Drug Detail:Unituxin (Dinutuximab [ din-ue-tux-i-mab ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
UNITUXIN® (dinutuximab) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
WARNING: SERIOUS INFUSION REACTIONS AND NEUROTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Infusion Reactions: Life-threatening infusion adverse reactions occur with Unituxin. Administer required prehydration and premedication. Immediately interrupt for severe infusion reactions and permanently discontinue for anaphylaxis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Neurotoxicity: Unituxin causes severe neuropathic pain. Administer intravenous opioid prior to, during, and for 2 hours following completion of the Unituxin infusion. Severe peripheral sensory neuropathy ranged from 2% to 9% in patients with neuroblastoma. Severe peripheral motor neuropathy has also been reported. Discontinue for severe unresponsive pain, severe sensory neuropathy, and moderate to severe peripheral motor neuropathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Indications and Usage for Unituxin
Unituxin is a GD2-binding monoclonal antibody indicated, in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and 13-cis-retinoic acid (RA), for the treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma who achieve at least a partial response to prior first-line multiagent, multimodality therapy. (1)
Unituxin Dosage and Administration
- 17.5 mg/m2/day as a diluted intravenous infusion over 10 to 20 hours for 4 consecutive days for up to 5 cycles. (2.1, 2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 17.5 mg/5 mL (3.5 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
- History of anaphylaxis to dinutuximab. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Neurological Disorders of the Eye: Interrupt Unituxin for dilated pupil with sluggish light reflex or other visual disturbances and permanently discontinue Unituxin for recurrent eye disorders or loss of vision. (5.2)
- Prolonged Urinary Retention and Transverse Myelitis: Permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive care. (5.2)
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS): Permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive care for signs and symptoms of RPLS. (5.2)
- Capillary Leak Syndrome and Hypotension: Administer required prehydration and monitor patients closely during treatment. Depending upon severity, manage by interruption, infusion rate reduction, or permanent discontinuation. (5.3, 5.4)
- Infection: Interrupt until resolution of systemic infection. (5.5)
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Monitor peripheral blood counts during Unituxin therapy. (5.6)
- Electrolyte Abnormalities: Monitor serum electrolytes closely. (5.7)
- Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management. (5.8)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.9, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse drug reactions (≥25%) are pain, pyrexia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, infusion reactions, hypotension, hyponatremia, increased alanine aminotransferase, anemia, vomiting, diarrhea, hypokalemia, capillary leak syndrome, neutropenia, urticaria, hypoalbuminemia, increased aspartate aminotransferase, and hypocalcemia. (5, 6.1)
The most common serious adverse reactions (≥5%) are infections, infusion reactions, hypokalemia, hypotension, pain, fever, and capillary leak syndrome. (5, 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact United Therapeutics Corp. at 1-866-458-6479 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Unituxin
Unituxin (dinutuximab) is indicated, in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and 13-cis-retinoic acid (RA), for the treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma who achieve at least a partial response to prior first-line multiagent, multimodality therapy [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Unituxin Dosage and Administration
- Verify that patients have adequate hematologic, respiratory, hepatic, and renal function prior to initiating each course of Unituxin [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Administer required premedication and hydration prior to initiation of each Unituxin infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
2.1 Recommended Dose
- The recommended dose of Unituxin is 17.5 mg/m2/day administered as an intravenous infusion over 10 to 20 hours for 4 consecutive days for a maximum of 5 cycles (Table 1 and Table 2) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Studies (14)].
- Initiate at an infusion rate of 0.875 mg/m2/hour for 30 minutes. The infusion rate can be gradually increased as tolerated to a maximum rate of 1.75 mg/m2/hour. Follow dose modification instructions for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
| Cycle Day | 1 through 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 through 24* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Unituxin | X | X | X | X | ||
| Cycle Day | 1 through 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 through 32* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Unituxin | X | X | X | X | ||
2.3 Dosage Modifications
Manage adverse reactions by infusion interruption, infusion rate reduction, dose reduction, or permanent discontinuation of Unituxin (Table 3 and Table 4) [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Adverse Reactions (6), and Clinical Studies (14)].
| Grade 3 or 4 anaphylaxis |
| Grade 3 or 4 serum sickness |
| Grade 3 pain unresponsive to maximum supportive measures |
| Grade 4 sensory neuropathy or Grade 3 sensory neuropathy that interferes with daily activities for more than 2 weeks |
| Grade 2 or greater peripheral motor neuropathy |
| Urinary retention that persists following discontinuation of opioids |
| Transverse myelitis |
| Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) |
| Subtotal or total vision loss |
| Grade 4 hyponatremia despite appropriate fluid management |
|
|
| Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Mild to moderate adverse reactions, such as transient rash, fever, rigors, and localized urticaria, that respond promptly to symptomatic treatment | |
| Onset of reaction: | Reduce Unituxin infusion rate to 50% of the previous rate and monitor closely. |
| After resolution: | Gradually increase infusion rate up to a maximum rate of 1.75 mg/m2/hour. |
| Prolonged or severe adverse reactions, such as mild bronchospasm without other symptoms, or angioedema that does not affect the airway | |
| Onset of reaction: | Immediately interrupt Unituxin. |
| After resolution: | If signs and symptoms resolve rapidly, resume Unituxin at 50% of the previous rate and observe closely. |
| First recurrence: |
Discontinue Unituxin until the following day. If symptoms resolve and continued treatment is warranted, premedicate with hydrocortisone 1 mg/kg (maximum dose 50 mg) intravenously and administer Unituxin at a rate of 0.875 mg/m2/hour in an intensive care unit. |
| Second recurrence: | Permanently discontinue Unituxin. |
| Neurological disorders of the eye [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |
| Onset of reaction: | Discontinue Unituxin infusion until resolution. |
| After resolution: | Reduce the Unituxin dose by 50%. |
| First recurrence or if accompanied by visual impairment: | Permanently discontinue Unituxin. |
| Capillary leak syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Moderate to severe but not life-threatening capillary leak syndrome | |
| Onset of reaction: | Immediately interrupt Unituxin. |
| After resolution: | Resume Unituxin infusion at 50% of the previous rate. |
| Life-threatening capillary leak syndrome | |
| Onset of reaction: | Discontinue Unituxin for the current cycle. |
| After resolution: | In subsequent cycles, administer Unituxin at 50% of the previous rate. |
| First recurrence: | Permanently discontinue Unituxin. |
| Hypotension* requiring medical intervention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| Onset of reaction: | Interrupt Unituxin infusion. |
| After resolution: |
Resume Unituxin infusion at 50% of the previous rate. If blood pressure remains stable for at least 2 hours, increase the infusion rate as tolerated up to a maximum rate of 1.75 mg/m2/hour. |
| Severe systemic infection or sepsis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| Onset of reaction: | Discontinue Unituxin until resolution of infection, and then proceed with subsequent cycles of therapy. |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 17.5 mg/5 mL (3.5 mg/mL) as a clear and colorless to slightly opalescent solution in a single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
Unituxin is contraindicated in patients with a history of anaphylaxis to dinutuximab.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Infusion Reactions
Serious infusion reactions requiring urgent intervention, including blood pressure support, bronchodilator therapy, corticosteroids, infusion rate reduction, infusion interruption, or permanent discontinuation of Unituxin, included facial and upper airway edema, dyspnea, bronchospasm, stridor, urticaria, and hypotension. Infusion reactions generally occurred during or within 24 hours of completing the Unituxin infusion. Due to overlapping signs and symptoms, it was not possible to distinguish between infusion reactions and hypersensitivity reactions in some cases.
In Study 1, Severe (Grade 3 or 4) infusion reactions occurred in 35 (26%) patients in the Unituxin/13-cis-retinoic acid (RA) group compared to 1 (1%) patient receiving RA alone. Severe urticaria occurred in 17 (13%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group but did not occur in the RA group. Serious adverse reactions consistent with anaphylaxis and resulting in permanent discontinuation of Unituxin occurred in 2 (1%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group. Additionally, 1 (0.1%) patient had multiple cardiac arrests and died within 24 hours after having received Unituxin in Study 2.
Prior to each Unituxin dose, administer required intravenous hydration and premedication with antihistamines, analgesics, and antipyretics [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of infusion reactions during and for at least 4 hours following completion of each Unituxin infusion in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available.
For mild to moderate infusion reactions, such as transient rash, fever, rigors, and localized urticaria, that respond promptly to antihistamines or antipyretics, decrease the Unituxin infusion rate and monitor closely. Immediately interrupt or permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management for severe or prolonged infusion reactions. Permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management for life-threatening infusion reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Capillary Leak Syndrome
In Study 1, severe (Grade 3 to 5) capillary leak syndrome occurred in 31 (23%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group and in no patients treated with RA alone. Additionally, capillary leak syndrome was reported as a serious adverse reaction in 9 (6%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group and in no patients treated with RA alone. Immediately interrupt or discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management in patients with symptomatic or severe capillary leak syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Hypotension
In Study 1, severe (Grade 3 or 4) hypotension occurred in 22 (16%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group compared to no patients in the RA group.
Prior to each Unituxin infusion, administer required intravenous hydration. Closely monitor blood pressure during Unituxin treatment. Immediately interrupt or discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management in patients with symptomatic hypotension, systolic blood pressure (SBP) less than lower limit of normal for age, or SBP that is decreased by more than 15% compared to baseline [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
5.5 Infection
In Study 1, severe (Grade 3 or 4) bacteremia requiring intravenous antibiotics or other urgent intervention occurred in 17 (13%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group compared to 5 (5%) patients treated with RA alone. Sepsis occurred in 24 (18%) patients in the Unituxin/RA group and in 10 (9%) patients in the RA group.
Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of systemic infection and temporarily discontinue Unituxin in patients who develop systemic infection until resolution of the infection [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Bone Marrow Suppression
In Study 1, severe (Grade 3 or 4) thrombocytopenia (39% vs. 25%), anemia (34% vs. 16%), neutropenia (34% vs. 13%), and febrile neutropenia (4% vs. 0 patients) occurred more commonly in patients in the Unituxin/RA group compared to patients treated with RA alone. Monitor peripheral blood counts closely during therapy with Unituxin.
5.7 Electrolyte Abnormalities
In Study 1, electrolyte abnormalities occurring in at least 25% of patients who received Unituxin/RA included hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and hypocalcemia. Severe (Grade 3 or 4) hypokalemia and hyponatremia occurred in 37% and 23% of patients in the Unituxin/RA group, respectively, compared to 2% and 4% of patients in the RA group. In a study of a related anti-GD2 antibody conducted in 12 adult patients with metastatic melanoma, 2 (13%) patients developed syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion resulting in severe hyponatremia. Monitor serum electrolytes daily during therapy with Unituxin.
5.8 Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Hemolytic uremic syndrome in the absence of documented infection and resulting in renal insufficiency, electrolyte abnormalities, anemia, and hypertension occurred in 2 patients enrolled in Study 2 following receipt of the first cycle of Unituxin. Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome recurred following rechallenge with Unituxin in 1 patient. Permanently discontinue Unituxin and institute supportive management for signs of hemolytic uremic syndrome.
5.9 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, Unituxin may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment, and for 2 months after the last dose of Unituxin [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious Infusion Reactions [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neurotoxicity, including Pain, Peripheral Neuropathy, Neurological Disorders of the Eye, Prolonged Urinary Retention, Transverse Myelitis, and Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Capillary Leak Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Bone Marrow Suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Electrolyte Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to Unituxin at the recommended dose and schedule in 1021 patients with high-risk neuroblastoma enrolled in an open-label, randomized (Study 1), or single-arm clinical trials (Study 2 and Study 3). Prior to enrollment, patients received therapy consisting of induction combination chemotherapy, maximum feasible surgical resection, myeloablative consolidation chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant, and radiation therapy to residual soft tissue disease. Patients received Unituxin in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and 13-cis-retinoic acid (RA). Treatment commenced within 95 days post autologous stem cell transplant in Study 1, within 210 days of autologous stem cell transplant in Study 2, and within 110 days of autologous stem cell transplant in Study 3.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay.
Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Among the 418 patients who were treated with Unituxin in combination with GM-CSF, IL-2, and RA in Study 2, Study 3 and Study DIV-NB-201, 86 patients (20.6%) tested positive for anti-dinutuximab antibodies (ADA). Of the 86 ADA positive patients, 45 (52.3%) tested positive for neutralizing antibodies.
Among the 27 patients who were treated with Unituxin in combination with lenalidomide and isotretinoin in Study NANT 2011-04, 13 patients (48.1%) tested positive for ADA. Of the 13 ADA positive patients, 2 (15.4%) also tested positive for neutralizing antibodies.
The clearance of dinutuximab was 60% higher for the ADA positive patients than the ADA negative patients. The presence of ADA did not have a clinically significant effect on the incidence or severity of adverse reactions. There were insufficient number of patients with ADA to determine whether ADA alters the efficacy of Unituxin.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Unituxin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Neurotoxicity: prolonged urinary retention, transverse myelitis, and reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Unituxin as part of multi-agent, multimodality therapy have been established in pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma based on results of an open-label, randomized (1:1) trial conducted in 226 patients aged 11 months to 15 years (median age 3.8 years) (Study 1). Prior to enrollment, patients achieved at least a partial response to prior first-line therapy for high-risk neuroblastoma consisting of induction combination chemotherapy, maximum feasible surgical resection, myeloablative consolidation chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant, and received radiation therapy to residual soft tissue disease. Patients randomized to the Unituxin/13-cis-retinoic acid (RA) arm (Unituxin/RA) received up to 5 cycles of Unituxin in combination with alternating cycles of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) plus RA, followed by 1 cycle of RA alone. Patients randomized to the RA arm received up to 6 cycles of RA monotherapy. Study 1 demonstrated an improvement in event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients in the Unituxin/RA arm compared to those in the RA arm [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12), and Clinical Studies (14)].
11. Unituxin Description
Dinutuximab is a glycolipid disialoganglioside (GD2)-binding chimeric monoclonal antibody composed of murine variable heavy and light chain regions and the human constant region for the heavy chain IgG1 and light chain kappa. Dinutuximab is produced in the murine myeloma cell line, SP2/0 and has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa.
Unituxin (dinutuximab) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear and colorless to slightly opalescent solution for intravenous infusion. Unituxin is supplied in single-dose vials of 17.5 mg/5 mL. Each mL of solution contains 3.5 mg of dinutuximab, and histidine (3.10 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.55 mg), sodium chloride (8.77 mg), and Water for Injection, USP; hydrochloric acid is added to adjust pH to 6.8.
12. Unituxin - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dinutuximab binds to the glycolipid GD2. This glycolipid is expressed on neuroblastoma cells and on normal cells of neuroectodermal origin, including the central nervous system and peripheral nerves. Dinutuximab binds to cell surface GD2 and induces cell lysis of GD2-expressing cells through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of dinutuximab was evaluated by a population pharmacokinetic analysis in a clinical study of Unituxin in combination with GM-CSF, IL-2, and RA. In this study, 27 children with high-risk neuroblastoma (age: 3.9±1.9 years) received up to 5 cycles of Unituxin at 17.5 mg/m2/day as an intravenous infusion over 10 to 20 hours for 4 consecutive days every 28 days. The observed maximum plasma dinutuximab concentration (Cmax) was 11.5 mcg/mL (20%, coefficient of variation [CV]). The mean volume of distribution at steady state (Vdss) was 5.4 L (28%). The clearance was 0.21 L/day (62%) and increased with body size. The terminal half-life was 10 days (56%).
No formal pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No animal studies have been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of dinutuximab.
Dedicated studies examining the effects of dinutuximab on fertility in animals have not been conducted. No clear effects on reproductive organs were observed in general toxicology studies conducted in rats.
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and effectiveness of Unituxin was evaluated in a randomized, open-label, multicenter trial conducted in pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (Study 1). All patients had received prior therapy consisting of induction combination chemotherapy, maximum feasible surgical resection, myeloablative consolidation chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant, and radiation therapy to residual soft tissue disease. Patients were randomized between Day 50 and Day 77 post-autologous stem cell transplantation.
Patients were required to have achieved at least a partial response prior to autologous stem cell transplantation, have no evidence of disease progression following completion of front-line multi-modality therapy, have adequate pulmonary function (no dyspnea at rest and peripheral arterial oxygen saturation of at least 94% on room air), adequate hepatic function (total bilirubin <1.5× the upper limit of normal and ALT <5× the upper limit of normal), adequate cardiac function (shortening fraction of >30% by echocardiogram, or if shortening fraction abnormal, ejection fraction of 55% by gated radionuclide study), and adequate renal function (glomerular filtration rate at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2). Patients with systemic infections or a requirement for concomitant systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressant usage were not eligible for enrollment.
Patients randomized to the Unituxin/RA arm received up to 5 cycles of Unituxin (clinical trials material) in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (Table 8) or interleukin-2 (IL-2) (Table 9) plus 13-cis-retinoic acid (RA), followed by 1 cycle of RA alone. Patients randomized to the RA arm received 6 cycles of RA. Unituxin was administered at a dose of 17.5 mg/m2/day (equivalent to 25 mg/m2/day of clinical trials material) on 4 consecutive days. Patients in both treatment arms received 6 cycles of RA at a dose of 160 mg/m2/day orally (for patients weighing more than 12 kg) or 5.33 mg/kg/day (for patients weighing less than or equal to 12 kg) in 2 divided doses for 14 consecutive days.
| Cycle Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15-24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||
| GM-CSF* | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Unituxin† | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| RA‡ | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| Cycle Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12-14 | 15-28 | 29-32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||
| IL-2* | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Unituxin† | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| RA‡ | X | |||||||||||||
A total of 226 patients were randomized, 113 patients to each arm. In general, demographic and baseline tumor characteristics were similar across study arms. Across the study population, 60% were male, the median age was 3.8 years and 3% of patients were less than 1.5 years, 82% were White and 7% were Black. The majority (80%) of patients had International Neuroblastoma Staging System Stage 4 disease. Thirty-five percent of patients had a complete response, 43% had a very good partial response, and 23% had a partial response to therapy received prior to autologous stem cell transplant. Forty-six percent of patients had neuroblastoma that was not MYCN-amplified, 36% had tumors with known MYCN-amplification, and MYCN status was unknown or missing in 19% of patients. Forty-three percent of patients had hyperdiploid tumors, 36% had diploid tumors, and DNA ploidy status was unknown or missing in 21% of patients.
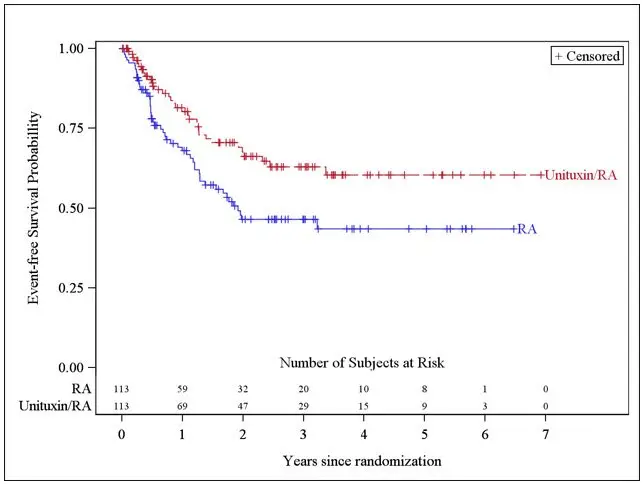
The major efficacy outcome measure was investigator-assessed event-free survival (EFS), defined as the time from randomization to the first occurrence of relapse, progressive disease, secondary malignancy, or death. Overall survival (OS) was also evaluated. After observing a numerical improvement in EFS based on the seventh interim analysis, the Data Monitoring Committee recommended termination of accrual. Efficacy results are shown in Table 10.
| Efficacy Parameter | Unituxin/RA arm n=113 | RA arm n=113 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| NR, not reached | |||
|
|||
| EFS | No. of Events (%) | 33 (29%) | 50 (44%) |
| Median (95% CI) (years) | NR (3.4, NR) | 1.9 (1.3, NR) | |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.57 (0.37, 0.89) | ||
| p-value (log-rank test)* | 0.01 | ||
| OS† | No. of Events (%) | 31 (27%) | 48 (42%) |
| Median (95% CI) (years) | NR (7.5, NR) | NR (3.9, NR) | |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.58 (0.37, 0.91) | ||
The Kaplan-Meier curve of EFS is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve of Event-Free Survival
16. How is Unituxin supplied
Unituxin (dinutuximab) injection as a clear and colorless to slightly opalescent solution is supplied in a carton containing one 17.5 mg/5 mL (3.5 mg/mL) single-dose vial.
NDC 66302-014-01
17. Patient Counseling Information
-
Serious Infusion Reactions
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of serious infusion reactions and anaphylaxis and to immediately report any signs or symptoms, such as facial or lip swelling, urticaria, difficulty breathing, lightheadedness, or dizziness that occur during or within 24 hours following the infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. -
Pain, Peripheral Neuropathy, Prolonged Urinary Retention, and Transverse Myelitis
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of severe pain, sensory and motor neuropathy, prolonged urinary retention, and transverse myelitis, and to promptly report severe or worsening pain and signs and symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, burning, weakness, or inability to urinate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. -
Neurological Disorders of the Eye
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of neurological disorders of the eye and to promptly report signs or symptoms, such as blurred vision, photophobia, ptosis, diplopia, or unequal pupil size [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. -
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of RPLS and to immediately report signs or symptoms, such as severe headache, hypertension, visual changes, lethargy, or seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. -
Capillary Leak Syndrome
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of capillary leak syndrome and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. -
Hypotension
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hypotension during the infusion and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. -
Infection
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of infection following treatment and to immediately report any signs or symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. -
Bone Marrow Suppression
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of bone marrow suppression, and to promptly report signs or symptoms of anemia, thrombocytopenia, or infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. -
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of electrolyte abnormalities, including hypokalemia, hyponatremia, and hypocalcemia, and to report any signs or symptoms, such as seizures, heart palpitations, and muscle cramping [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. -
Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hemolytic uremic syndrome and to report any signs or symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, fainting, pallor, edema, decreased urine output, or hematuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. -
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise women of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus if administered during pregnancy and the need for use of effective contraception during and for at least 2 months after completing therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
| UNITUXIN
dinutuximab injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - United Therapeutics Corporation (965460025) |





