Drug Detail:Belladonna and opium (rectal) (Belladonna and opium (rectal) [ bel-a-don-a-and-oh-pee-um ])
Drug Class: Narcotic analgesic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BELLADONNA and OPIUM suppositories, for rectal use, CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1938
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
• Belladonna and opium suppositories expose users to risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess patient’s risk before prescribing and monitor regularly for these behaviors or conditions. (5.1)
• Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur. Monitor closely, especially upon initiation or following a dose increase. (5.2)
• Accidental exposure of belladonna and opium suppositories, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of opium. (5.2)
• Prolonged use of belladonna and opium suppositories during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. If prolonged opioid use is required in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available. (5.3)
• Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate; limit dosages and durations to the minimum required; and follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. (5.4, 7)
Recent Major Changes
Dosage and Administration (2.2) 04/2023
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4) 04/2023
Indications and Usage for Belladonna and Opium Suppository
Belladonna and opium suppositories are an opioid agonist indicated for the management of ureteral spasm pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate. (1)
Limitations of Use (1)
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, reserve belladonna and opium suppositories for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options (e.g., non-opioid analgesics or opioid combination products):
- •
- Have not been tolerated, or are not expected to be tolerated,
- •
- Have not provided adequate analgesia, or are not expected to provide adequate analgesia
Belladonna and Opium Suppository Dosage and Administration
- •
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. (2.1)
- •
- Individualize dosing based on the severity of pain, patient response, and prior analgesic experience, and risk factor for addiction, abuse, and misuse. (2.1)
- •
- Discuss availability of naloxone with the patient and caregiver and assess each patient's need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with belladonna and opium suppositories. Consider prescribing naloxone based on the patient's risk factors for overdose. (2.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.4)
- •
- Initiate dosing with one suppository once or twice daily as needed for pain. (2.3)
- •
- Do not abruptly discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories in a physically-dependent patient because rapid discontinuation of opioid analgesics has resulted in serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Suppositories: (3)
- •
- Belladonna 16.2 mg and opium 30 mg
- •
- Belladonna 16.2 mg and opium 60 mg
Contraindications
- •
- Significant respiratory depression. (4)
- •
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in absence of resuscitative equipment. (4)
- •
- Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use of MAOIs within the last 14 days. (4)
- •
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus. (4)
- •
- Known hypersensitivity to opium or belladonna. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- •
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Monitor closely, particularly during initiation and titration. (5.5)
- •
- Adrenal Insufficiency: If diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids, and wean patient off of the opioid. (5.7)
- •
- Severe Hypotension: Monitor during dosage initiation and titration. Avoid use of belladonna and opium suppositories in patients with circulatory shock. (5.8)
- •
- Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness: Monitor for sedation and respiratory depression. Avoid use of belladonna and opium suppositories in patients with impaired consciousness or coma. (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions are drowsiness, dry mouth, urinary retention, photophobia, rapid pulse, dizziness and blurred vision, constipation, nausea and vomiting. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Padagis® at 1-866-634-9120 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- •
- Serotonergic Drugs: Concomitant use may result in serotonin syndrome. Discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories if serotonin syndrome is suspected. (7)
- •
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Can potentiate the effects of opium. Avoid concomitant use in patients receiving MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping treatment with an MAOI. (7)
- •
- Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics: Avoid use with belladonna and opium suppositories because they may reduce analgesic effect of belladonna and opium suppositories or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2023
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Belladonna and opium suppositories expose patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess each patient’s risk prior to prescribing belladonna and opium suppositories, and monitor all patients regularly for the development of these behaviors or conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of belladonna and opium suppositories. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of belladonna and opium suppositories or following a dose increase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Accidental Exposure
Accidental exposure of even one dose of belladonna and opium suppositories, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of opium [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of belladonna and opium suppositories during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Risks From Concomitant Use With Benzodiazepines Or Other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7)].
• Reserve concomitant prescribing of belladonna and opium suppositories and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
• Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required.
• Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
1. Indications and Usage for Belladonna and Opium Suppository
Belladonna and opium suppositories are indicated for the management of ureteral spasm pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate.
Limitations of Use
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], reserve belladonna and opium suppositories for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options [e.g., non-opioid analgesics or opioid combination products]:
- •
- Have not been tolerated, or are not expected to be tolerated,
- •
- Have not provided adequate analgesia, or are not expected to provide adequate analgesia
2. Belladonna and Opium Suppository Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Initiate the dosing regimen for each patient individually, taking into account the patient's severity of pain, patient response, prior analgesic treatment experience, and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24-72 hours of initiating therapy and following dosage increases with belladonna and opium suppositories and adjust the dosage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver and assess the potential need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with belladonna and opium suppositories [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program).
Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient's risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose. The presence of risk factors for overdose should not prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4)].
Consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or overdose.
2.3 Dosing
One belladonna and opium suppository rectally once or twice daily, not to exceed four doses daily or as recommended by the physician. Moisten finger and suppository with water before inserting. Absorption is dependent on body hydration and not on body temperature. Not recommended for use in children 12 years of age and under.
Conversion from Other Opioids to Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
There is inter-patient variability in the potency of opioid drugs and opioid formulations. Therefore, a conservative approach is advised when determining the total daily dosage of belladonna and opium suppositories. It is safer to underestimate a patient’s 24-hour belladonna and opium suppositories dosage than to overestimate the 24-hour belladonna and opium suppositories dosage and manage an adverse reaction due to overdose.
Conversion from Belladonna and Opium suppositories to Extended-Release Opioid
The relative bioavailability of belladonna and opium suppositories compared to extended-release opioid is unknown, so conversion to extended-release drug product must be accompanied by close observation for signs of excessive sedation and respiratory depression.
2.4 Maintenance of Therapy
Continually reevaluate patients receiving belladonna and opium suppositories to assess the maintenance of pain control and the relative incidence of adverse reactions, as well as monitoring for the development of addiction, abuse, or misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Frequent communication is important among the prescriber, other members of the healthcare team, the patient, and the caregiver/family during periods of changing analgesic requirements, including initial titration.
If the level of pain increases after dosage stabilization, attempt to identify the source of increased pain before increasing the belladonna and opium suppositories dosage. If unacceptable opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, consider reducing the dosage. Adjust the dosage to obtain an appropriate balance between management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions.
2.5 Safe Reduction or Discontinuation of Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
Do not abruptly discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories in patients who may be physically dependent on opioids. Rapid discontinuation of opioid analgesics in patients who are physically dependent on opioids has resulted in serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug seeking for abuse. Patients may also attempt to treat their pain or withdrawal symptoms with illicit opioids, such as heroin, and other substances.
When a decision has been made to decrease the dose or discontinue therapy in an opioid dependent patient taking belladonna and opium suppositories, there are a variety of factors that should be considered, including the dose of belladonna and opium suppositories the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, the type of pain being treated, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. It is important to ensure ongoing care of the patient and to agree on an appropriate tapering schedule and follow-up plan so that patient and provider goals and expectations are clear and realistic. When opioid analgesics are being discontinued due to a suspected substance use disorder, evaluate and treat the patient, or refer for evaluation and treatment of the substance use disorder. Treatment should include evidence-based approaches, such as medication assisted treatment of opioid use disorder. Complex patients with co-morbid pain and substance use disorders may benefit from referral to a specialist.
There are no standard opioid tapering schedules that are suitable for all patients. Good clinical practice dictates a patient-specific plan to taper the dose of the opioid gradually. For patients on belladonna and opium suppositories who are physically opioid-dependent, initiate the taper by a small enough increment (e.g., no greater than 10% to 25% of the total daily dose) to avoid withdrawal symptoms, and proceed with dose-lowering at an interval of every 2 to 4 weeks. Patients who have been taking opioids for briefer periods of time may tolerate a more rapid taper. It may be necessary to provide the patient with lower dosage strengths to accomplish a successful taper. Reassess the patient frequently to manage pain and withdrawal symptoms, should they emerge. Common withdrawal symptoms include restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate. If withdrawal symptoms arise, it may be necessary to pause the taper for a period of time or raise the dose of the opioid analgesic to the previous dose, and then proceed with a slower taper. In addition, monitor patients for any changes in mood, emergence of suicidal thoughts, or use of other substances.
When managing patients taking opioid analgesics, particularly those who have been treated for a long duration and/or with high doses for chronic pain, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper. A multimodal approach to pain management may optimize the treatment of chronic pain, as well as assist with the successful tapering of the opioid analgesic [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Belladonna and Opium Suppositories are available in two strengths.
- •
- Belladonna 16.2 mg and opium 30 mg
- •
- Belladonna 16.2 mg and opium 60 mg
4. Contraindications
- Belladonna and opium suppositories are contraindicated in patients with:
- •
- Significant respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use of MAOIs within the last 14 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Drug Interactions (7)]
- •
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- •
- Hypersensitivity to opium or belladonna [see Adverse Events (6)]
- •
- Glaucoma2
- •
- Severe hepatic or renal disease2
- •
- Narcotic idiosyncrasies2
- •
- Convulsive disorders2
- •
- Acute alcoholism2
- •
- Delirium tremens2
- •
- Premature labor2
5. Warnings and Precautions
These preparations are not recommended for use in children.
5.1 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Belladonna and opium suppositories contains opium, a Schedule II controlled substance. As an opioid, belladonna and opium suppositories expose users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed belladonna and opium suppositories. Addiction can occur at recommended dosages and if the drug is misused or abused.
Assess each patient’s risk for opioid addiction, abuse, or misuse prior to prescribing belladonna and opium suppositories, and monitor all patients receiving belladonna and opium suppositories for the development of these behaviors or conditions. Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). The potential for these risks should not, however, prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Patients at increased risk may be prescribed opioids such as belladonna and opium suppositories, but use in such patients necessitates intensive counseling about the risks and proper use of belladonna and opium suppositories along with intensive monitoring for signs of addiction, abuse, and misuse. Consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing belladonna and opium suppositories. Strategies to reduce these risks include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the proper disposal of unused drug [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status [see Overdosage (10)]. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of belladonna and opium suppositories, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dosage increase. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24-72 hours of initiating therapy with and following dosage increases of belladonna and opium suppositories.
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing of belladonna and opium suppositories is essential [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Overestimating the belladonna and opium suppositories dosage when converting patients from another opioid product can result in a fatal overdose with the first dose.
Accidental exposure of even one dose of belladonna and opium suppositories, especially by children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of opium.
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Opioids can cause sleep-related breathing disorders including central sleep apnea (CSA) and sleep-related hypoxemia. Opioid use increases the risk of CSA in a dose-dependent fashion. In patients who present with CSA, consider decreasing the opioid dosage using best practices for opioid taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver and assess the potential need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with belladonna and opium suppositories. Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program). Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help, even if naloxone is administered [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient's risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose. The presence of risk factors for overdose should not prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Also consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or overdose. If naloxone is prescribed, educate patients and caregivers on how to treat with naloxone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.3 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of belladonna and opium suppositories during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. Advise pregnant women using opioids for a prolonged period of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.4 Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of belladonna and opium suppositories with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioid analgesics alone. Because of similar pharmacological properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with the concomitant use of other CNS depressant drugs with opioid analgesics [see Drug Interactions (7)].
If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant than indicated in the absence of an opioid, and titrate based on clinical response. If an opioid analgesic is initiated in a patient already taking a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid analgesic, and titrate based on clinical response. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when belladonna and opium suppositories are used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol and illicit drugs). Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant have been determined. Screen patients for risk of substance use disorders, including opioid abuse and misuse, and warn them of the risk for overdose and death associated with the use of additional CNS depressants including alcohol and illicit drugs [see Drug Interactions (7) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.5 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients
The use of belladonna and opium suppositories in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment is contraindicated.
Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease: Belladonna and opium suppositories-treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and those with a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression are at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive including apnea, even at recommended dosages of belladonna and opium suppositories [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Elderly, Cachetic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients because they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating belladonna and opium suppositories and when belladonna and opium suppositories is given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Alternatively, consider the use of non-opioid analgesics in these patients.
5.6 Interactions with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may potentiate the effects of opioids, including respiratory depression, coma, and confusion. Belladonna and opium suppositories should not be used in patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment.
5.7 Adrenal Insufficiency
Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
5.8 Severe Hypotension
Belladonna and opium suppositories may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dosage of belladonna and opium suppositories. In patients with circulatory shock, belladonna and opium suppositories may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of belladonna and opium suppositories in patients with circulatory shock.
5.9 Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness
In patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors), belladonna and opium suppositories may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with belladonna and opium suppositories.
Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of belladonna and opium suppositories in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
5.10 Risks of Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
Belladonna and opium suppositories are contraindicated in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus.
The opium in belladonna and opium suppositories may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Opioids may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms.
5.11 Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorders
The opium in belladonna and opium suppositories may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders, and may increase the risk of seizures occurring in other clinical settings associated with seizures. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during belladonna and opium suppositories therapy.
5.12 Withdrawal
Do not abruptly discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories in a patient physically dependent on opioids. When discontinuing belladonna and opium suppositories in a physically dependent patient, gradually taper the dosage. Rapid tapering of opium in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to a withdrawal syndrome and return of pain [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
Additionally, avoid the use of mixed agonist/antagonist (e.g., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) or partial agonist (e.g., buprenorphine) analgesics in patients who are receiving a full opioid agonist analgesic, including belladonna and opium suppositories. In these patients, mixed agonist/antagonist and partial agonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.13 Risks of Driving and Operating Machinery
Belladonna and opium suppositories may impair the mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to the effects of belladonna and opium suppositories and know how they will react to the medication.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Belladonna may cause drowsiness, dry mouth, urinary retention, photophobia, rapid pulse, dizziness and blurred vision7. Opium usage may result in constipation, nausea or vomiting. Pruritis and urticaria may occasionally occur. Hypersensitivity to opium or belladonna may occur.
The following serious adverse reactions are described, or described in greater detail, in other sections:
- •
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- •
- Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other CNS Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Adrenal Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- •
- Severe Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- •
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- •
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- •
- Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of opioids. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Serotonin syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs.
Adrenal insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use.
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis has been reported with products containing opioids.
Androgen deficiency: Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with chronic use of opioids.
7. Drug Interactions
Table 1 includes clinically significant drug interactions with belladonna and opium suppositories.
Table 1: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
|
Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Due to additive pharmacologic effect, the concomitant use of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, can increase the risk of hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. |
|
Intervention: |
Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients closely for signs of respiratory depression and sedation. If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4)]. |
|
Examples: |
Benzodiazepines and other sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol. |
|
Serotonergic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. Discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
|
Examples: |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that effect the serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). |
|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome or opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] If urgent use of an opioid is necessary, use test doses and frequent titration of small doses to treat pain while closely monitoring blood pressure and signs and symptoms of CNS and respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
The use of belladonna and opium suppositories is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. |
|
Examples: |
phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid |
|
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
May reduce the analgesic effect of belladonna and opium suppositories and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. |
|
Intervention: |
Avoid concomitant use. |
|
Examples: |
butorphanol, nalbuphine, pentazocine, buprenorphine |
|
Muscle Relaxants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Opium may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected and decrease the dosage of belladonna and opium suppositories and/or the muscle relaxant as necessary. Due to the risk of respiratory depression with concomitant use of skeletal muscle relaxants and opioids, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)]. |
|
Diuretics |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic as needed. |
|
Anticholinergic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs may increase risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when belladonna and opium suppositories are used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy may cause neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome. There are no available data with belladonna and opium suppositories in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy for medical or nonmedical purposes can result in physical dependence in the neonate and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome shortly after birth.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration, and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome vary based on the specific opioid used, duration of use, timing and amount of last maternal use, and rate of elimination of the drug by the newborn. Observe newborns for symptoms of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Belladonna refers to plant alkaloids that contain anticholinergic agents such as atropine. Atropine used in human pregnancies has not been associated with birth defects or adverse fetal effects although the drug readily crosses the placenta. Use during pregnancy may increase risk of respiratory abnormalities, hypospadias, and eye or ear malformations but causal relationship is unclear. The Collaborative Perinatal Project found no relationship between first trimester use of atropine and birth defects in the offspring but found an increase in birth defects in general in the offspring of pregnancies where the mother had taken belladonna. There was no relationship to any particular syndrome of anomalies. A statistically significant (although weak) association was discovered between congenital anomalies and maternal use of belladonna. A study was conducted based on the infants of 554 women who took belladonna during the first four months of pregnancy. The study was conducted in the Collaborative Perinatal Project and showed that belladonna is unlikely to cause minor congenital abnormalities. The estimated maximum risk is most likely less than 3% if maternal belladonna is used early in pregnancy.1
Labor or Delivery
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression and psycho-physiologic effects in neonates. An opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, must be available for reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the neonate. Belladonna and opium suppositories is not recommended for use in pregnant women during or immediately prior to labor, when other analgesic techniques are more appropriate. Opioid analgesics, including belladonna and opium suppositories, can prolong labor through actions which temporarily reduce the strength, duration, and frequency of uterine contractions. However, this effect is not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilation, which tends to shorten labor. Monitor neonates exposed to opioid analgesics during labor for signs of excess sedation and respiratory depression.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for belladonna and opium suppositories and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from belladonna and opium suppositories or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to belladonna and opium suppositories through breast milk should be monitored for excess sedation and respiratory depression. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of an opioid analgesic is stopped, or when breast-feeding is stopped.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Chronic use of opioids may cause reduced fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of belladonna and opium suppositories in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients (aged 65 years or older) may have increased sensitivity to belladonna and opium. In general, use caution when selecting a dosage for an elderly patient, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Respiratory depression is the chief risk for elderly patients treated with opioids, and has occurred after large initial doses were administered to patients who were not opioid-tolerant or when opioids were co-administered with other agents that depress respiration. Titrate the dosage of belladonna and opium suppositories slowly in geriatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
Belladonna and opium suppositories contains opium, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Belladonna and opium suppositories contains opium, a substance with a high potential for abuse similar to other opioids including fentanyl, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone, oxymorphone, and tapentadol. Belladonna and opium suppositories can be abused and is subject to misuse, addiction, and criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
All patients treated with opioids require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, since use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use.
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and includes: a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes a physical withdrawal.
“Drug-seeking” behavior is very common in persons with substance use disorders. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing, or referral, repeated “loss” of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating health care provider(s). “Doctor shopping” (visiting multiple prescribers) to obtain additional prescriptions is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Health care providers should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
Belladonna and opium suppositories, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Risks Specific to Abuse of Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
Belladonna and opium suppositories are for rectal use only. Abuse of belladonna and opium suppositories poses a risk of overdose and death. The risk is increased with concurrent abuse of belladonna and opium suppositories with alcohol and other central nervous system depressants.
Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during chronic opioid therapy. Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs, and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Physical dependence results in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dosage reduction of a drug. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity (e.g., naloxone, nalmefene), mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine), or partial agonists (buprenorphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued opioid usage.
Belladonna and opium suppositories should not be abruptly discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. If belladonna and opium suppositories is abruptly discontinued in a physically-dependent patient, a withdrawal syndrome may occur. Some or all of the following can characterize this syndrome: restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including: irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
Do not abruptly discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories in a patient physically dependent on opioids. Rapid tapering of belladonna and opium suppositories in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug-seeking for abuse.
When discontinuing belladonna and opium suppositories, gradually taper the dosage using a patient-specific plan that considers the following: the dose of belladonna and opium suppositories the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. To improve the likelihood of a successful taper and minimize withdrawal symptoms, it is important that the opioid tapering schedule is agreed upon by the patient. In patients taking opioids for a long duration at high doses, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal signs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
10. Overdosage
Clinical Presentation
Acute overdose with belladonna and opium suppositories can be manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, hypotension, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, and death. Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with hypoxia in overdose situations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
Treatment of Overdose
In case of overdose, priorities are the reestablishment of a patent and protected airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation, if needed. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen and vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life-support techniques.
Opioid antagonists, such as naloxone or nalmefene, are specific antidotes to respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. For clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to opium overdose, administer an opioid antagonist.
Because the duration of opioid reversal is expected to be less than the duration of action of opium in belladonna and opium suppositories, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably re-established. If the response to an opioid antagonist is suboptimal or only brief in nature, administer additional antagonist as directed by the product’s prescribing information.
In an individual physically dependent on opioids, administration of the recommended usual dosage of the antagonist will precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome. The severity of the withdrawal symptoms experienced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. If a decision is made to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, administration of the antagonist should be initiated with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses of the antagonist.
11. Belladonna and Opium Suppository Description
Each belladonna and opium suppository contains (in a water-soluble base consisting of polyethylene glycol 400, 1450, 8000 and polysorbate 60):
Belladonna (16.2 mg) and Opium (30 mg):
Powdered belladonna extract 16.2 mg and powdered opium 30 mg.
Belladonna (16.2 mg) and Opium (60 mg):
Powdered belladonna extract 16.2 mg and powdered opium 60 mg.
This drug falls into the pharmacological/therapeutic class of narcotic analgesic/antispasmotic agents.
The pharmacologically active principles present in the belladonna extract component of belladonna and opium suppositories are:
Established Name: Atropine
Chemical Name: dl Tropyl Tropate
Established Name: Scopolamine
Chemical Name: dl Scopolamine
Opium contains more than twenty alkaloids, the principle ones being morphine (10%), narcotine (6%), papaverine (1%) and codeine (0.5%). The major pharmacologically active principle of the powdered opium component of belladonna and opium suppositories, however, is:
Name: Morphine
Chemical Name: 7, 8-Didehydro-4, 5-epoxy-17-Methyl-morphinan-3, 6-diol
12. Belladonna and Opium Suppository - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Belladonna/opium rectal suppository is a combination narcotic analgesic/antispasmodic agent. The belladonna extract component of the rectal suppository provides the active alkaloids atropine and scopolamine, while the opium component provides primarily morphine (among more than 20 alkaloids). The atropine alkaloid is parasympatholytic, exerting antispasmodic activity by relaxation of smooth muscle that is stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system. The atropine alkaloid is also the dl isomer of l-hyoscyamine and exerts the same pharmacologic activity; however, it exerts about one-half the activity peripherally as l-hyoscyamine. Atropine activity also counteracts morphine induced smooth muscle spasm without affecting the analgesia. The morphine alkaloid of opium exerts analgesic activity by increasing the pain threshold and decreasing the sensitivity to pain. The oxidative dealkylated nor-metabolites of morphine begin the analgesic process. Additionally, the side effect of euphoria may contribute to sense of pain relief.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Through its parasympatholytic action, atropine (belladonna) relaxes smooth muscle resulting from parasympathetic stimulation. It is the dl isomer of l-hyoscyamine and therefore exhibits the same clinical effects. It is, however, approximately one-half as active peripherally as l-hyoscyamine, the latter being the major active plant alkaloid. The dl isomer atropine is formed during the process of isolation of the belladonna extract.1
Morphine, the major active principle of powdered opium, is responsible for the action of powdered opium although the other alkaloids present also contribute to it. The sedative and analgesic action of morphine, the effect desired by inclusion in belladonna and opium suppositories of powdered opium, are thought to be due to the depressant effect on the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and medullary centers. In large doses, the opiates and their analogs also exhibit synaptic conduction in the spinothalamic tracts, depress the function of the reticular formation, the lemniscus and the thalamic relays, and inhibit spinal synaptic reflexes: but these inhibitor actions should not be elicited with therapeutic doses of the drug. Moderate doses of powdered opium should not alter the electroencephalogram.
The action of morphine consists mainly of a descending depression of the central nervous system. It exerts its analgesic action by increasing the pain threshold or the magnitude of stimulus required to evoke pain and by dulling the sensibility or reaction to pain. In addition to its action in abolishing pain, morphine induces a sense of well-being (euphoria) facilitating certain mental processes while retarding others.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Upon absorption of morphine, oxidative dealkylation to produce nor-compounds appears to be the first step in the reaction sequence which imparts analgesia. Morphine is conjugated in the liver to form the 3-glucuronide which passes into the bile and is reabsorbed and excreted in the urine. The atropine effect of the belladonna extract serves to eliminate morphine induced smooth muscle spasm without affecting the sedative analgesic action of powdered opium.1
15. References
1. Belladonna. DrugPoints Summary. Micromedex 2.0. Truven Health Analytics, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. Accessed October 2, 2017.
2. Olin BR. Drug Facts and Comparisons, 50th ed. Facts and Comparisons, St Louis, MO; 1999.
16. How is Belladonna and Opium Suppository supplied
Belladonna (16.2 mg) and Opium (30 mg) suppositories are brown, bullet shaped suppositories.
NDC 0574-7045-04: Carton of 4 suppositories
NDC 0574-7045-12: Carton of 12 suppositories
Belladonna (16.2 mg) and Opium (60 mg) suppositories are brown, bullet shaped suppositories.
NDC 0574-7040-04: Carton of 4 suppositories
NDC 0574-7040-12: Carton of 12 suppositories
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. DO NOT REFRIGERATE. PROTECT FROM MOISTURE DURING STORAGE.
Rx Only
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Storage and Disposal
Because of the risks associated with accidental ingestion, misuse, and abuse, advise patients to store belladonna and opium suppositories securely, out of sight and reach of children, and in a location not accessible by others, including visitors to the home [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)]. Inform patients that leaving belladonna and opium suppositories unsecured can pose a deadly risk to others in the home.
Advise patients and caregivers that when medicines are no longer needed, they should be disposed of promptly. Expired, unwanted, or unused belladonna and opium suppositories should be disposed of by flushing the unused medication down the toilet if a drug take-back option is not readily available. Inform patients that they can visit www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for a complete list of medicines recommended for disposal by flushing, as well as additional information on disposal of unused medicines.
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Inform patients that the use of belladonna and opium suppositories, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Instruct patients not to share belladonna and opium suppositories with others and to take steps to protect belladonna and opium suppositories from theft or misuse.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting belladonna and opium suppositories or when the dosage is increased, and that it can occur even at recommended dosages.
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss with the patient and caregiver the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, both when initiating and renewing treatment with belladonna and opium suppositories. Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an overdose. Explain to patients and caregivers that naloxone's effects are temporary, and that they must call 911 or get emergency medical help right away in all cases of known or suspected opioid overdose, even if naloxone is administered [see Overdosage (10)].
If naloxone is prescribed, also advise patients and caregivers:
-
- •
- How to treat with naloxone in the event of an opioid overdose
- •
- To tell family and friends about their naloxone and to keep it in a place where family and friends can access it in an emergency
- •
- To read the Patient Information (or other educational material) that will come with their naloxone. Emphasize the importance of doing this before an opioid emergency happens, so the patient and caregiver will know what to do.
Accidental Exposure
Inform patients that accidental exposure (including ingestion), especially by children, may result in respiratory depression or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other CNS Depressants
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if belladonna and opium suppositories are used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, and not to use these concomitantly unless supervised by a healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients that belladonna and opium suppositories could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare providers if they are taking, or plan to take serotonergic medications [see Drug Interactions (7)].
MAOI Interaction
Inform patients to avoid taking belladonna and opium suppositories while using any drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase. Patients should not start MAOIs while taking belladonna and opium suppositories [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Adrenal Insufficiency
Inform patients that belladonna and opium suppositories could cause adrenal insufficiency, a potentially life-threatening condition. Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Advise patients to seek medical attention if they experience a constellation of these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Important Administration Instructions
Instruct patients how to properly take belladonna and opium suppositories.
-
- •
- Advise patients not to adjust the dose of belladonna and opium suppositories without consulting with a physician or other healthcare professional.
Important Discontinuation Instructions
In order to avoid developing withdrawal symptoms, instruct patients not to discontinue belladonna and opium suppositories without first discussing a tapering plan with the prescriber [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Hypotension
Inform patients that belladonna and opium suppositories may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Anaphylaxis
Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in belladonna and opium suppositories. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Pregnancy
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that prolonged use of belladonna and opium suppositories during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that belladonna and opium suppositories can cause fetal harm and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise nursing mothers to monitor infants for increased sleepiness (more than usual), breathing difficulties, or limpness. Instruct nursing mothers to seek immediate medical care if they notice these signs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Inform patients that chronic use of opioids may cause reduced fertility. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Use in Specific Population (8.3)].
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery
Inform patients that belladonna and opium suppositories may impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating heavy machinery. Advise patients not to perform such tasks until they know how they will react to the medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Constipation
Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation, including management instructions and when to seek medical attention [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.padagis.com/medguide/BLOPB.
Manufactured by Padagis®
Minneapolis, MN 55427
www.padagis.com
Rev 04-23
4D800 RC PH4
2204541
Medication Guide
Medication Guide
Belladonna (bell ah DON ah) and Opium (OH pee um) Suppositories, CII
Belladonna and opium suppositories are:
- •
- A strong prescription pain medicine that contains an opioid (narcotic) that is used to manage ureteral spasm pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic, when other pain treatments such as non-opioid pain medicines do not treat your pain well enough or you cannot tolerate them.
- •
- An opioid pain medicine that can put you at risk for overdose and death. Even if you take your dose correctly as prescribed you are at risk for opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse that can lead to death.
Important information about belladonna and opium suppositories:
- •
- Get emergency help or call 911 right away if you take too much belladonna and opium suppositories (overdose). When you first start taking belladonna and opium suppositories, when your dose is changed, or if you take too much (overdose), serious or life-threatening breathing problems that can lead to death may occur. Talk to your healthcare provider about naloxone, a medicine for the emergency treatment of an opioid overdose.
- •
- Taking belladonna and opium suppositories with other opioid medicines, benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other central nervous system depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, decreased awareness, breathing problems, coma, and death.
- •
- Never give anyone else your belladonna and opium suppositories. They could die from taking them. Selling or giving away belladonna and opium suppositories is against the law.
- •
- Store belladonna and opium suppositories securely, out of sight and reach of children, and in a location not accessible by others, including visitors to the home.
Do not take belladonna and opium suppositories if you have:
- •
- severe asthma, trouble breathing, or other lung problems.
- •
- a bowel blockage or have narrowing of the stomach or intestines.
Before taking belladonna and opium suppositories, tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of:
- •
- head injury, seizures
- •
- liver, kidney, thyroid problems
- •
- problems urinating
- •
- pancreas or gallbladder problems
- •
- abuse of street or prescription drugs, alcohol addiction, opioid overdose, or mental health problems.
Tell your healthcare provider if you are:
- •
- pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Prolonged use of belladonna and opium suppositories during pregnancy can cause withdrawal symptoms in your newborn baby that could be life-threatening if not recognized and treated.
- •
- breastfeeding. Opium passes into breastmilk and may harm your baby.
- •
- living in a household where there are small children or someone who has abused street or prescription drugs.
- •
- taking prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. Taking belladonna and opium suppositories with certain other medicines can cause serious side effects that could lead to death.
When taking belladonna and opium suppositories:
- •
- Do not change your dose. Take belladonna and opium suppositories exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Use the lowest dose possible for the shortest time needed.
- •
- Do not take more than your prescribed dose. If you miss a dose, consult with your healthcare provider.
- •
- Call your healthcare provider if the dose you are taking does not control your pain.
- •
- If you have been taking belladonna and opium suppositories regularly, do not stop taking belladonna and opium suppositories without talking to your healthcare provider.
- •
- After you stop taking belladonna and opium suppositories, return unused suppositories to the pharmacy or deliver to an accredited disposal site. Visit www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for additional information on disposal of unused medicines.
- •
- Unwrap suppository, then moisten finger and suppository with water before inserting.
While taking belladonna and opium suppositories DO NOT:
- •
- Drive or operate heavy machinery, until you know how belladonna and opium suppositories affects you. Belladonna and opium suppositories can make you sleepy, dizzy, or lightheaded.
- •
- Drink alcohol or use prescription or over-the-counter medicines that contain alcohol. Using products containing alcohol during treatment with belladonna and opium suppositories may cause you to overdose and die.
The possible side effects of belladonna and opium suppositories:
- •
- Constipation, nausea, sleepiness, vomiting, tiredness, headache, dizziness, abdominal pain. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms and they are severe.
Get emergency medical help if you have:
- •
- Trouble breathing, shortness of breath, fast heartbeat, chest pain, swelling of your face, tongue, or throat, extreme drowsiness, light-headedness when changing positions, feeling faint, agitation, high body temperature, trouble walking, stiff muscles, or mental changes such as confusion.
These are not all the possible side effects of belladonna and opium suppositories. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. For more information go to dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
Manufactured by Padagis®
Minneapolis, MN 55427
www.padagis.com or call 1-866-634-9120
Rev 04/2023
4D800 RC MG1
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Belladonna and Opium Suppository 16.2 mg/30 mg
NDC 0574-7045-12
Rx Only
Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
16.2 mg/30 mg
CII
Each suppository contains: Powdered Opium 30 mg
(Warning – May be habit forming)
Powdered Belladonna Extract 16.2 mg
Print Medication Guides at: www.padagis.com/medguide/BLOPB
12 Suppositories
UNIT DOSE
FOR RECTAL USE ONLY
The following image is a placeholder representing the product identifier that is either affixed or imprinted on the drug package label during the packaging operation.
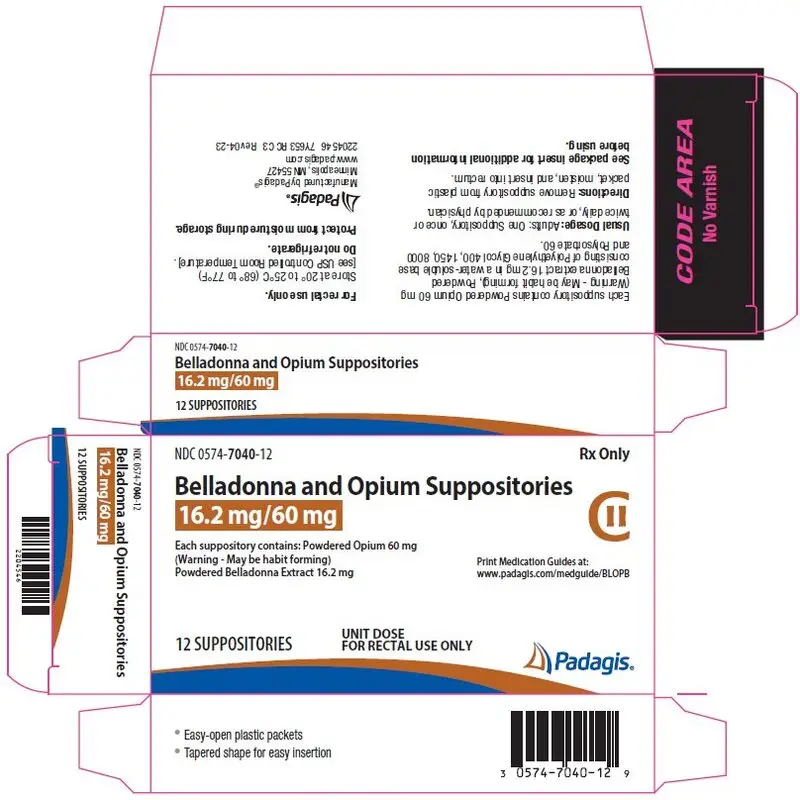
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Belladonna and Opium Suppository 16.2 mg/60 mg
0574-7040-12
Rx Only
Belladonna and Opium Suppositories
16.2 mg/60 mg
CII
Each suppository contains: Powdered Opium 60 mg
(Warning – May be habit forming)
Powdered Belladonna Extract 16.2 mg
Print Medication Guides at: www.padagis.com/medguide/BLOPB
12 Suppositories
UNIT DOSE
FOR RECTAL USE ONLY
The following image is a placeholder representing the product identifier that is either affixed or imprinted on the drug package label during the packaging operation.
| BELLADONNA AND OPIUM
atropa belladonna and opium suppository |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BELLADONNA AND OPIUM
atropa belladonna and opium suppository |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Padagis US LLC (967694121) |