Drug Class: Ophthalmic steroids with anti-infectives
Indications and Usage for Blephamide
BLEPHAMIDE® ophthalmic ointment is indicated for steroid-responsive inflammatory ocular conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and where superficial bacterial ocular infection or a risk of bacterial ocular infection exists.
Ocular corticosteroids are indicated in inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe where the inherent risk of corticosteroid use in certain infective conjunctivitides is accepted to obtain diminution in edema and inflammation. They are also indicated in chronic anterior uveitis and corneal injury from chemical, radiation or thermal burns or penetration of foreign bodies.
The use of a combination drug with an anti-infective component is indicated where the risk of superficial ocular infection is high or where there is an expectation that potentially dangerous numbers of bacteria will be present in the eye.
The particular antibacterial drug in this product is active against the following common bacterial eye pathogens: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus (viridans group), Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella species, and Enterobacter species.
The product does not provide adequate coverage against: Neisseria species, Pseudomonas species, and Serratia marcescens.
A significant percentage of staphylococcal isolates are completely resistant to sulfa drugs.
Warnings
NOT FOR INJECTION INTO THE EYE.
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in posterior subcapsular cataract formation and may increase intraocular pressure in susceptible individuals, resulting in ocular hypertension/glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision.
If the product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be routinely monitored even though it may be difficult in children and uncooperative patients. Corticosteroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. Intraocular pressure should be checked frequently.
The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation.
In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforation has been known to occur with the use of topical corticosteroids.
In acute purulent conditions of the eye, corticosteroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection.
The use of ocular corticosteroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). Employment of corticosteroid medication in the treatment of herpes simplex requires great caution.
Prolonged use of BLEPHAMIDE® ophthalmic ointment may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections.
Prolonged use of topical anti-bacterial agents may give rise to overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms including fungi.
A significant percentage of staphylococcal isolates are completely resistant to sulfonamides.
Acute anterior uveitis may occur in susceptible individuals, primarily Blacks.
Fatalities have occurred, although rarely, due to severe reactions to sulfonamides including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and other blood dyscrasias. Sensitization may recur when a sulfonamide is readministered, irrespective of the route of administration.
If signs of hypersensitivity, skin rash, or other serious reaction occur, discontinue use of this preparation. Cross-sensitivity among corticosteroids has been demonstrated (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). BLEPHAMIDE® ophthalmic ointment contains the preservative phenylmercuric acetate, which may cause allergic-type reactions in susceptible patients.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions have been identified during use of BLEPHAMIDE® ophthalmic ointment. Because reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions have occurred with corticosteroid/antibacterial combination drugs which can be attributed to the corticosteroid component, the antibacterial component, or the combination.
Reactions occurring with BLEPHAMIDE® ophthalmic ointment include: cataract, dizziness, eye discharge, eyelid edema, eyelid erythema, eye irritation, eye pain, eye pruritus, and hypersensitivity including rash, skin pruritus, urticaria, ocular hyperemia, and visual disturbance (blurry vision).
Reactions occurring most often from the presence of the antibacterial ingredient are allergic sensitizations. Fatalities have occurred, although rarely, due to severe reactions to sulfonamides including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and other blood dyscrasias (see WARNINGS).
The reactions due to the corticosteroid component in decreasing order of frequency are: delayed wound healing, elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) with possible development of glaucoma and infrequent optic nerve damage, and posterior subcapsular cataract formation.
Although systemic effects are extremely uncommon, there have been rare occurrences of systemic hypercorticoidism after use of topical corticosteroids.
Corticosteroid-containing preparations can also cause acute anterior uveitis or perforation of the globe. Mydriasis, loss of accommodation and ptosis have occasionally been reported following local use of corticosteroids.
Secondary Infection
The development of secondary infection has occurred after use of combinations containing corticosteroids and antibacterials. Fungal and viral infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term applications of corticosteroid. The possibility of fungal invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where corticosteroid treatment has been used.
Secondary bacterial ocular infection following suppression of host responses also occurs.
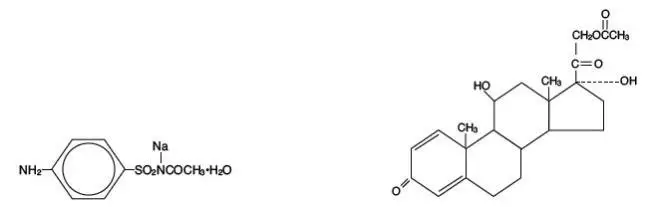
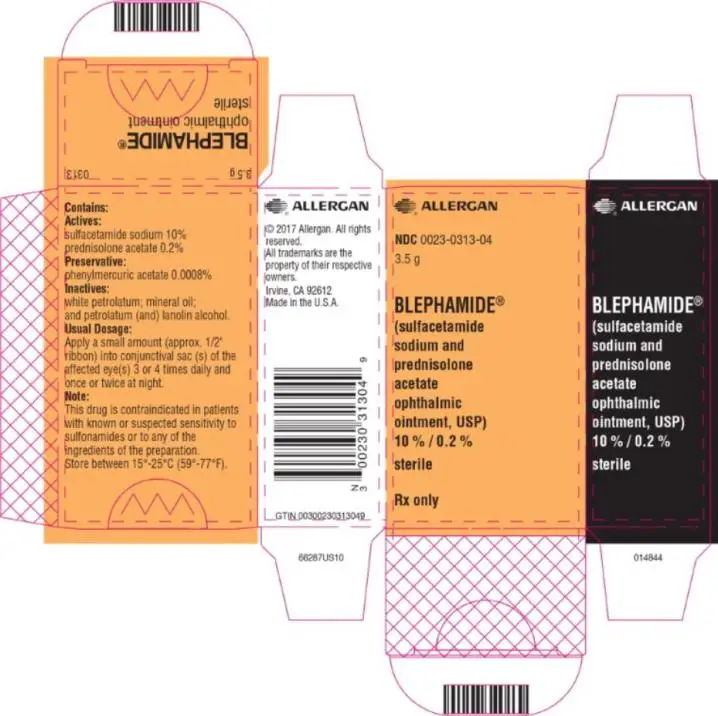
| BLEPHAMIDE
sulfacetamide sodium and prednisolone acetate ointment |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |