienced peripheral neuropathy, 17% had complete resolution and 17% had partial improvement (defined as a decrease in severity by one or more grades from the worst grade) at last follow up. Peripheral neuropathy led to discontinuation of TIVDAK in 8% of patients with cervical cancer.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neuropathy, such as paresthesia, tingling or a burning sensation, neuropathic pain, muscle weakness, or dysesthesia. For patients experiencing new or worsening peripheral neuropathy, withhold dose, then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity of peripheral neuropathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage occurred in 62% of patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common all grade hemorrhage adverse reactions were epistaxis (44%), hematuria (10%), and vaginal hemorrhage (10%). Grade 3 hemorrhage occurred in 5% of patients.
The median time to onset of hemorrhage was 0.3 months (range, 0-6.5). Of the patients who experienced hemorrhage, 71% had complete resolution and 11% had partial resolution (defined as a decrease in severity by one or more grades from the worst grade) at last follow-up.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage. For patients experiencing pulmonary or CNS hemorrhage, permanently discontinue TIVDAK. For grade ≥2 hemorrhage in any other location, withhold until bleeding has resolved, blood hemoglobin is stable, there is no bleeding diathesis that could increase the risk of continuing therapy, and there is no anatomical or pathologic condition that can increase the risk of hemorrhage recurrence. After resolution, either resume treatment or permanently discontinue TIVDAK [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Pneumonitis
Severe, life-threatening, or fatal pneumonitis can occur in patients treated with antibody drug conjugates containing vedotin including TIVDAK. Among patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials, 2 patients (1.3%) experienced pneumonitis, including 1 patient who had a fatal outcome.
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of pneumonitis. Symptoms may include hypoxia, cough, dyspnea or interstitial infiltrates on radiologic exams. Infectious, neoplastic, and other causes for such symptoms should be excluded through appropriate investigations.
Withhold TIVDAK for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2 pneumonitis and consider dose reduction. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including events of fatal or life-threatening SJS, can occur in patients treated with TIVDAK.
Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions, which include target lesions, worsening skin reactions, blistering or peeling of the skin, painful sores in mouth, nose, throat, or genital area, fever or flu-like symptoms, and swollen lymph nodes. If signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions occur, withhold TIVDAK until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. Early consultation with a specialist is recommended to ensure greater diagnostic accuracy and appropriate management. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK for confirmed Grade 3 or 4 severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including SJS [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on the mechanism of action and findings in animals, TIVDAK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. The small molecule component of TIVDAK, MMAE, administered to rats caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality and structural abnormalities, at exposures below those occurring clinically at the recommended dose.
Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 2 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Ocular Adverse Reactions [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS section reflect exposure to TIVDAK in 158 patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer who received at least one dose of TIVDAK at 2 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks in innovaTV 204 (NCT03438396), innovaTV 201 (NCT02001623), innovaTV 202 (NCT02552121) and innovaTV 203 (NCT03245736).
The data described in this section reflect exposure to TIVDAK from innovaTV 204 (NCT0348396), a single arm study in patients (n=101) with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer with disease progression on or after chemotherapy. Patients received TIVDAK 2.0 mg/kg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median duration of treatment was 4.2 months (range: 0.7-16).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 43% of patients. The most common (≥3%) serious adverse reactions were ileus (6%), hemorrhage (5%), pneumonia (4%), peripheral neuropathy, sepsis, constipation, and pyrexia (each 3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients who received TIVDAK, including septic shock (1%), pneumonitis (1%), sudden death (1%), and multisystem organ failure (1%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 13% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation were peripheral neuropathy (5%) and corneal adverse reactions (4%).
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 47% of patients; the most (≥3%) common adverse reactions leading to dose interruption were peripheral neuropathy (8%), conjunctival adverse reactions (4%), and hemorrhage (4%).
Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 23% of patients; the most common (≥3%) adverse reactions leading to dose reduction were conjunctival adverse reactions (9%) and corneal adverse reactions (8%).
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were hemoglobin decreased, fatigue, lymphocytes decreased, nausea, peripheral neuropathy, alopecia, epistaxis, conjunctival adverse reactions, hemorrhage, leukocytes decreased, creatinine increased, dry eye, prothrombin international normalized ratio increased, activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged, diarrhea, and rash.
Table 4 summarizes the all grade and Grade 3-4 adverse reactions from innovaTV 204.
| 1. Fatigue includes fatigue and asthenia 2. Nausea includes nausea and retching 3. Diarrhea includes diarrhea, gastroenteritis, and colitis 4. Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal distention and abdominal discomfort 5. Peripheral neuropathy includes neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, polyneuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, burning sensation, neuralgia, sensory loss, peripheral motor neuropathy, muscular weakness, gait disturbance, and hyperesthesia 6. Rash includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash macular, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis allergic, and erythema 7. Hemorrhage includes vaginal hemorrhage, hematuria, rectal hemorrhage, cystitis hemorrhagic, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, urinary bladder hemorrhage, hematochezia, anal hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, post procedural hemorrhage, radiation associated with hemorrhage, metrorrhagia, large intestinal hemorrhage, paranasal sinus hemorrhage, and hemoptysis 8. Conjunctival adverse reactions includes conjunctivitis, conjunctival abrasion, conjunctival erosion, conjunctival hyperemia, conjunctival scar, noninfective conjunctivitis, ocular hyperemia, and conjunctival hemorrhage 9. Dry eye includes dry eye and lacrimation increased 10. Corneal adverse reactions includes keratitis, punctate keratitis, ulcerative keratitis, corneal erosion, corneal scar, keratopathy, and corneal bleeding 11. Periorbital adverse reactions includes blepharitis, meibomianitis, eye pruritus, entropion, trichiasis, chalazion, and meibomian gland dysfunction 12. Myalgia includes myalgia, musculoskeletal discomfort, and musculoskeletal pain 13. Pain in extremity includes pain in extremity and limb discomfort 14. Urinary tract infection includes urinary tract infection, urinary tract infection bacterial, and cystitis |
||
| Adverse Reaction | TIVDAK
N=101 |
|
| All Grades | Grade 3-4 | |
| % | % | |
| General |
|
|
| Fatigue1 | 50 | 7 |
| Pyrexia | 16 | 1 |
| Pruritis | 13 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea2 | 41 | 0 |
| Diarrhea3 | 25 | 2 |
| Constipation | 23 | 2 |
| Abdominal Pain4 | 23 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 17 | 2 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Peripheral Neuropathy5 | 39 | 7 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Alopecia | 39 | 0 |
| Rash6 | 25 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders
| ||
| Epistaxis | 39 | 0 |
| Hemorrhage7
| 32 | 6 |
| Eye disorders
| ||
| Conjunctival adverse reactions8
| 37 | 0 |
| Dry eye9
| 29 | 0 |
| Corneal adverse reactions 10
| 21 | 3 |
| Periorbital adverse reactions11
| 16 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
| ||
| Myalgia12
| 21 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 16 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity13
| 13 | 1 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders
| ||
| Decreased appetite | 16 | 1 |
| Infections
| ||
| Urinary tract infection14
| 14 | 2 |
| Investigations
| ||
| Weight decreased | 12 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received TIVDAK in innovaTV 204 included venous thrombosis (3%), pulmonary embolism (3%), and pneumonitis (2%).
Table 5 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in innovaTV 204.
| 1. The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 96 to 101 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TIVDAK1 | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Hematology | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 52 | 7 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 42 | 8 |
| Leukocytes decreased | 30 | 0 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 21 | 3 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Creatinine increased | 29 | 4.1 |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 24 | 0 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase increased | 22 | 0 |
| Urate increased | 20 | 0 |
| Glucose decreased | 19 | 0 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 18 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 20 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 17 | 0 |
| Creatinine kinase increased | 16 | 2.1 |
| Magnesium decreased | 17 | 2.1 |
| Albumin decreased | 16 | 0 |
| Coagulation | ||
| Prothrombin international normalized ratio increased | 26 | 0 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged | 26 | 2 |
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for an immune response to TIVDAK. The detection of antibody formation against tisotumab vedotin-tftv is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to tisotumab vedotin-tftv in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
In innovaTV 204, a total of 93 patients were tested for immunogenicity to TIVDAK; 5 patients (5%) developed treatment-emergent anti-tisotumab vedotin-tftv antibodies. Neutralizing anti-tisotumab vedotin-tftv antibodies were detected in 2 patients in Study innovaTV 204. Across all studies, 8 cervical cancer patients (5.5%) out of 145 evaluable patients developed treatment-emergent anti-tisotumab vedotin-tftv antibodies. Given the low number of patients who developed anti-tisotumab vedotin-tftv antibodies, no conclusions can be drawn concerning a potential effect of immunogenicity on PK, efficacy or safety.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on TIVDAK
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
MMAE is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use of TIVDAK with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated MMAE exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of TIVDAK adverse reactions. Closely monitor patients for adverse reactions of TIVDAK when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action and findings in animals, TIVDAK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available human data on TIVDAK use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In an animal reproduction study, administration of the small molecule component of TIVDAK, MMAE, to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal mortality and structural abnormalities at exposures below the clinical exposure at the recommended dose (see Data). Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No embryo-fetal development studies in animals have been performed with tisotumab vedotin-tftv. In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats, administration of two intravenous doses of MMAE, the small molecule component of TIVDAK, on gestational days 6 and 13 caused embryo-fetal mortality and structural abnormalities, including protruding tongue, malrotated limbs, gastroschisis, and agnathia compared to controls at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg (approximately 0.5-fold the human area under the curve [AUC] at the recommended dose).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tisotumab vedotin-tftv in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with TIVDAK and for 3 weeks after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
TIVDAK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TIVDAK treatment.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 2 months after the last dose.
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 4 months after the last dose.
Infertility
Males
Based on findings from animal studies, TIVDAK may impair male fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TIVDAK in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 101 patients treated with TIVDAK in innovaTV 204, 13% were ≥65 years of age. Grade ≥3 adverse reactions occurred in 69% patients ≥65 years and in 59% patients <65 years. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 54% patients ≥65 years and in 41% patients <65 years. No patients aged ≥65 years treated with TIVDAK in innovaTV 204 experienced a tumor response.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use of TIVDAK in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 × ULN) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST >ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST), closely monitor patients for adverse reactions of TIVDAK, but no dosage adjustment in the starting dose of TIVDAK is recommended.
11. Tivdak Description
Tisotumab vedotin-tftv is a Tissue Factor (TF) directed antibody drug conjugate (ADC) comprised of a human anti-TF IgG1-kappa antibody conjugated to the microtubule-disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via a protease-cleavable vc (valine-citrulline) linker. The monoclonal antibody is produced in a mammalian cell cline (Chinese hamster ovary). MMAE and the linker are produced by chemical synthesis. Each monoclonal antibody molecule carries an average of 4 MMAE molecules. Tisotumab vedotin-tftv has an approximate molecular weight of 153 kDa. The chemical structure is as follows:
Figure 1. Structural Formula
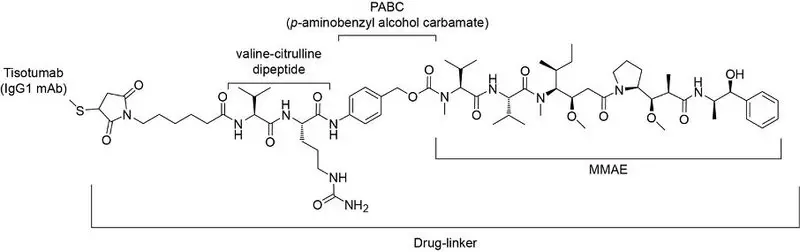
TIVDAK (tisotumab vedotin-tftv) for injection, is provided as a sterile, preservative-free, white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder in a single-dose vial for infusion after dilution. Following reconstitution with 4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to brownish-yellow solution containing 10 mg/mL tisotumab vedotin-tftv is produced [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Each mL of reconstituted solution contains 10 mg of tisotumab vedotin-tftv, d-mannitol (30 mg), l-histidine (2.11 mg), l-histidine monohydrochloride (3.44 mg), and sucrose (30 mg), at pH 6.0.
12. Tivdak - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tisotumab vedotin-tftv is a tissue factor (TF)-directed antibody drug conjugate (ADC). The antibody is a human IgG1 directed against cell surface TF. TF is the primary initiator of the extrinsic blood coagulation cascade. The small molecule, MMAE, is a microtubule-disrupting agent, attached to the antibody via a protease-cleavable linker. Nonclinical data suggests that the anticancer activity of tisotumab vedotin-tftv is due to the binding of the ADC to TF expressing cancer cells, followed by internalization of the ADC-TF complex, and release of MMAE via proteolytic cleavage. MMAE disrupts the microtubule network of actively dividing cells, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. In vitro, tisotumab vedotin-tftv also mediates antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Tisotumab vedotin-tftv exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamics response have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended dose, tisotumab vedotin-tftv had no large mean effect on QTc prolongation (>20 msec).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Table 6 summarizes the exposure parameters of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE (the cytotoxic component of tisotumab vedotin-tftv) following administration of one 3-week cycle of tisotumab vedotin-tftv 2 mg/kg to patients. Tisotumab vedotin-tftv concentrations peaked near the end of the infusion, while unconjugated MMAE concentrations peaked approximately 2 to 3 days after tisotumab vedotin-tftv dosing. Tisotumab vedotin-tftv Cmax increased proportionally, while AUC0-last increased in a more than dose-proportional manner, after a single dose ranging from 0.3–2.2 mg/kg (0.15 to 1.1 times the approved recommended dose). There was no accumulation of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE. Steady-state concentrations of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE were reached after 1 treatment cycle.
| Cmax =maximum concentration, AUC = area under the concentration-time curve from time 0 to 21 days (3 weeks) | ||
| Tisotumab Vedotin-tftv Mean (± SD) | Unconjugated MMAE Mean (± SD) |
|
| Cmax | 40.8 (8.12) μg/mL | 5.91 (4.2) ng/mL |
| AUC | 57.5 (13.4) day*μg/mL | 50 (35.8) day*ng/mL |
Distribution
The tisotumab vedotin-tftv steady state volume of distribution is 7.83 (%CV: 19.1) L. Plasma protein binding of MMAE ranged from 68% to 82%, in vitro.
Elimination
The median terminal half-life of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE is 4.04 (range: 2.26-7.25) days and 2.56 (range: 1.81-4.10) days, respectively. The linear clearance of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE was 1.54 (%CV: 28.8) L/day and 45.9 (%CV: 61.1) L/day, respectively. Elimination of MMAE appeared to be limited by its rate of release from tisotumab vedotin-tftv.
Metabolism
Tisotumab vedotin-tftv is expected to undergo catabolism to small peptides, amino acids, unconjugated MMAE, and unconjugated MMAE-related catabolites. Tisotumab vedotin-tftv releases unconjugated MMAE via proteolytic cleavage, and unconjugated MMAE is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 in vitro.
Excretion
The excretion of tisotumab vedotin-tftv is not fully characterized. Following a single-dose of another ADC that contains MMAE, 17% of the total MMAE administered was recovered in feces and 6% in urine over a 1-week period, primarily as unchanged drug. A similar excretion profile of MMAE is expected after tisotumab vedotin-tftv administration.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of tisotumab vedotin-tftv were observed based on age (21 to 81 years), sex, race (white vs non-white) or ethnicity (Hispanic or Latino vs non-Hispanic or non-Latino). No clinically significant differences in exposures of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE were observed in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to < 90 mL/min using the Cockcroft-Gault equation) compared to patients with normal renal function. The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to < 30 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease with or without dialysis on pharmacokinetics of tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE is unknown.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Unconjugated MMAE exposures were 37% higher, but there were no clinically significant differences in exposures of tisotumab vedotin-tftv in patients with mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin of 1 to 1.5 X ULN and AST < ULN, or bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN) compared to patients with normal hepatic function. The effect of moderate or severe hepatic impairment (AST > 3 x ULN or total bilirubin > 1.5 x ULN) or liver transplantation on the pharmacokinetics of tisotumab vedotin-tftv or unconjugated MMAE is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
No clinical studies evaluating the drug-drug interaction potential of tisotumab vedotin-tftv have been conducted. To characterize the drug-drug interaction potential of unconjugated MMAE, clinical studies with another ADC that contains MMAE are described below, and similar effects on tisotumab vedotin-tftv and unconjugated MMAE exposures are expected with concomitant use of TIVDAK.
There were no clinically significant differences in midazolam (sensitive CYP3A4 substrate) pharmacokinetics when used concomitantly with another ADC that contains MMAE.
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Ketoconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) used concomitantly with another ADC that contains MMAE increased unconjugated MMAE Cmax by 25% and AUC by 34%, with no change in ADC exposure.
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Rifampin (strong CYP3A4 inducer) used concomitantly with another ADC that contains MMAE decreased unconjugated MMAE Cmax by 44% and AUC by 46%, with no change in ADC exposure.
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: MMAE does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6. MMAE did not induce any major CYP450 enzymes in human hepatocytes.
Transporter Systems: MMAE is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), but not an inhibitor of P-gp.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed with tisotumab vedotin-tftv or MMAE.
MMAE was positive for genotoxicity in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus study through an aneugenic mechanism. MMAE was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or the L5178 TK+/- mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay.
Fertility studies with tisotumab vedotin-tftv or MMAE have not been conducted. However, results of a repeat-dose toxicity study in monkeys indicate the potential for tisotumab vedotin-tftv to impair male reproductive function and fertility.
In a repeat-dose toxicology study conducted in monkeys for 13 weeks, doses ≥1 mg/kg tisotumab vedotin-tftv (≥0.6 times the human exposure [AUC] at the recommended dose) resulted in decreased testicular size and seminiferous tubule atrophy, reduction or absence in sperm count, and decreased sperm motility. Findings of sperm absence and decreased motility did not reverse by the end of the recovery period at doses ≥3 mg/kg (≥1.7 times the human exposure [AUC] at the recommended dose).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical Cancer
The efficacy of TIVDAK was evaluated in innovaTV 204 (NCT03438396), an open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial that treated 101 patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer who had received no more than two prior systemic regimens in the recurrent or metastatic setting, including at least one prior platinum-based chemotherapy regimen. Patients were excluded if they had active ocular surface disease, any prior episode of cicatricial conjunctivitis or Stevens Johnson syndrome, Grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy or known coagulation defects leading to an increased risk of bleeding.
Patients received TIVDAK 2 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Tumor response assessments were performed every 6 weeks for the first 30 weeks and every 12 weeks thereafter.
The median age was 50 years (range: 31 to 78); 95% were White, 2% were Asian, and 1% were Black. Six percent of patients were Hispanic or Latino. Sixty-eight percent of patients had squamous cell carcinoma, 27% had adenocarcinoma, and 5% had adenosquamous histology. ECOG performance status was 0 (58%) or 1 (42%). Seventy percent of patients had received 1 prior line of systemic therapy, and 30% had 2 prior lines of systemic therapy. Sixty-nine percent of patients previously received bevacizumab as part of their prior systemic therapy. Sixty-three percent received bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy (paclitaxel and cisplatin or carboplatin, or paclitaxel and topotecan) as first-line therapy.
The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed objective response rate (ORR) as assessed by an independent review committee (IRC) using RECIST v1.1 criteria and duration of response (DOR).
Efficacy results are presented in Table 7.
| 1 Based on patients (n=24) with a response by IRC CI: confidence interval NR: not reached |
|
| Endpoint | N=101 |
| Confirmed ORR (95% CI) | 24% (15.9, 33.3) |
| Complete response rate | 7% |
| Partial response rate | 17% |
| Duration of Response | |
| Median Duration of Response, months1 (95% CI) | 8.3 (4.2, NR) |
16. How is Tivdak supplied
How Supplied
TIVDAK (tisotumab vedotin-tftv) is supplied as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder in a 40 mg single-dose vial for reconstitution. TIVDAK vials are available in the following packages:
- Carton of one 40 mg single-dose vial [NDC 51144-003-01]
Storage
Store TIVDAK vials refrigerated at 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
Special Handling
TIVDAK is a hazardous drug. Follow special handling and disposal procedures.1
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Ocular Adverse Reactions
- Inform patients about the eye exam they will receive before treatment and prior to each dose.
- Inform patients that ocular adverse reactions may occur during treatment with TIVDAK and to contact their healthcare provider if they experience new or worsening ocular signs and symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Instruct patients to bring their eye drops to each infusion and advise on how to administer the eye drops throughout treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Inform patients to avoid wearing contact lenses during treatment unless directed by an eye care provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Peripheral Neuropathy
- Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider any numbness and tingling of the hands or feet or muscle weakness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hemorrhage
- Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider to seek immediate medical attention for signs or symptoms of unusual severe bleeding or hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pneumonitis
- Advise patients to immediately report new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
- Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including life-threatening and potentially fatal SJS, which include target lesions, worsening skin reactions, blistering or peeling of the skin, painful sores in mouth, nose, throat, or genital area, fever or flu-like symptoms, and swollen lymph nodes. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider to seek immediate medical attention for signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including SJS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 2 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
- Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TIVDAK and for 3 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured by:
Seagen Inc.
Bothell, WA 98021
1-855-4SEAGEN
Marketed by:
Seagen Inc.
Bothell, WA 98021
and
Genmab US, Inc.
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
U.S. License 2257
TIVDAK® is a trademark owned by Seagen Inc.
©2023 Seagen Inc. and Genmab US, Inc.
USPI-761208-v03
Medication Guide
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 7/2023 | |
| MEDICATION GUIDE TIVDAK (TIV-dack) (tisotumab vedotin-tftv) for injection, for intravenous use |
||
| What is the most important information I should know about TIVDAK? TIVDAK can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
| What is TIVDAK?
TIVDAK is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with cervical cancer:
|
||
| Before receiving TIVDAK, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||
|
||
| How will I receive TIVDAK? | ||
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of TIVDAK?
TIVDAK can cause serious side effects, including: |
||
|
||
|
|
|
| The most common side effects of TIVDAK include: | ||
|
|
|
| TIVDAK may cause fertility problems in males, which may affect your ability to father children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all the possible side effects of TIVDAK. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TIVDAK.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. If you would like more information about TIVDAK, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TIVDAK that is written for healthcare professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in TIVDAK?
Active ingredient: tisotumab vedotin-tftv Inactive ingredients: d-mannitol, l-histidine, l-histidine monohydrochloride, and sucrose. Manufactured by: Seagen Inc., Bothell, WA 98021, 1-855-4SEAGEN Marketed by: Seagen Inc., Bothell, WA 98021 and Genmab US, Inc., Plainsboro, NJ 08536 U.S. License 2257 TIVDAK® is a trademark owned by Seagen Inc. ©2023 Seagen Inc. and Genmab US, Inc. MG-761208-v03 For more information, go to www.tivdak.com or call 1-855-4SEAGEN |
||
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Rx Only
NDC 51144-003-01
tivdak®
(tisotumab vedotin-tftv)
for injection
40 mg/vial
CAUTION: Hazardous Agent
For intravenous infusion only
Must reconstitute and dilute before use
One single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.
Provide the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient
Seagen®
Genmab
Dosage:
See Prescribing Information.
Storage:
Store vial refrigerated at
2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) in
original carton to protect from
light. DO NOT FREEZE.
DO NOT SHAKE.
No U.S. Standard of Potency
U.S. License 2257
TIVDAK and the TIVDAK logo
are US registered trademarks
owned by Seagen Inc.
 Seagen is US registered
Seagen is US registered
trademark of Seagen Inc.
©2021 Seagen Inc. and Genmab.
All rights reserved.
Printed in USA
PRODUCT OF SWITZERLAND
Each vial contains 40 mg of
tisotumab vedotin-tftv.
No Preservative
After reconstitution with
4 mL of Sterile Water for
Injection, USP, the
concentration of TIVDAK
(tisotumab vedotin-tftv) is
10 mg/mL
Each mL of reconstituted
solution contains 10 mg of
tisotumab vedotin-tftv,
D-mannitol (30 mg),
L-histidine (2.11 mg),
L-histidine monojhydrochloride
(3.44 mg), and sucrose (30mg)
Mfg by:
Seagen Inc.
Bothell, WA 98021
For more information:
1-855-4SEAGEN
GTIN 00351144003014
1401 - 02
Rx Only
NDC 51144-003-01
tivdak®
(tisotumab vedotin-tftv)
for injection
40 mg/vial
For intravenous infusion only
Must reconstitute and dilute before use
Single-dose vial. Discard unused portion.
CAUTION: Hazardous Agent
Store at 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF)
Protect from light.
DO NOT FREEZE. DO NOT SHAKE.
Dosage: See Prescribing Information
Provide the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Mfg by: Seagen Inc. U.S. License 2257
PRODUCT OF SWITZERLAND
Seagen®
Genmab
1400-02

| TIVDAK
tisotumab vedotin injection, powder, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Seagen Inc. (028484371) |




