Drug Detail:Oravig (Miconazole oral (buccal) [ mye-kon-a-zole ])
Drug Class: Azole antifungals
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ORAVIG (miconazole) buccal tablets Initial U.S. Approval: January 1974
Indications and Usage for Oravig
ORAVIG is an azole antifungal indicated for the local treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis in adults. (1)
Oravig Dosage and Administration
- Application of one ORAVIG 50 mg buccal tablet to the gum region once daily for 14 consecutive days (2.1).
- Instruct patients not to crush, chew, or swallow tablets (2.2).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
50 mg buccal tablets (3)
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to miconazole, milk protein concentrate, or any other component of the product. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions: Anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients receiving miconazole. Discontinue ORAVIG immediately at the first sign of hypersensitivity (5.1). (5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) are: diarrhea, headache, nausea, dysgeusia, upper abdominal pain, and vomiting (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC Marietta, GA 30067 at 1-833-757-0904 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
Drug Interactions
Warfarin: Miconazole may enhance anticoagulant effect. Monitor prothrombin time, INR, and watch for bleeding (7.1). (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1).
- Pediatric Use: Safety and efficacy not established in patients less than 16 years of age (8.4).
See 12 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2021
Related/similar drugs
fluconazole, nystatin, clotrimazole, Diflucan, itraconazole, miconazoleFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Oravig
ORAVIG is indicated for the local treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) in adults.
2. Oravig Dosage and Administration
2.1 Basic Dosing Information
The recommended dosing schedule for ORAVIG is the application of one 50 mg buccal tablet to the upper gum region (canine fossa) once daily for 14 consecutive days.
2.2 Administration Instructions
ORAVIG should be applied in the morning, after brushing the teeth. The tablet should be applied with dry hands. The rounded side surface of the tablet should be placed against the upper gum just above the incisor tooth (canine fossa) and held in place with slight pressure over the upper lip for 30 seconds to ensure adhesion. The tablet is round on one side for comfort, but either side of the tablet can be applied to the gum.
Once applied, ORAVIG stays in position and gradually dissolves. [ See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] Subsequent applications of ORAVIG should be made to alternate sides of the mouth. Before applying the next tablet, the patient should clear away any remaining tablet material. In addition,
- ORAVIG should not be crushed, chewed or swallowed.
- Food and drink can be taken normally when ORAVIG is in place but chewing gum should be avoided.
- If ORAVIG does not adhere or falls off within the first 6 hours, the same tablet should be repositioned immediately. If the tablet still does not adhere, a new tablet should be placed.
- If ORAVIG is swallowed within the first 6 hours, the patient should drink a glass of water and a new tablet should be applied only once.
- If ORAVIG falls off or is swallowed after it was in place for 6 hours or more, a new tablet should not be applied until the next regularly scheduled dose. [ see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ORAVIG is a buccal tablet containing 50 mg of miconazole. ORAVIG tablets are round, off-white tablets, with a rounded side and a flat side. The tablets are marked with an “L” on the flat side.
4. Contraindications
ORAVIG is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis) to miconazole, milk protein concentrate, or any other component of the product.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and hypersensitivity, have been reported with the administration of miconazole products, including ORAVIG. Discontinue ORAVIG immediately at the first sign of hypersensitivity.
There is no information regarding cross-hypersensitivity between miconazole and other azole antifungal agents. Monitor patients with a history of hypersensitivity to azoles.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse drug reactions are discussed in detail in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The overall safety of ORAVIG was assessed in 480 adult subjects: 315 HIV-infected subjects, 147 subjects with head and neck cancer, and 18 healthy subjects.
HIV Infected Patients
Two trials were conducted in immunocompromised HIV-infected patients: one randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled design (N = 290 ORAVIG, 287 control) and one non-comparative trial (N = 25).
In the randomized, double blind trial (Study 1), 290 HIV infected subjects used ORAVIG once daily for 14 days, and 287 subjects used 10 mg clotrimazole troches five times daily for 14 days. Adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% of patients in either treatment are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Adverse Reactions (Treatment-Emergent) Occurring in ≥ 2% of HIV-Infected Patients in the Controlled Clinical Trial
| Adverse Reaction
(MedDRA v 9.1 System Organ Class and Preferred Term) | ORAVIG
N = 290 (%) | Clotrimazole troches
N = 287 (%) |
| Patients with any adverse reaction during the study
| 158 (54.5)
| 146 (50.9)
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Dry mouth Abdominal pain upper | 25.9
9.0 6.6 3.8 2.8 1.7 | 23.7
8.0 7.7 3.1 1.7 2.8 |
| Infections and infestations
Upper respiratory infection Gastroenteritis | 15.9
2.1 1.4 | 17.1
2.4 2.8 |
| Nervous system disorders
Headache Ageusia | 13.1
7.6 2.4 | 8.4
6.6 0.3 |
| Blood and lymphatic disorders
Anemia Lymphopenia Neutropenia | 6.9
2.8 1.7 0.7 | 8.4
1.7 2.1 2.1 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue Pain | 6.6
2.8 1.0 | 8.0
2.1 2.8 |
| Respiratory/thoracic
Cough Pharyngeal pain | 5.2
2.8 0.7 | 7.7
1.7 2.4 |
| Investigations
Increased GGT | 5.5
1.0 | 6.3
2.8 |
Overall local adverse reactions, including oral discomfort, oral burning, oral pain, gingival pain, gingival swelling, gingival pruritis, tongue ulceration, mouth ulceration, glossodynia, dry mouth, application site pain or discomfort, toothache, loss of taste, and altered taste, were reported by 35 (12.1%) patients who received miconazole buccal tablet compared to 27 (9.4%) patients who received clotrimazole troches.
Head and Neck Cancer Patients
In the randomized, open-label comparative trial of oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients with head and neck cancer who had received radiation therapy (Study 2), 147 patients used ORAVIG once daily for 14 days and 147 patients used 125 mg of miconazole oral gel four times daily for 14 days. Adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients in either arm are listed in Table 2.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions (Treatment-Emergent) Occurring in ≥ 2% of Patients with Head and Neck Cancer who had Received Radiation Therapy (Controlled Clinical Trial)
| Adverse Reaction
(MedDRA v 9.1 System Organ Class and Preferred Term) | ORAVIG
N = 147 (%) | Miconazole gel
N = 147 (%) |
| Patients with at least one adverse reaction
| 30 (20.4)
| 32 (21.8)
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders
Abdominal pain, upper Oral discomfort Nausea Vomiting Glossodynia | 8.8
1.4 2.7 0.7 0.7 0 | 13.6
2.0 2.7 2.7 2.0 2.0 |
| Nervous system disorders
Dysgeusia | 5.4
4.1 | 1.4
0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous
Pruritus | 3.4
2.0 | 0.7
0.7 |
Overall local adverse reactions, including oral discomfort, oral pain, dry mouth, glossodynia, loss of taste, altered taste, tongue ulceration, mouth ulceration, tooth disorder, and application site discomfort or pain, were experienced by 14 (9.5%) patients who used ORAVIG compared to 16 (10.9%) patients who used miconazole gel.
Overall ORAVIG Safety Experience In Patients and Healthy Subjects
Adverse reactions reported in the overall safety database of 480 subjects who received miconazole buccal tablet is listed in Table 3.
Table 3 Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 2% of Patients and Healthy Subjects who Received ORAVIG in Clinical Trials
| Adverse reaction
(MedDRA v 9.1 System Organ Class and Preferred Term) | ORAVIG
N = 480 (%) |
| Patients with at least one AE
| 209 (43.5)
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea Nausea Abdominal pain upper Vomiting | 20.6
6.0 4.6 2.5 2.5 |
| Infections and infestations
| 11.9
|
| Nervous system disorders
Headache Dysgeusia | 10.6
5.0 2.9 |
Discontinuation of ORAVIG due to adverse drug reactions occurred in 0.6% overall.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Warfarin
Concomitant administration of miconazole and warfarin has resulted in enhancement of anticoagulant effect. Cases of bleeding and bruising following the concomitant use of warfarin and topical, intravaginal, or oral miconazole were reported. Closely monitor prothrombin time, International Normalized Ratio (INR), or other suitable anticoagulation tests if ORAVIG is administered concomitantly with warfarin. Also monitor for evidence of bleeding.
7.2 Drugs Metabolized Through CYP 2C9 and 3A4
No formal drug interaction studies have been performed with ORAVIG. Miconazole is a known inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. Although the systemic absorption of miconazole following ORAVIG administration is minimal and plasma concentrations of miconazole are substantially lower than when given intravenously, the potential for interaction with drugs metabolized through CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 such as oral hypoglycemics, phenytoin, or ergot alkaloids cannot be ruled out.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal data, ORAVIG may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There are no available data on ORAVIG use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, prolonged gestation, dystocia and/or increased number of resorptions were observed after oral administration of miconazole nitrate during organogenesis to pregnant rats and rabbits. (See Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data:
Miconazole nitrate administered orally at doses of 80 mg/kg/day or higher to pregnant rats or rabbits crossed the placenta and resulted in embryo- and fetotoxicity, including increased fetal resorptions. These doses also resulted in prolonged gestation and dystocia in rats, but not in rabbits. Embryofetotoxicity was not observed in intravenous studies with miconazole at lower doses of 40 mg/kg/day in rats and 20 mg/kg/day in rabbits, which are approximately 8 times higher than the dose a patient would receive if she swallowed an ORAVIG buccal tablet, based on body surface area comparisons. Teratogenicity was not reported in any animal study with miconazole.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no available information on the presence of miconazole in human milk, or the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production following use of ORAVIG.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ORAVIG and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ORAVIG or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ORAVIG in pediatric patients below the age of 16 years have not been established. The ability of pediatric patients to comply with the application instructions has not been evaluated. Use in younger children is not recommended due to potential risk of choking.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ORAVIG did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
10. Overdosage
Overdose with miconazole in humans has not been reported in the literature.
Miconazole absorption and systemic exposure following application of ORAVIG are minimal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Symptomatic and supportive care is the basis for management.
11. Oravig Description
ORAVIG (miconazole) buccal tablets are applied topically to the gum once daily and release miconazole as the buccal tablet gradually dissolves [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
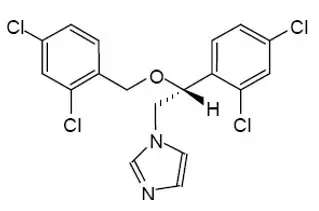
Miconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent and is described chemically as 1-[(2RS)-2-[(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)oxy]-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole with an empirical formula of C
18H
14Cl
4N
2O and a molecular weight of 416.13. The structural formula is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1:
Structural Formula of Miconazole
Miconazole drug substance is a white to almost white powder.
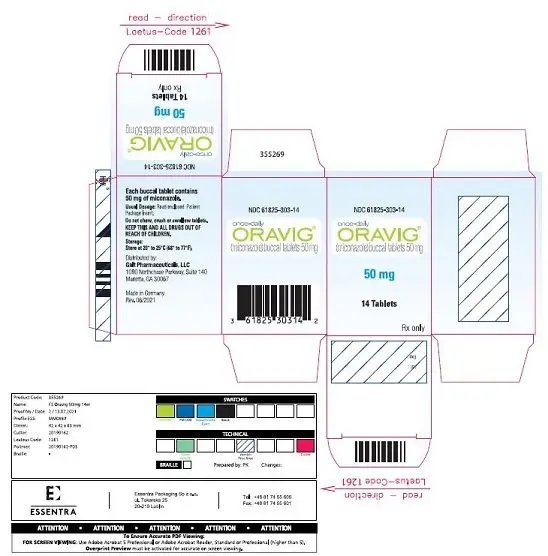
ORAVIG contains 50 mg of miconazole base, USP and the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, USP; milk protein concentrate; corn starch, NF; lactose monohydrate, NF; sodium lauryl sulfate, NF; magnesium stearate, NF; and talc, USP.
12. Oravig - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
Salivary
Single dose application of ORAVIG containing 50 mg of miconazole to the buccal mucosa of 18 healthy volunteers provided mean maximum salivary concentrations of 15 mcg/mL at 7 hours after application of the tablet. This provided an average saliva exposure to miconazole estimated from the AUC (0-24h) of 55.23 mcg·h/mL. The pharmacokinetic parameters of miconazole in the saliva of healthy volunteers are provided in Table 4.
Table 4: Pharmacokinetic (PK) Parameters of Miconazole in Saliva Following Application of a Single ORAVIG 50 mg Tablet in Healthy Volunteers (N = 18)
| Salivary PK Parameters (N = 18)
| Mean ±SD
(Min - Max) |
| AUC
0-24h (mcg-h/mL)
| 55.2 ±35.1
(0.5 – 128.3) |
| C
max (mcg/mL)
| 15.1 ±16.2
(0.5 – 64.8) |
| T
max (hour)
| 7*
(2.0 – 24.1) |
*Median
In healthy volunteers, the duration of buccal adhesion was on average 15 hours following a single dose application of ORAVIG 50 mg.
Plasma
Plasma concentrations of miconazole were below the lower limit of quantification (0.4 mcg/mL) in 157/162 (97%) samples from healthy volunteers following single-dose application of ORAVIG 50 mg. Measurable plasma concentrations ranged from 0.5 to 0.83 mcg/mL.
Plasma concentrations of miconazole evaluated after 7 days of treatment in 40 HIV-positive patients were all below the limit of quantification (0.1 mcg/mL).
Metabolism and Excretion
Most of the absorbed miconazole is metabolized by the liver with less than 1% of the administered dose found unchanged in urine. In healthy volunteers, the terminal half-life is 24 hours following systemic administration. There are no active metabolites of miconazole.
Food Effect
There was no formal food effect study conducted with ORAVIG; however, in clinical studies patients were allowed to eat and drink while taking ORAVIG.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Miconazole inhibits the enzyme cytochrome P450 14α-demethylase which leads to inhibition of ergosterol synthesis, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. Miconazole also affects the synthesis of triglycerides and fatty acids and inhibits oxidative and peroxidative enzymes, increasing the amount of reactive oxygen species within the cell.
Antimicrobial Activity
Miconazole is active against Candidaalbicans,C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis. Correlation between minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) results in vitro and clinical outcome has yet to be established.
Resistance
In vitro studies have shown that some Candida strains that demonstrate reduced susceptibility to one antifungal azole may also exhibit reduced susceptibility to other azoles suggesting cross-resistance.
Clinically relevant resistance to systemically utilized triazoles may occur in Candida species. Resistance may occur by multiple mechanisms such as changes in amino acids and/or in the regulation of the target enzyme and of a variety of efflux pump proteins. Multiple mechanisms may co‑exist in the same isolate. Resistance breakpoints, correlating in vitro activity with clinical efficacy, have not been established for miconazole.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with miconazole have not been conducted.
Miconazole nitrate was not genotoxic when tested in vitro in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus test. Intraperitoneal injections of miconazole to mice induced chromosomal aberrations in spermatocytes and bone marrow cells, and morphologic abnormalities in sperm at doses similar to or below clinical doses. However, no impairment of fertility was observed in intravenous studies with miconazole at 40 mg/kg/day in rats or 20 mg/kg/day in rabbits, which are approximately 8 times higher than the dose a patient would receive if she swallowed an ORAVIG buccal tablet, based on body surface area comparisons.
14. Clinical Studies
Study in HIV Infected Patients
The efficacy and safety of ORAVIG in the treatment of OPC was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, multicenter trial comparing ORAVIG 50 mg once daily for 14 consecutive days (n = 290) with clotrimazole troches 10 mg 5 times per day for 14 days (n = 287) in HIV-positive patients with OPC. Seventy-five percent of patients were not receiving highly active antiretroviral treatment, 5% had CD4+ cell count < 50 cells/mm 3, and 17% had a history of previous OPC. The mean viral load was 117,000 copies/mL. Patients were required to have symptoms and microbiological documentation of OPC for study entry. Most of the infections were caused by C. albicans (85%), followed by C. tropicalis (9%), and C. parapsilosis (3%). About 2% of the subjects were infected with more than one Candida species.
Clinical cure [defined as a complete resolution of both signs and symptoms of OPC at the test of cure (TOC) visit (days 17-22)], and clinical relapse by days 35-38 (21-24 days after end of therapy) are presented in Table 5. Mycological cure [defined as eradication (i.e., no yeast isolates) of Candida species] at the TOC visit (days 17-22) is also reported in the table.
Table 5: Clinical Cure and Mycological Cure at the TOC Visit and Relapse at Days 35-38 in HIV Infected Patients
|
| ORAVIG
50 mg N=290 a (%) | Clotrimazole
troches N=287 a (%) |
| Clinical cure†
| 176 (60.7%)
| 187 (65.2%)
|
| Clinical relapse‡
|
|
|
| Yes
b
| 48 (27.3%)
| 52 (27.8%)
|
| No
| 124 (70.5%)
| 133 (71.1%)
|
| Missing
| 4 (2.3%)
| 2 (1.1%)
|
| Mycological cure
| 79 (27.2%)
| 71 (24.7%)
|
a Analysis population includes all randomized patients who took at least 1 dose of study medication. One randomized subject excluded from the ORAVIG arm.
b In those subjects who relapsed, the mean time to relapse was 15.3 days (SD 4.6) and 15.7 days (SD 6.6), in the ORAVIG and Clotrimazole treatment arms, respectively.
† Difference in clinical cure rates (ORAVIG-clotrimazole troche) was -4.5%, with a 95% CI: (-12.4%, 3.4%).
‡ Percentage based on those who had clinical cure.
Study in Head and Neck Cancer Patients
The efficacy and safety of ORAVIG 50 mg was evaluated in an open-label, randomized, multicenter trial comparing ORAVIG 50 mg once daily for 14 days to miconazole oral gel 125 mg four times daily for 14 days in head and neck cancer patients who had received radiation therapy. Most of the infections were caused by C. albicans (71%), and C. tropicalis (8%). About 7% of the subjects were infected with more than one Candida species. Success rates of treatment at day 14 [defined as a complete (complete disappearance of candidiasis lesions) or partial response (improvement by at least 2 points of the score for extent of oral lesion compared with the score at day 1) based on a blind assessment] are shown in Table 6. Also reported in Table 6 are relapse rate at day 30, and mycologic cure assessed at day 14.
Table 6: Clinical Success and Mycological Cure at Day 14, in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer who had Received Radiation Therapy
|
| ORAVIG
50 mg N=148 a (%) | Miconazole oral gel
N=146 a (%) |
| Success rate (CR+PR)
b
| 79 (53.4%)
| 69 (46.6%)
|
| CR
†
| 74 (50.0%)
| 64 (43.8%)
|
| Clinical relapse‡
|
|
|
| Yes
c
| 14 (18.9%)
| 8 (12.5%)
|
| No
| 59 (79.7%)
| 56 (87.5%)
|
| Missing
| 1 (1.4%)
| 0
|
| Mycological cure
| 66 (44.6%)
| 78 (53.4%)
|
a Analysis population includes all subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. Reasons for not receiving treatment included negative mycological culture, informed consent withdrawn, or lost during screening. Six patients excluded per arm.
bCR: complete response; PR: partial response
cIn those subjects who relapsed, the mean time to relapse was 18.8 days (SD 16.3) and 20.6 days (SD 13.5), in the ORAVIG and Miconazole oral gel group, respectively.
†Difference in clinical complete response rates (ORAVIG-Miconazole oral gel) was 6.2%, with a 95% CI: (-5.2%, 17.6%).
‡Percentage based on those who had complete response.
16. How is Oravig supplied
ORAVIG 50 mg buccal tablets are supplied as off-white tablets containing 50 mg of miconazole. ORAVIG tablets have a rounded side and a flat side. ORAVIG tablets are packaged in bottles of 14 tablets (NDC 61825-303-14).
ORAVIG should be stored at 20 to 25 oC (68 to 77 oF) [see USP controlled room temperature]; excursions between 15 and 30 oC permitted at room temperature. Protect from moisture, and keep out of reach of children.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Important Administration Instructions
The tablet should be used immediately after removal from the bottle.
• Instruct patients not to crush, chew, or swallow the tablet.
• The rounded side of the tablet should be applied to the upper gum above the incisor tooth in the morning, after brushing the teeth.
• The tablet should be held in place for 30 seconds with a slight pressure of the finger over the upper lip to make the tablet stick to the gum.
• The tablet may be used if it sticks to the cheek, inside of the lip or the gum.
• If the tablet does not adhere, it should be repositioned.
• As the ORAVIG tablet absorbs moisture from the mouth, it will slowly dissolve over time and should be left in place – there is no need to remove the tablet.
• Subsequent applications of ORAVIG should be made to alternate sides of the gum.
•
If ORAVIG does not stick or falls off within the first 6 hours, the same tablet should be repositioned immediately. If the tablet does not adhere, a new tablet should be placed.
•
If ORAVIG is swallowed within the first 6 hours, the patient should drink a glass of water and a new tablet should be applied only once.
•
If ORAVIG falls off or is swallowed after it was in place for 6 hours or more, a new tablet should not be applied until the next regularly scheduled dose.
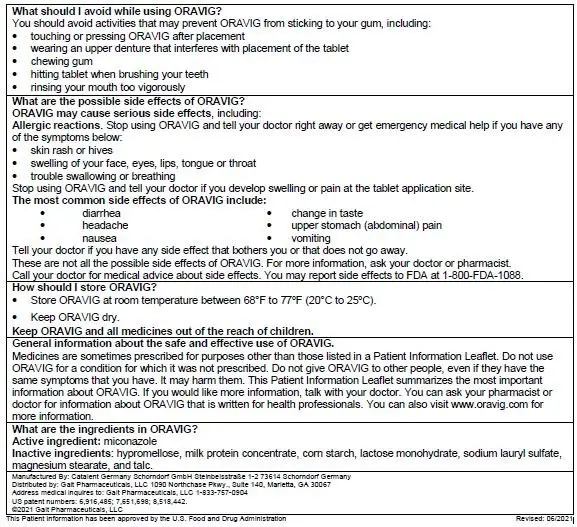
Patients should avoid situations that could interfere with the sticking of the tablet including:
• touching or pressing the tablet after placement
• wearing upper denture
• chewing gum
• hitting tablet when brushing teeth
• rinsing mouth too vigorously
Hypersensitivity and Other Adverse Reactions
Patients who develop hives, skin rash, or other symptoms of an allergic reaction, and patients who develop swelling or pain, at the tablet application site should stop ORAVIG and contact a healthcare provider. Patients may experience other adverse reactions including diarrhea, headache, nausea, and change in taste.
Potential Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Manufactured By:
Catalent Germany Schorndorf GmbH
Steinbeisstraße 1-2
73614 Schorndorf
Germany
Distributed by:
Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC
1090 Northchase Pkwy., Suite 140
Marietta, GA 30067
Address medical inquires to:
Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC
1-833-757-0904
US patent numbers: 6,916,485; 7,651,698; 8,518,442.
©2021 Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Oravig (OR-a-vig)
(miconazole)
buccal tablets
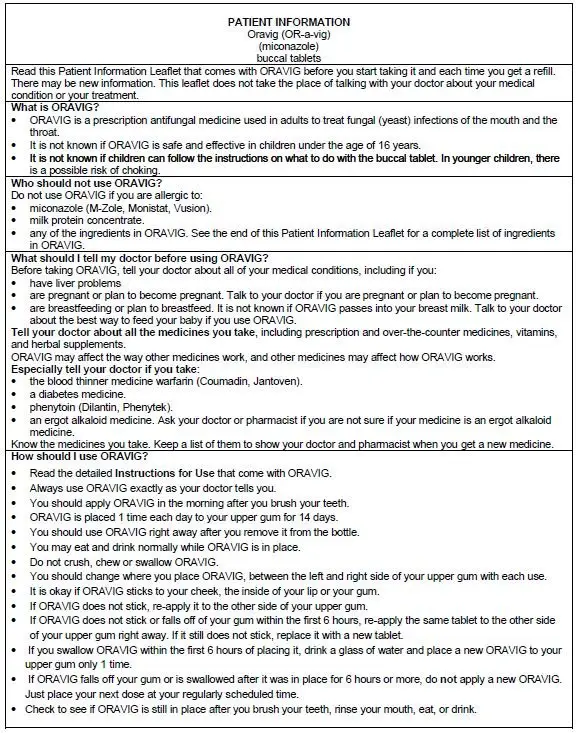
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using ORAVIG and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about how to use ORAVIG.
How should I store ORAVIG?
• Store ORAVIG at room temperature between 68°F to 77oF (20°C to 25oC).
• Keep ORAVIG dry.
Keep ORAVIG and all medicines out of the reach of children.
How to use ORAVIG?
Before applying the ORAVIG tablet
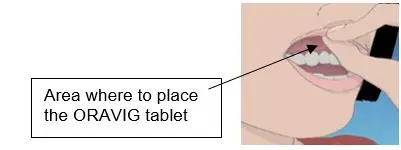
Step 1. Locate the area on the upper gum, just above the left or the right incisor tooth. The incisor tooth is the tooth just to the right or left of your two front teeth (See Figure A).
Step 2. With dry hands, take 1 ORAVIG tablet out of the bottle. ORAVIG is round on one side and flat on the other side (See Figure B). The tablet is marked with an “L” on the flat side.

Applying the ORAVIG tablet
Step 3. Place the flat side of the ORAVIG tablet on your dry fingertip. Gently push the round side of the tablet against your upper gum in the area shown in Figure C. Push the ORAVIG tablet up as high as it will go on your gum. The flat side will be facing the inside of your lip.
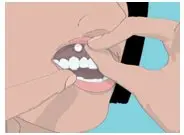
Step 4. Hold the ORAVIG tablet in place by applying a slight pressure with your finger on the outside of your upper lip for 30 seconds (See Figure D). This will make the tablet stick to your gum.
Step 5. Leave the ORAVIG tablet in place until it dissolves. Do not remove the tablet.
Step 6. Before applying your next dose, be sure to clear away any remaining ORAVIG tablet material on
your gum.
Manufactured By: Catalent Germany Schorndorf GmbH Steinbeisstraße 1-2 73614 Schorndorf Germany
Distributed by: Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC 1090 Northchase Pkwy., Suite 140, Marietta, GA 30067
Address medical inquires to: Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC 1-833-757-0904
US patent numbers: 6,916,485; 7,651,698; 8,518,442.
©2021 Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Approved: 06/2021
| ORAVIG
miconazole tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Galt Pharmaceuticals, LLC (079214973) |